Pandas DataFrame.to_csv() method writes (exports) a DataFrame object to a comma-separated values (csv) file or a string.
import pandas as pd
dict = {
'Transport_Mode': ["Metro", "Bus", "Train", "Metro", "Ferry", "Train", "Bus"],
'City': ["NY", "Chicago", "LA", "NY", "SF", "Boston", "Chicago"],
'Daily_Ridership': [5000000, 800000, 600000, 5000000, 200000, 500000, 800000]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict)
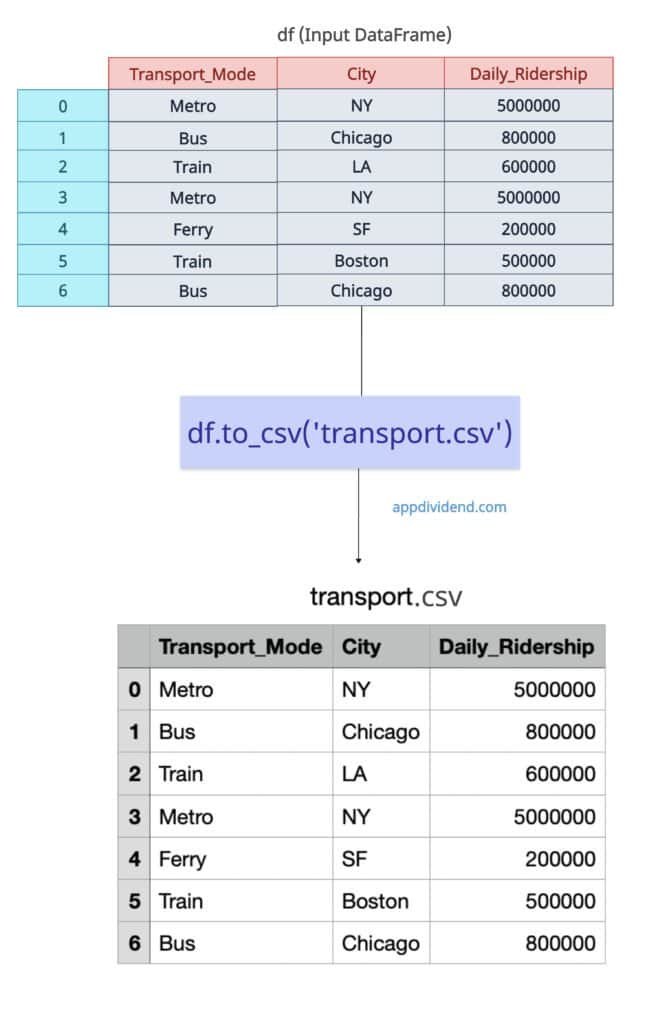
df.to_csv('transport.csv')
print("Exported the data to transport.csv")
# Output: Exported the data to transport.csv
From the above output figure, you can see that it transformed the input DataFrame df into a transport.csv file with a proper header and index.
