To upload a file with React and Laravel, create a React file component and backend it in Laravel. Then, use the Axios library to send the file request to the Laravel server and save the image on the server.
In this tutorial, we will upload an image from the React JS component. First, we install dependencies using npx, then download the laravel project.
Here is the step-by-step guide.
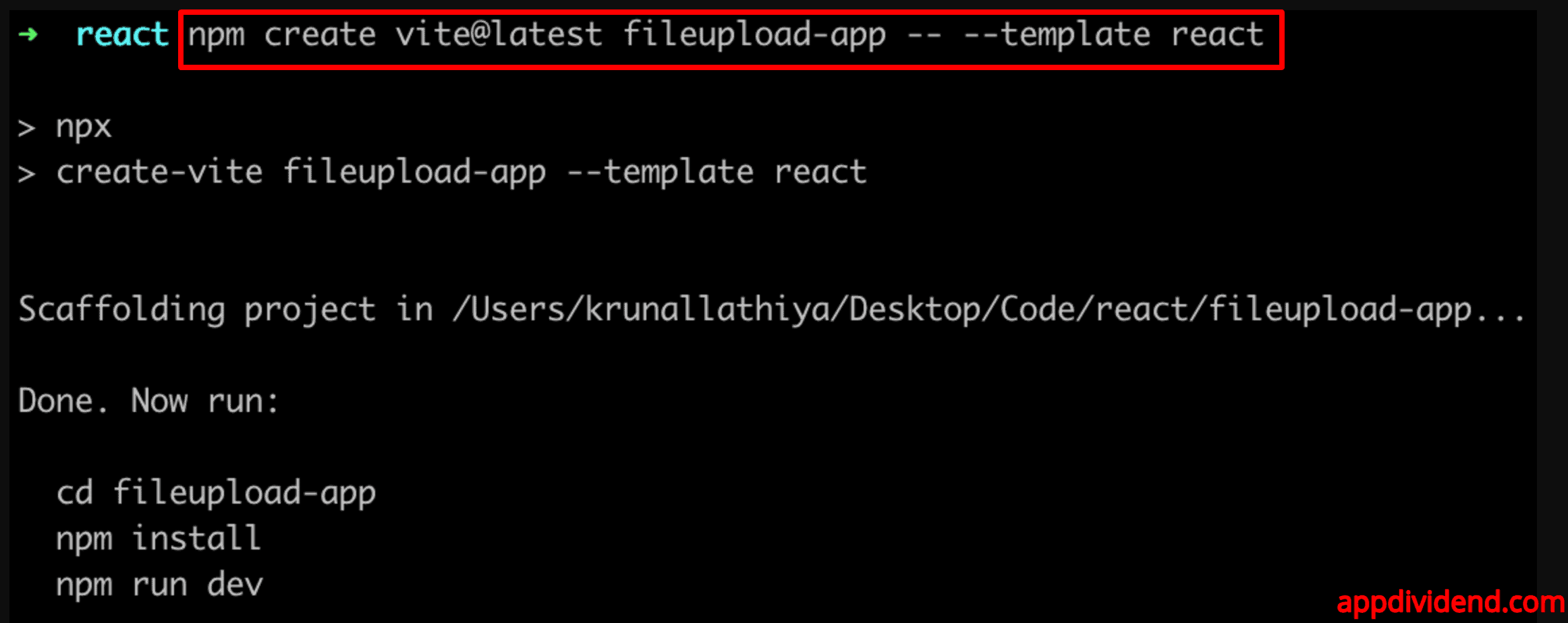
Step 1: Create a new React.js Project.
Open your terminal and type the following command.
npm create vite@latest fileupload-app -- --template react
Go inside the project:
cd fileupload-app
Install the project dependencies:
npm install
Start the Vite frontend development server using this command:
npm run dev
It will start a development server, and you can access your project by going to this URL: http://localhost:5173/
Step 2: Install Bootstrap 5
We will use Bootstrap CSS Framework to style our React components.
npm install bootstrap --save
Import the Bootstrap CSS file inside the “src/main.jsx” file:
import React from 'react'
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom/client'
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css';
import App from './App.jsx'
ReactDOM.createRoot(document.getElementById('root')).render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
)
Step 3: Add a form to upload a file.
