Here are three ways to download a video from a URL with Python:
- Using the requests module
- Using urllib module
- Using FFMpeg via subprocess
To demonstrate this tutorial, we will use free and open-source URLs that allow us to download videos to our local system. Those URLs are:
https://static.videezy.com/system/resources/previews/000/008/220/original/Triangles_01.mp4 https://www.shutterstock.com/shutterstock/videos/1111470671/preview/stock-footage-electric-light-bulb-bright-polygonal-connections-on-a-dark-blue-background-technology-concept.webm
Shutterstock is a renowned website where you can find free, licensed images and videos for educational purposes.
My intent here is to teach you how to do it without breaking the law. Having said that, let’s explore three ways.
Method 1: Using the “requests” module
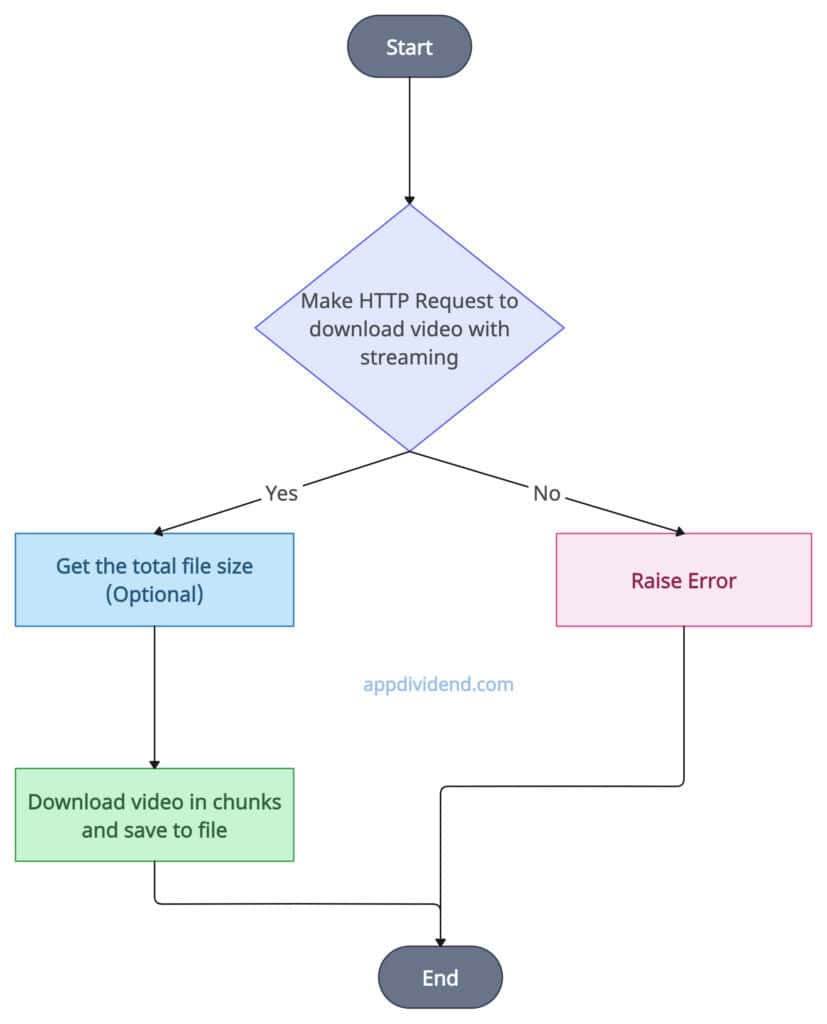
The requests module provides a requests.get() method to download video files with streaming enabled. If any error occurs during the process, we will catch and log it. If the file is too large, then download it in chunks and then save it locally.
Decision Tree Diagram
The diagram above illustrates the process flow. This provides a basic overview of how operations will be conducted.