Syntax
DataFrame.to_csv(
path_or_buf=None,
sep=',',
na_rep='',
float_format=None,
columns=None,
header=True,
index=True,
index_label=None,
mode='w',
encoding=None,
compression='infer',
quoting=None,
quotechar='"',
line_terminator=None,
chunksize=None,
date_format=None,
doublequote=True,
escapechar=None,
decimal='.',
errors='strict',
storage_options=None,
)
Parameters
| Name | Description |
| filepath_or_buffer |
It represents the path to the output file or file-like object. If it is None, the output will be a CSV data string (not a file). |
| sep or delimiter | It represents a character to break strings into columns. It is a field delimiter. |
| na_rep |
It represents missing (NaN) values. |
| float_format |
It formats for floating-point numbers (e.g., ‘%.2f’). |
| columns | It is a subset of columns to write. |
| header |
It is a True or False flag. If it is True, it writes column names in the output CSV file. If False, it won’t write column names. |
| index | If it is True, it writes the index in the output CSV file. |
| index_label | It represents a label(s) for an index column(s). |
| mode |
It defines file mode: ‘w’ truncates, ‘x’ creates exclusively (fails if exists), ‘a’ appends. |
| encoding |
It is an encoding for the output file. |
| compression |
It defines the compression formats and supports ‘gzip’, ‘bz2’, ‘zip’, ‘xz’, ‘zstd’, ‘tar’ formats. |
| quoting | It is a quotation strategy. |
| quotechar |
It is a character for quoting fields. |
| lineterminator |
It is a line ending (e.g., ‘\n’ on Linux, ‘\r\n’ on Windows). |
|
chunksize |
It represents the number of rows to write per chunk. |
|
date_format |
It is a format for datetime objects. |
| doublequote |
If it is True, it escapes quotechar by doubling it inside fields. |
|
escapechar |
It is a character to escape special characters. |
|
decimal |
It is a decimal separator. |
|
errors |
It is a handle for encoding/decoding errors. |
|
storage_options |
It is an extra option for storage backends. |
Exporting without an index and a header
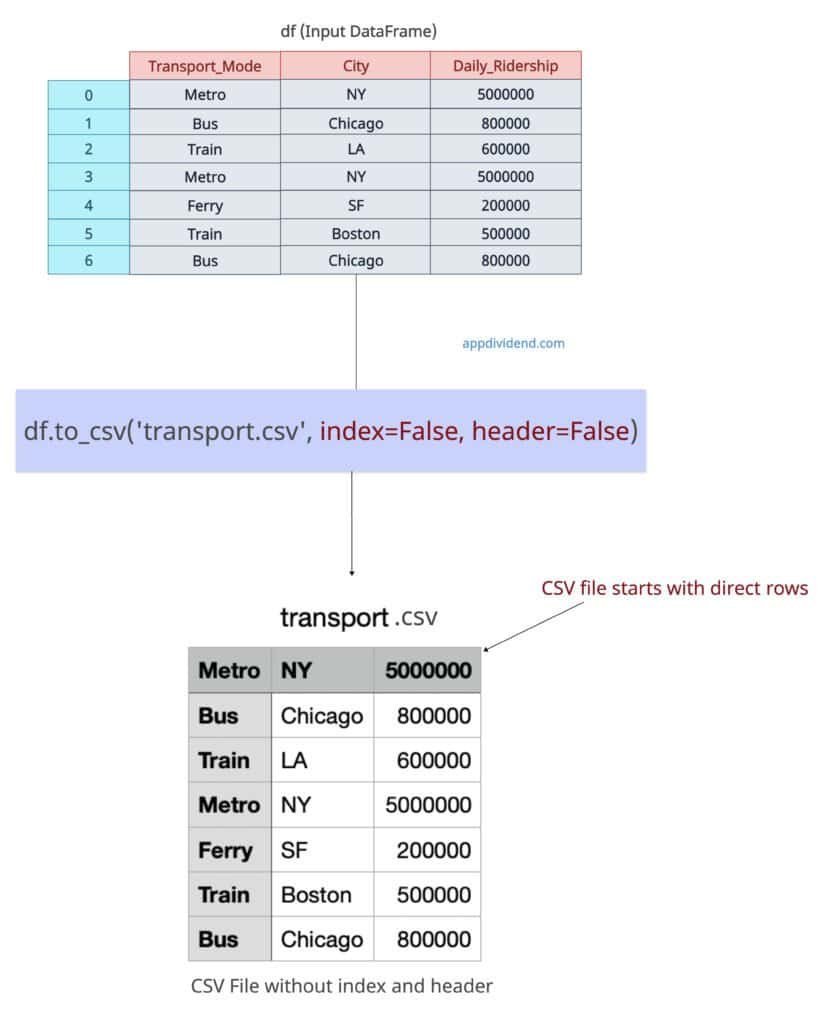
Let’s pass header=False and index=False to the to_csv() method to exclude index and header from the output CSV file.
