To split a string into substrings (tokens), you need to define separators. The separators can be the same (repetitive) and different, and can appear single or multiple times.
Here are three ways to split a string based on multiple delimiters:
- Using re.split()
- Using str.replace() and str.split()
- Using str.translate() and str.maketrans()
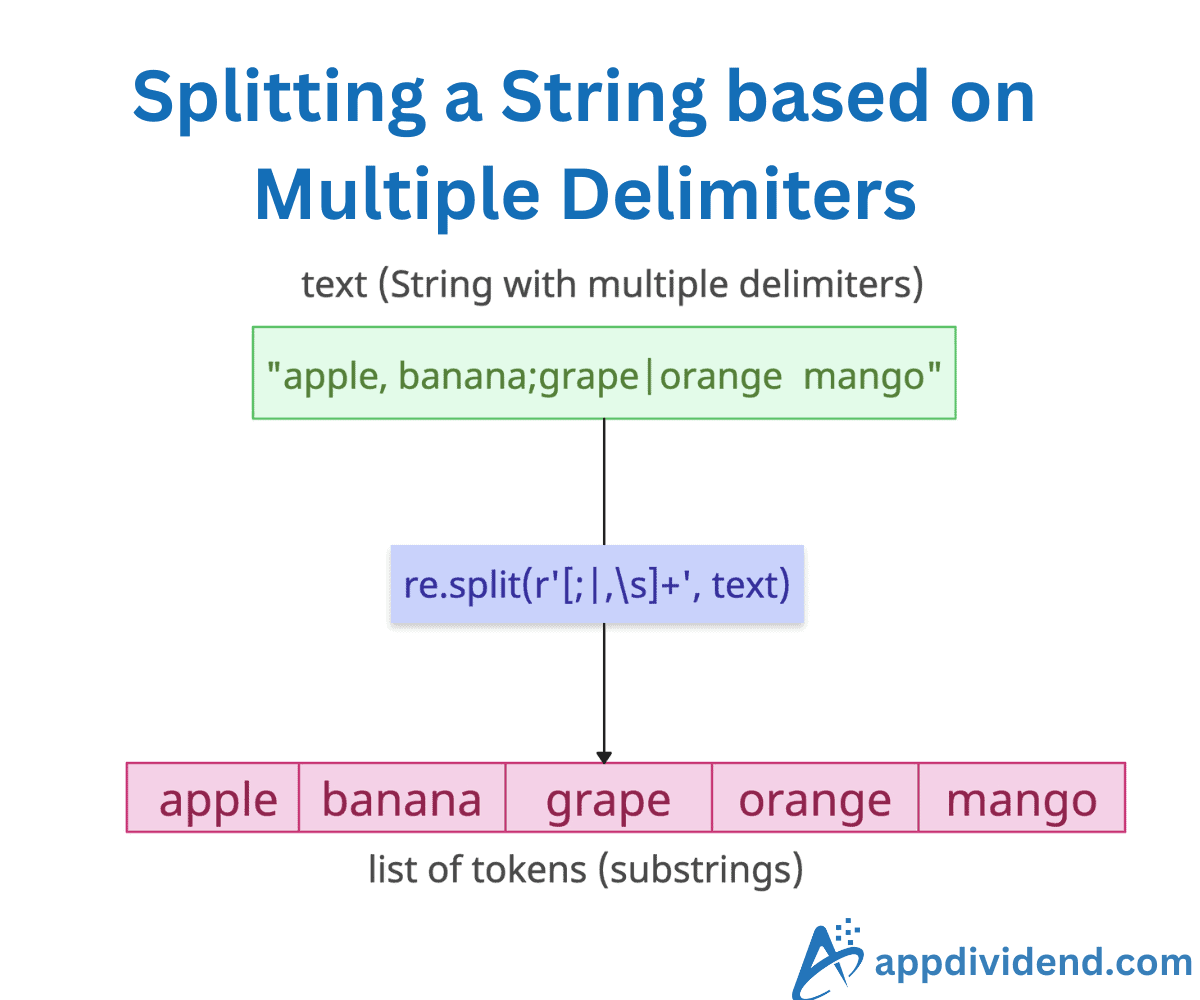
Method 1: Using the re.split()
The re.split() function uses a regular expression pattern, where each delimiter is separated by the pipe character (|), which represents an or condition in regular expressions.
In the pattern argument, you need to define your main logic of separators. What type of separator do you want to include, and how many times? It always depends on your requirements, which vary from project to project.
Remember, there is only one string, but that string contains multiple special characters or patterns.