Install the “requests” library using the command below:
pip install requests
Code example
import requests
import os
# Custom function that accepts url and local save_path
def download_video(url, save_path):
try:
# Ensuring the directory exists
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_path), exist_ok=True)
# Requesting the video file with streaming
response = requests.get(url, stream=True)
response.raise_for_status() # Check for HTTP errors
# Getting the total file size from the response headers (optional)
total_size = int(response.headers.get('content-length', 0))
# Download and save the video in chunks
with open(save_path, 'wb') as f:
for chunk in response.iter_content(chunk_size=8192):
if chunk: # Filter out keep-alive new chunks
f.write(chunk)
print(f"Video downloaded successfully and saved to {save_path}")
# Catch and print the exceptions
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as e:
print(f"HTTP error occurred: {e}")
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as e:
print(f"Request error occurred: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
# Calling the custom function with video_url and save path
video_url = 'https://static.videezy.com/system/resources/previews/000/008/220/original/Triangles_01.mp4'
save_path = './videos/sample.mp4'
download_video(video_url, save_path)
Output
Video downloaded successfully and saved to ./videos/sample.mp4
In my current project folder, there is a “videos” folder, and I saved the video sample.mp4 inside this folder.
The requests library is easy to implement, has a clear syntax, and is the fastest way to download a video.
However, if the download is interrupted, it does not natively support resuming. Moreover, if you are working with complex streaming protocols, then it might not work either.
This approach is ideal when the URL does not require authentication or additional processing to fetch it. The time complexity for the process is O(n), where n is the video file size. If the file is big, it will take longer.
The space complexity is O(1) because it writes the file in chunks without loading it into memory.
Method 2: Using the “urllib” module
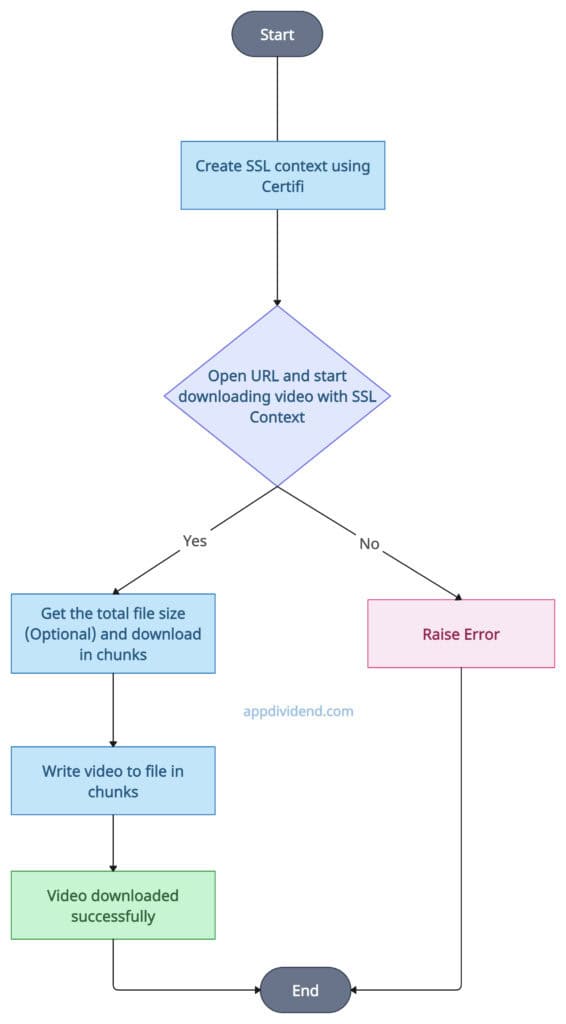
When working with the “urllib” library, ensure that you create a secure connection using the ssl.create_default_context() function with the certifi library.
Python certifi is a third-party package that provides Mozilla’s CA Bundle.
Open the URL with SSL and start reading video data.
If you encounter no errors, read the video in chunks and save it to the specified file locally. While downloading, display the progress; once the video is downloaded, print a success message.