If you go to the “src” folder, you will see a file called “App.jsx”. Update that file with the below code.
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div className="container mt-5">
<form>
<h1 className="mb-3">React File Upload</h1>
<div className="mb-3">
<input className="form-control" type="file" />
</div>
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-primary">Upload</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
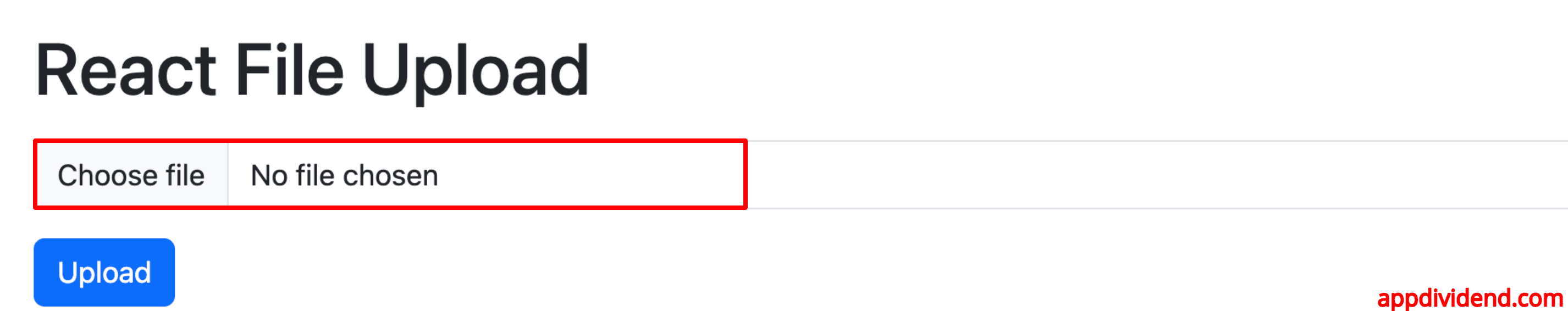
In this code, we added some bootstrap classes for styling and a form field to upload a file.
Save this file and go to the browser, and you will see your upload field like this:
Step 4: Adding a state and event
In this step, we will create a state variable called “file” that will be null on initialization.
When the user uploads a file, we will assign that file to this variable.
We will also add a handleChange() event that will update the state of the “file” variable. This function will keep track of what file the user chooses to upload.
import React, { useState } from "react";
function App() {
const [file, setFile] = useState(null);
function handleChange(event) {
setFile(event.target.files[0]);
}
return (
<div className="container mt-5">
<form>
<h1 className="mb-3">React File Upload</h1>
<div className="mb-3">
<input className="form-control" type="file" onChange={handleChange} />
</div>
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-primary">
Upload
</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Step 5: Install axios
To upload a file to a Laravel server, we need a client-side HTTP library to send an HTTP POST request to a server.
Axios is the go-to choice for front-end developers when sending a network request.
If you want to know more about how Axios works in React, I recommend that you check out the article Using Axios with React.
npm install axios --save
Step 6: Handling submitted event
Our next step is to import the axios library, create a post request, append a file to the form data, and send a file to the server.
Write the following code inside the App.jsx file:
import { useState } from "react";
import axios from "axios";
function App() {
const [file, setFile] = useState(null);
function handleChange(event) {
setFile(event.target.files[0]);
}
function handleSubmit(event) {
event.preventDefault();
const url = "http://localhost:8000/api/upload";
const formData = new FormData();
formData.append("file", file);
const config = {
headers: {
"content-type": "multipart/form-data",
},
};
axios.post(url, formData, config).then((response) => {
console.log(response.data);
});
}
return (
<div className="container mt-5">
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<h1 className="mb-3">React File Upload</h1>
<div className="mb-3">
<input className="form-control" type="file" onChange={handleChange} />
</div>
<button type="submit" className="btn btn-primary">
Upload
</button>
</form>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Here, we added a function handleSubmit(), called when the user clicks the submit button.
Step 7: Install Laravel 11
Now is the time to create a backend, and Laravel 11 is the latest version.