import pandas as pd
dict = {
'Transport_Mode': ["Metro", "Bus", "Train", "Metro", "Ferry", "Train", "Bus"],
'City': ["NY", "Chicago", "LA", "NY", "SF", "Boston", "Chicago"],
'Daily_Ridership': [5000000, 800000, 600000, 5000000, 200000, 500000, 800000]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict)
df.to_csv('transport.csv', index=False, header=False)
print("Exported the data without header and index to transport.csv file")
# Output: Exported the data without header and index to transport.csv file
Selecting columns
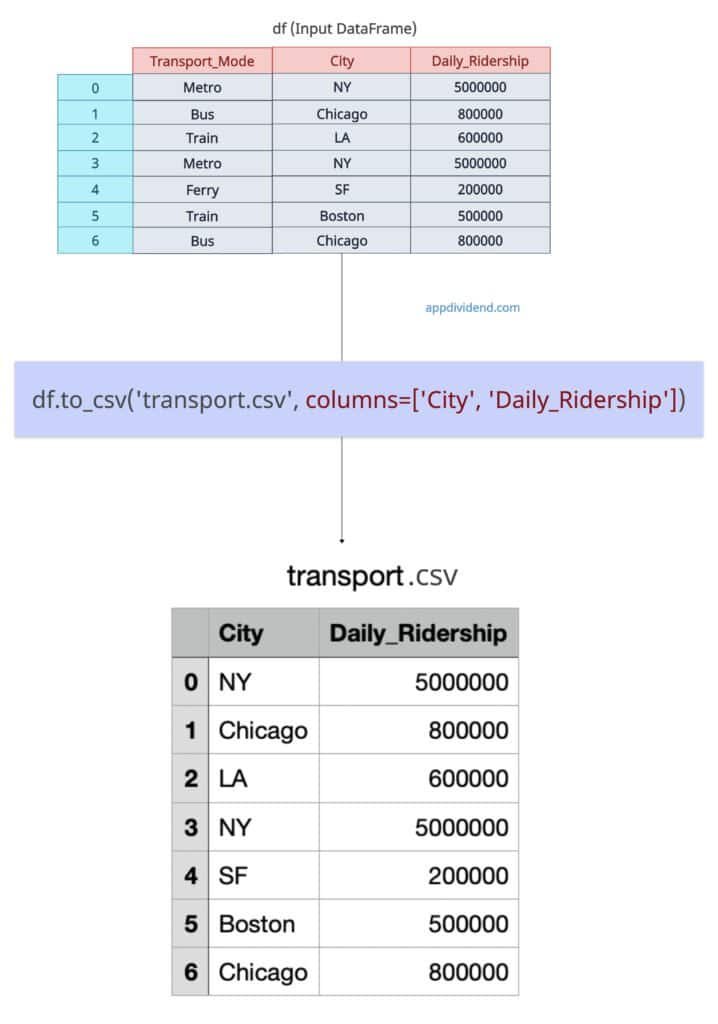
If you want specific columns that need to be exported, you can use the columns argument and pass the array of only the columns that need to be there in the output csv file.
import pandas as pd
dict = {
'Transport_Mode': ["Metro", "Bus", "Train", "Metro", "Ferry", "Train", "Bus"],
'City': ["NY", "Chicago", "LA", "NY", "SF", "Boston", "Chicago"],
'Daily_Ridership': [5000000, 800000, 600000, 5000000, 200000, 500000, 800000]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict)
df.to_csv('transport.csv', columns=['City', 'Daily_Ridership'])
print("Exported the data with only two columns")
# Output: Exported the data with only two columns


pavlos
python3 issue with NaN … df shows NaN but df1 shows .
Since I pass na_values=[‘.’], I expect df to show me .
df = pd.read_csv(‘f.csv’, na_values=[‘.’]); print(df,”\n”)
df1 = df.fillna(“.”); print(df1)