Decision Tree Diagram
Install the certifi library using the command below:
pip install certifi
Also, install the SSL module:
pip install ssl
Code example
import urllib.request
import os
import ssl
import certifi
# Custom function to download a video
def download_video(url, save_path):
try:
# Ensuring the directory exists
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_path), exist_ok=True)
# Creating an SSL context using certifi's CA bundle
context = ssl.create_default_context(cafile=certifi.where())
# Opening the URL with the SSL context
with urllib.request.urlopen(url, context=context) as response:
total_size = int(response.getheader('Content-Length', 0))
block_size = 8192 # 8 Kibibytes
downloaded = 0
with open(save_path, 'wb') as out_file:
while True:
buffer = response.read(block_size)
if not buffer:
break
out_file.write(buffer)
downloaded += len(buffer)
if total_size > 0:
percent = downloaded / total_size * 100
print(f"\rDownloading: {percent:.2f}%", end='')
else:
print(f"\rDownloaded: {downloaded} bytes", end='')
print(f"\nVideo downloaded successfully and saved to {save_path}")
# Printing the error if occurs
except urllib.error.URLError as e:
print(f"URL Error: {e.reason}")
except urllib.error.HTTPError as e:
print(f"HTTP Error: {e.code} {e.reason}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
# Calling the custom function with input url and output directory
video_url = 'https://www.shutterstock.com/shutterstock/videos/1111470671/preview/stock-footage-electric-light-bulb-bright-polygonal-connections-on-a-dark-blue-background-technology-concept.webm'
save_path = './videos/urllib_video.mp4'
download_video(video_url, save_path)
Output
Downloading: 100.00% Video downloaded successfully and saved to ./videos/urllib_video.mp4
It provides limited flexibility compared to the “requests” module approach, and is harder to handle chunked downloads.
It is suitable for simpler downloads where authentication is not required, and streaming is not needed.
The time complexity is O(n), where n is proportional to the video size.
The space complexity is O(1).
Method 3: Using ffmpeg via subprocess
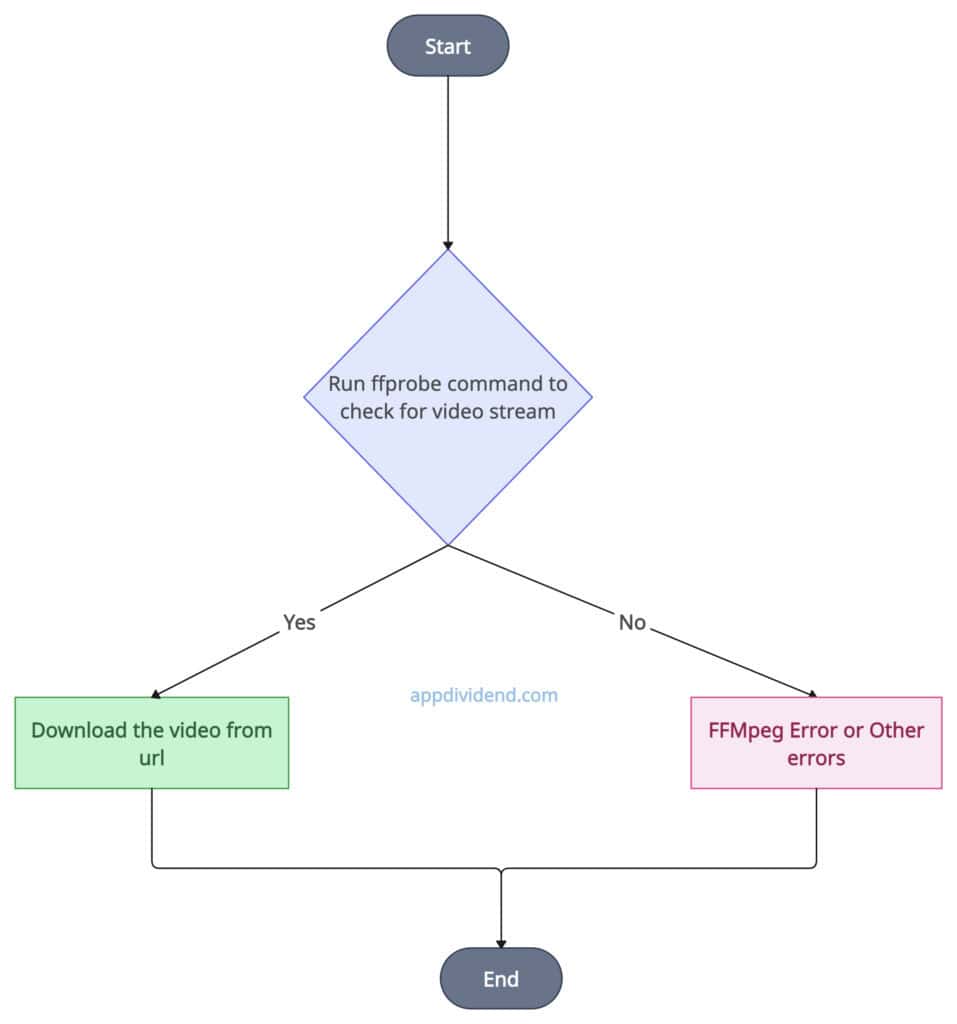
It is a straightforward solution that involves creating an FFMpeg command and running it using the subprocess module.