Let’s create a Laravel project using the below command:
composer create-project laravel/laravel fileupload --prefer-dist
Step 8: Configure the database.
Add your database credentials in the .env file.
DB_CONNECTION=mysql DB_HOST=127.0.0.1 DB_PORT=8889 DB_DATABASE=fileupload DB_USERNAME=root DB_PASSWORD=root
Step 9: Create one model and migration file.
php artisan make:model File -m
It will create both model and migration files.
Step 10: Define the schema in the migration file.
Go to the create_files_table.php file and add the schema to it.
public function up(): void
{
Schema::create('files', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('file_name');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
Step 11: Publish api.php file
By default, Laravel 11 does not come with an api.php file.
To publish the api.php file, you need to publish the api.php route file using this command:
php artisan install:api
It will create an api.php file inside the routes folder.
Before defining routes, we can create a controller called FileController.php.
php artisan make:controller FileController --resource
Define the following route in the routes/api.php file.
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Route;
use App\Http\Controllers\FileController;
Route::get('/user', function (Request $request) {
return $request->user();
})->middleware('auth:sanctum');
Route::resource('upload', FileController::class);
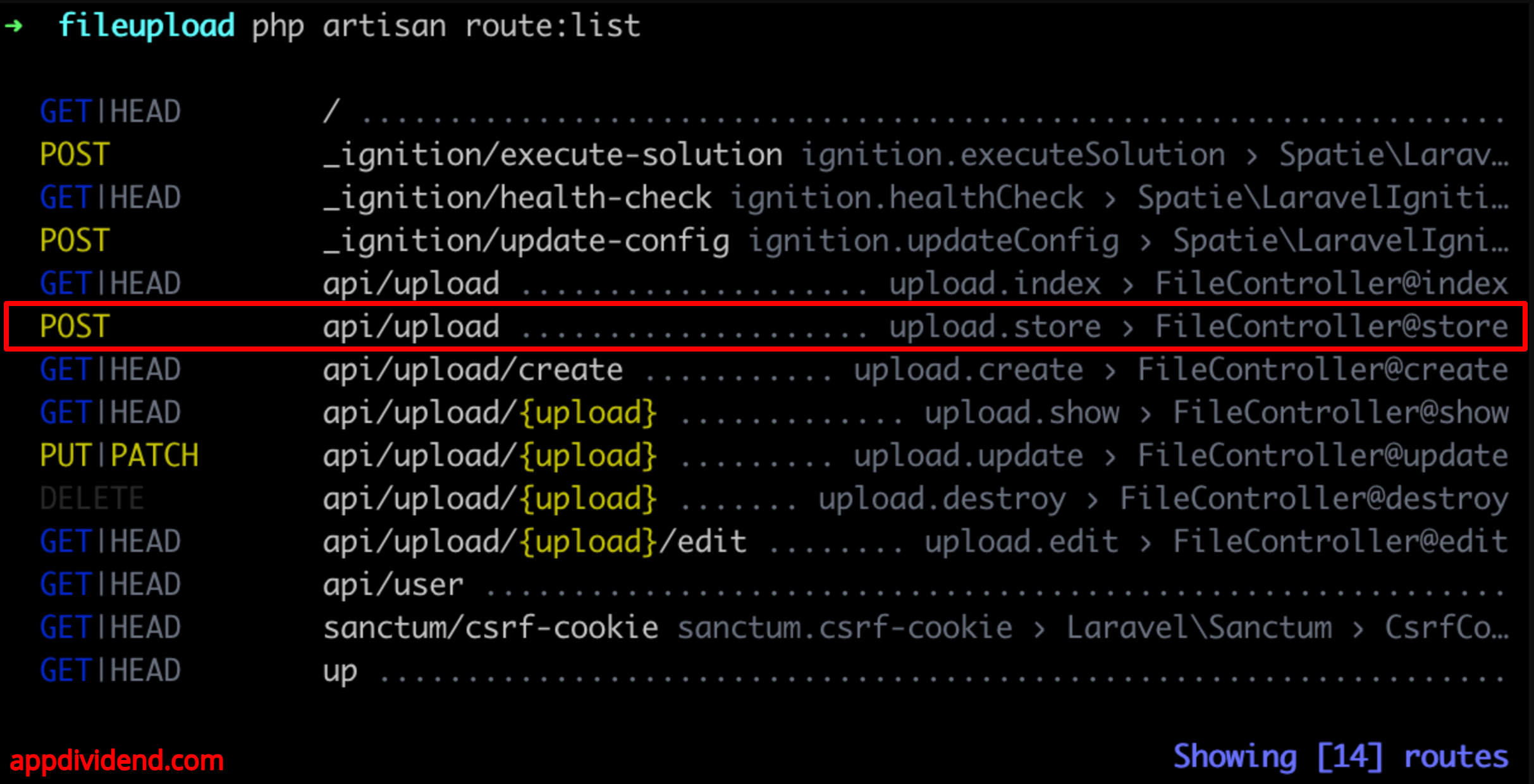
You can always get a quick overview of your application’s routes by running the route:list Artisan command.
