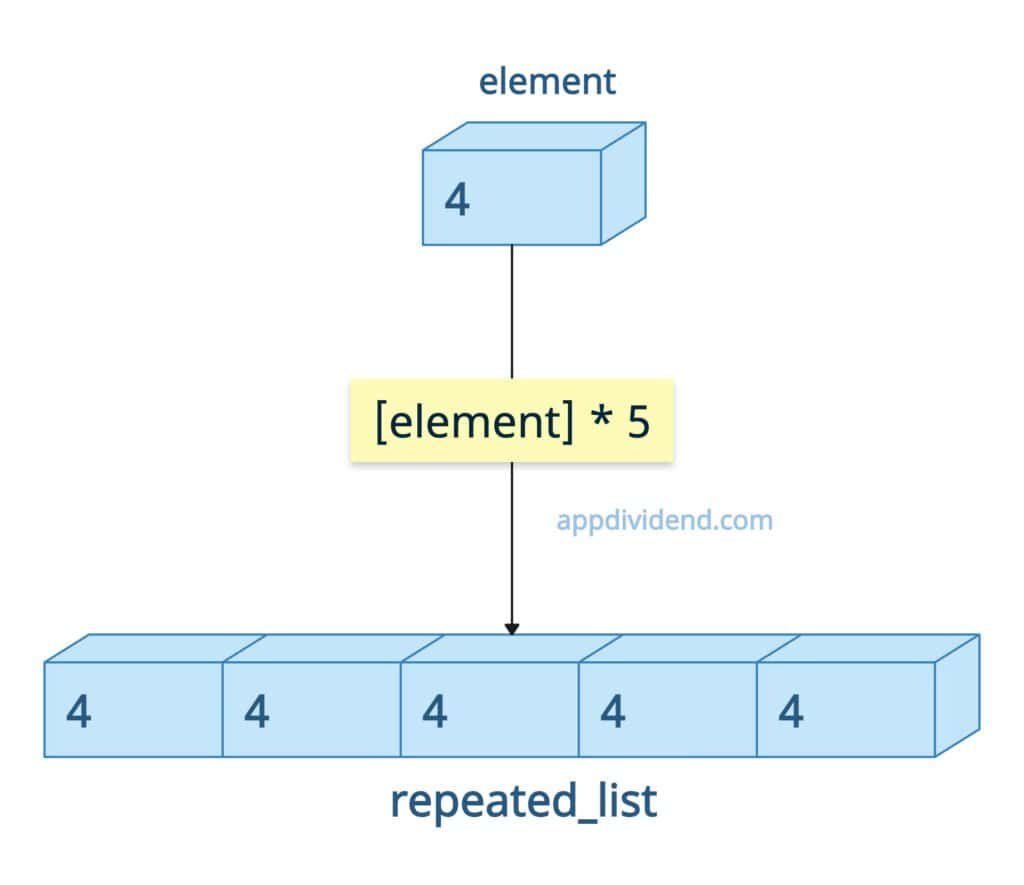
Repeating an element means creating a list in which a value appears multiple times.
The figure above shows a list with the element 4 repeated 5 times.
You can create a list where a single element appears multiple times, or where multiple elements appear multiple times.
Method 1: Using Multiplication (*)
The fastest and efficient way to create a list with repeated elements is to use multiplication (*).
Let’s create a list of length five where a single element appears five times.
element = 4 repeated_list = [element] * 5 print(repeated_list) # Output: [4, 4, 4, 4, 4]
In this code, we repeated the element 4 five times, and the final list has 5 length.
It is the safe approach for repeated scalars and only use when you have immutable values (int, float, str, tuple).
For mutable elements
What if the list value is immutable, like a list? So, the output list will be a list of lists, where each list element inside a list references the same object.
inner_list = [0] outer_list = [inner_list] * 3 print(outer_list) # Output: [[0], [0], [0]] outer_list[0][0] = 9 print(outer_list) # Output: [[9], [9], [9]]
In this code, the inner_list is mutable (a list).
When you do [inner_list] * 3, Python does not create three separate copies. Instead, it puts the same object reference into outer_list three times.
So, if you change any inner_list, it will change all the inner_lists due to the same reference, and that’s why the final outer_list has all three [9] elements.
Method 2: Using List Comprehension
In the above approach, it is not very efficient for mutable elements. To fix this problem, you can use a list comprehension. It ensures each repeated element is an independent copy.
inner_list = [[0]] outer_list = [inner_list[:] for _ in range(3)] print(outer_list) # Output: [[0], [0], [0]] outer_list[0][0] = 9 print(outer_list) # Output: [[9], [9], [9]]
In the above code, each element in the outer_list is a separate object. It works for mutable values safely. You can use this approach to repeat dictionaries, lists, and sets in the list.
Method 3: Using a list.extend()
If you want an inplace operation where a list has some elements and you want to extend it with repeated elements, you can use the list.extend() method. It modifies the original list and does not create a new list.
existing_list = [1, 2] existing_list.extend([5] * 3) print(existing_list) # Output: [1, 2, 5, 5, 5]
The existing_list has only two elements at the initial stage, but using the extend() method, we are adding 5 elements 3 times.
The updated existing_list contains a total of five elements with 5 appearing 3 times.