When the command is executed, it initiates the file download. If an error occurs, it will be printed to the console.
Decision Tree Diagram
This approach requires the “ffmpeg” library installed on your machine. I am using MacOS, so I can download it if I have not by using the command below:
brew install ffmpeg
If you are using Windows or Linux, visit its website and download the software.
Code example
import subprocess
import os
# Creating a custom function
def download_video_ffmpeg(url, save_path):
try:
# Ensuring the directory exists
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_path), exist_ok=True)
# FFmpeg command to download video
command = [
'ffmpeg',
'-i', url,
'-c', 'copy',
save_path
]
# Running the FFmpeg command
subprocess.run(command, check=True)
print(f"Video downloaded successfully and saved to {save_path}")
# Catching and print the exceptions
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(
f"Error: {e}. Ensure FFmpeg is installed and available in your PATH.")
except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e:
print(f"Error downloading video: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
# Calling the custom function
video_url = 'https://static.videezy.com/system/resources/previews/000/008/220/original/Triangles_01.mp4'
save_path = './videos/ffmpeg_video.mp4'
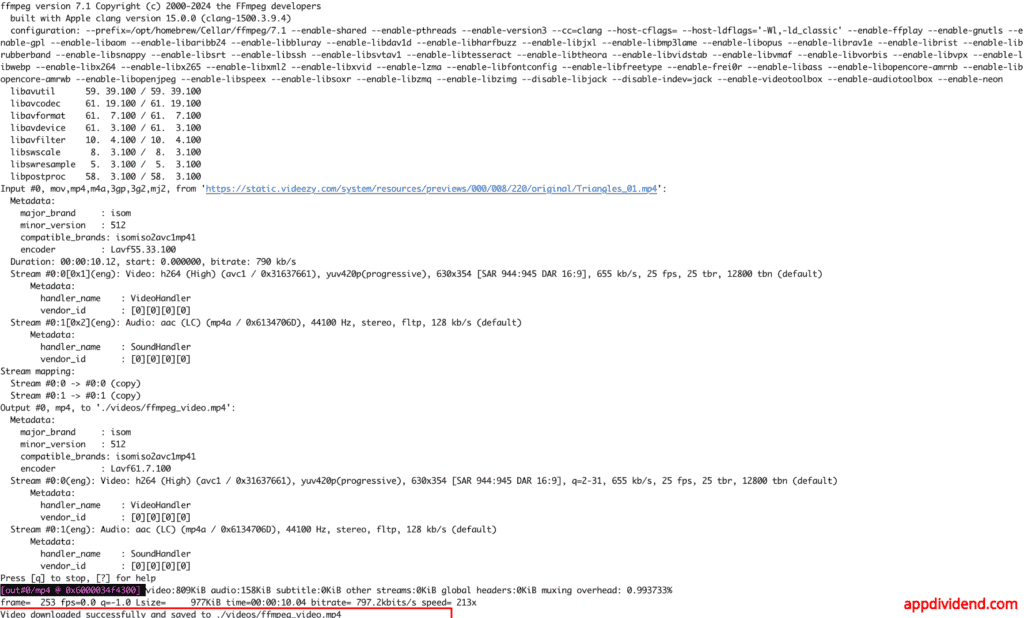
download_video_ffmpeg(video_url, save_path)
Output
Here is the video stored locally:
The ffmpeg approach via subprocess is a powerful method that can handle various streaming protocols, formats, and encoding options. It can process large multimedia files.
However, you need to install ffmpeg and be familiar with command-line tools. It may be the slowest of the three approaches.
The ffmpeg method is ideal for processing and downloading videos from streaming services.