php artisan route:list
You can see that our POST request route should be like this: http://localhost:8000/api/upload
Step 12: Create a CORS Middleware
Our React.js project is running on one server, and the Laravel Project is running on another server.
If you try to send a request from the React development server to the Laravel API server, you will get this error: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource. Origin ‘http://localhost:8000’ is therefore not allowed access. The response had HTTP status code 400.
To fix this error, we need to create a middleware CORS in the Laravel Project.
To create a middleware in Laravel, type the following command:
php artisan make:middleware Cors
It will create a new file called Cors.php inside the app/Http/Middleware folder.
Add the below code inside the Cors.php file:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
class Cors
{
/**
* Handle an incoming request.
*
* @param \Closure(\Illuminate\Http\Request): (\Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response) $next
*/
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next): Response
{
$response = $next($request);
$response->headers->set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
$response->headers->set('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'POST, GET, OPTIONS, PUT, DELETE');
$response->headers->set('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type, X-Auth-Token, Origin, Authorization');
return $response;
}
}
Basically, here we are allowing incoming requests coming from different servers.
Now, we need to register this Cors.php middleware into our Laravel application.
To do that, open the bootstrap/app.php file and add the below code:
<?php
use Illuminate\Foundation\Application;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Configuration\Exceptions;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Configuration\Middleware;
use App\Http\Middleware\Cors;
return Application::configure(basePath: dirname(__DIR__))
->withRouting(
web: __DIR__.'/../routes/web.php',
api: __DIR__.'/../routes/api.php',
commands: __DIR__.'/../routes/console.php',
health: '/up',
)
->withMiddleware(function (Middleware $middleware) {
$middleware->api(prepend: [
Cors::class,
]);
})
->withExceptions(function (Exceptions $exceptions) {
//
})->create();
Here, we are prepending the Cors middleware to the Global API middleware.
Step 13: Uploading a file to the Server
We will store a filename in the database and upload a file to the storage folder.
Add the following code inside the FileController.php file’s store() function.
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\File;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Storage;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class FileController extends Controller
{
public function store(Request $request)
{
// Store the uploaded file
$file = $request->file('file');
if ($file) {
$fileName = time() . '_' . $file->getClientOriginalName();
$destinationPath = 'uploads';
try {
Storage::disk('local')->putFileAs(
$destinationPath,
$file,
$fileName
);
// Store file information in the database
$uploadedFile = new File();
$uploadedFile->file_name = $fileName;
$uploadedFile->save();
// Return a JSON response with success message
return response()->json(['message' => "File uploaded successfully.", 'file_name' => $fileName], 200);
} catch (\Exception $e) {
// Return a JSON response with error message
return response()->json(['message' => "Failed to upload the file.", 'error' => $e->getMessage()], 500);
}
} else {
// Return a JSON response if no file was uploaded
return response()->json(['message' => "No file uploaded."], 400);
}
}
}
Here, we store the whole file inside the “storage/app/uploads” folder and save the file name in our database.
You can start the Laravel Development Server.