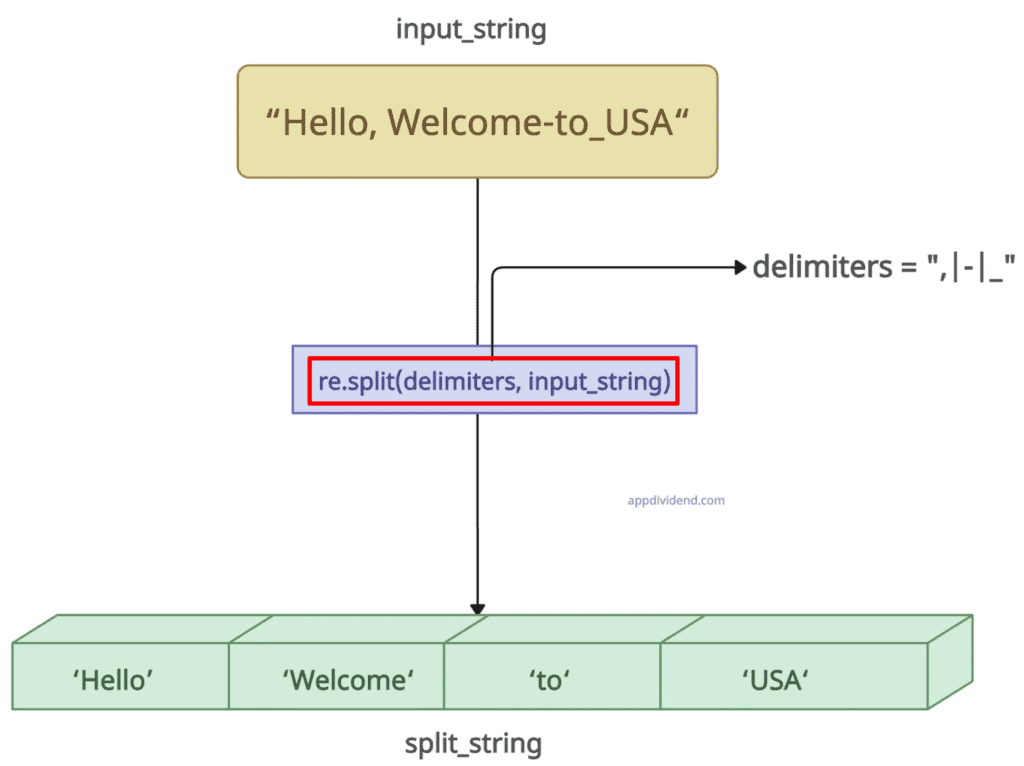
The re.split() method accepts two arguments: delimiters and an input_string. The delimiters are like wildcards [ ,;|] separated by pipes. It splits on all the matches.
The main advantage of split() is that you can define a complex pattern in one line.
import re input_string = "Hello, Welcome-to_USA" # Delimiters: comma, hyphen, and underscore (Multiple) delimiters = ",|-|_" split_string = re.split(delimiters, input_string) print(split_string) # Output: ['Hello', ' Welcome', 'to', 'USA']
In this code, there is an input_string, and we split it based on commas, hyphens, and underscores. The output list contains four elements.
Method 2: Using str.replace() and str.split()
The primary purpose of the str.replace() method is to replace a specific character. But how can we use it here?
Replace all the delimiters with spaces (‘ ‘) and then split the string into a list of substrings using the str.split(). So, you need to use the combination of these functions.
input_string = "Hello, Welcome!to;USA"
delimiters = [",", "!", ";"]
for delim in delimiters:
input_string = input_string.replace(delim, " ")
split_string = input_string.split()
print(split_string)
# Output: ['Hello', 'Welcome', 'to', 'USA']
In this code, we defined a string and then defined a list of all the delimiters. We loop through that list and pick one delimiter at a time, replacing the delimiter with a space.
So, it returns a string with empty spaces. In the next step, we split the string based on these empty spaces. The output is a list of separated values.
Method 3: Using str.maketrans() and str.translate()
In this approach, we need to create a translation table using str.maketrans(). It builds a mapping table telling Python how to replace characters. For example, in our case, it maps delimiters with empty spaces.
To apply the transition, we need to use the str.translate() method.
Finally, the processed string has only white spaces, and we can split the string based on those multiple whitespaces using the str.split() method and get a list of separated values.
input_string = "Hello, Welcome-to_USA" delimiters = ", -, _" trans_table = str.maketrans(delimiters, ' ' * len(delimiters)) translated_string = input_string.translate(trans_table) split_string = translated_string.split() print(split_string) # Output: ['Hello', 'Welcome', 'to', 'USA']
In this code, we defined an input_string and delimiters. The delimiter (“, -, _”) is mapped to a space (‘ ‘).
Then the .split() function (without an argument) automatically splits on any amount of whitespace (1 or more spaces) and returns a list with four elements.