If you want to stream and perform manipulative tasks, I highly recommend using this approach.
The time complexity is O(n), where n is the video size.
The space complexity is O(n) because we stream it in real time.
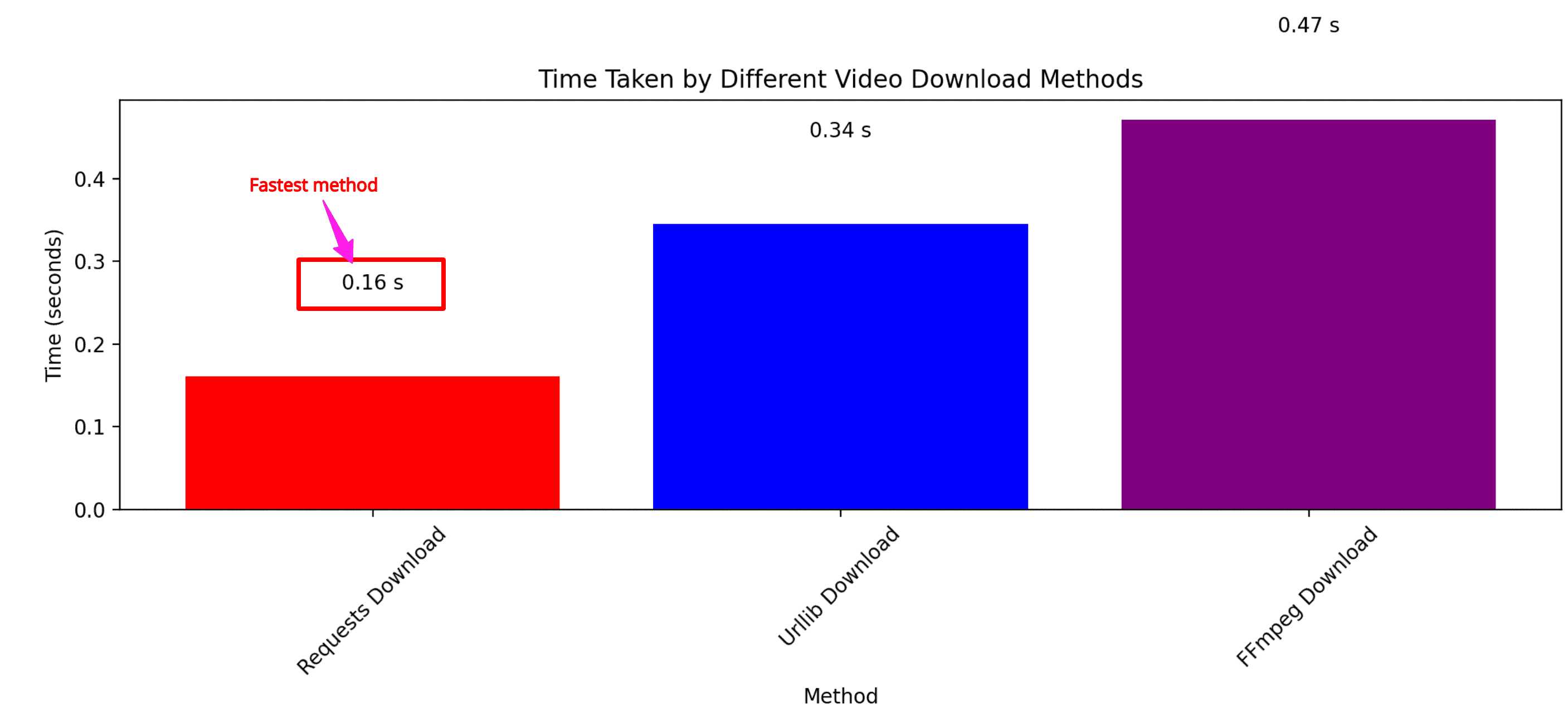
Time measurement to execute each method
I ran an experiment to execute all three approaches and record their time. Not surprisingly, the fastest approach is using the “requests” module, and the slowest approach is “ffmpeg via subprocess”.
Here is the bar chart supporting my findings:
As shown in the bar chart above, “requests” took 0.16 seconds and FFmpeg took 0.47 seconds.
Here, I used the same URL for all methods to ensure accurate results.