Type the following command.
php artisan serve
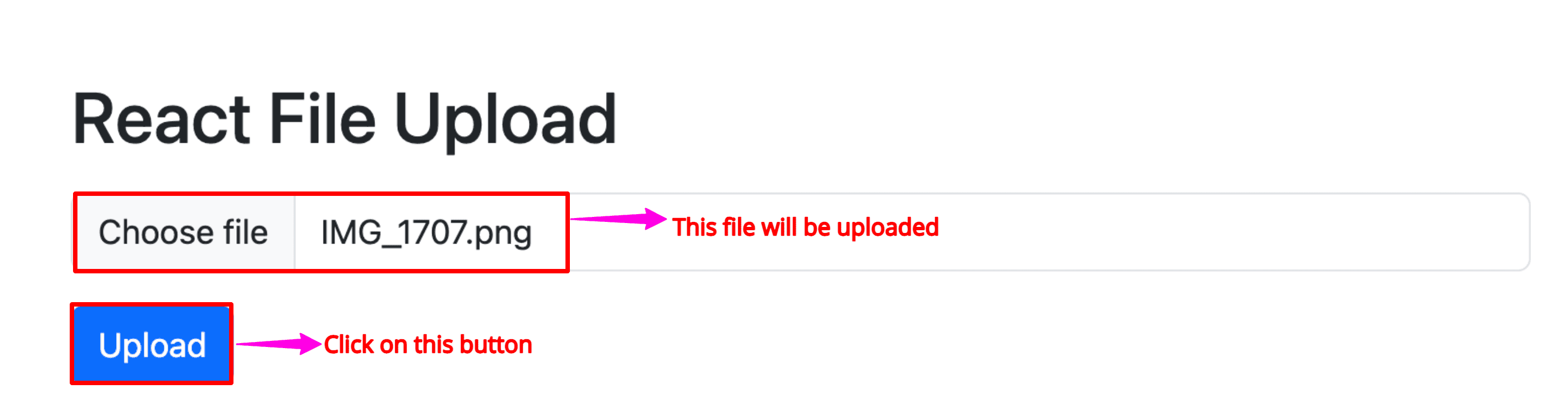
Go to the React project and try to upload a file:
If everything is set up correctly, and both Laravel and React.js servers are running fine, then you will be able to upload a file and get the success message like this:
Now, you can check the MySQL database and see image name entries:
Let’s check out the storage/app/uploads folder and see if the uploaded image is there:
That’s it.






fie
thansk before, its very usefull for me as beginer. i’m trying this code, but im getting an error “Undefined variable: name” in FileuploadController.php.. could u mind to help me, please?
Tai Ly
You should show me your code first, use any website that can hightlight php code and give me the link so I could help you.
Tai Ly
Thanks, your post is awesome 😀
John
Works only on image file .. what about docs,excel ,can you help me?
John Navarro
It work’s ! would you mind helping me in uploading excel or doc files, please?
mat
you managed to do it with excel files?
Fitra
Thank you for your tutorial..
I have to try your post, but when I click the upload button, there is show error in console “Access to XMLHttpRequest has been blocked by CORS policy: Response to preflight request doesn’t pass access control check: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource.”
Maybe someone can help me to solve this.
Thank you very much…
Jamin
Thanks a lot for this, It saved me.
please how can I delete the uploaded file from the database when a user clicks delete after uploading it?
Robin
Also in 2020 usable !!! – also with Laravel 5.8. Thanks a lot for this.
jafar
how retrieve file
in react
Akib
Thank you for your tutorial..
I have to try your post, but when I click the upload button, there is show error in console “Access to XMLHttpRequest has been blocked by CORS policy: Response to preflight request doesn’t pass access control check: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource.”
Maybe someone can help me to solve this.
Thank you very much…
Akib
I have to try your post, but when I click the upload button, there is show error in console “Access to XMLHttpRequest has been blocked by CORS policy: Response to preflight request doesn’t pass access control check: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource.”
Michael
Is it possible to upload any kind of files using your script?
Can you tell me the way?
Thanks!
Alejandra Avila Perez
Oh thanks!, would you mind helping me in uploading PDF, please?
sujon
Brother webp formate image does not upload if have any solution please mail me
my email suzonice15@gmail.com