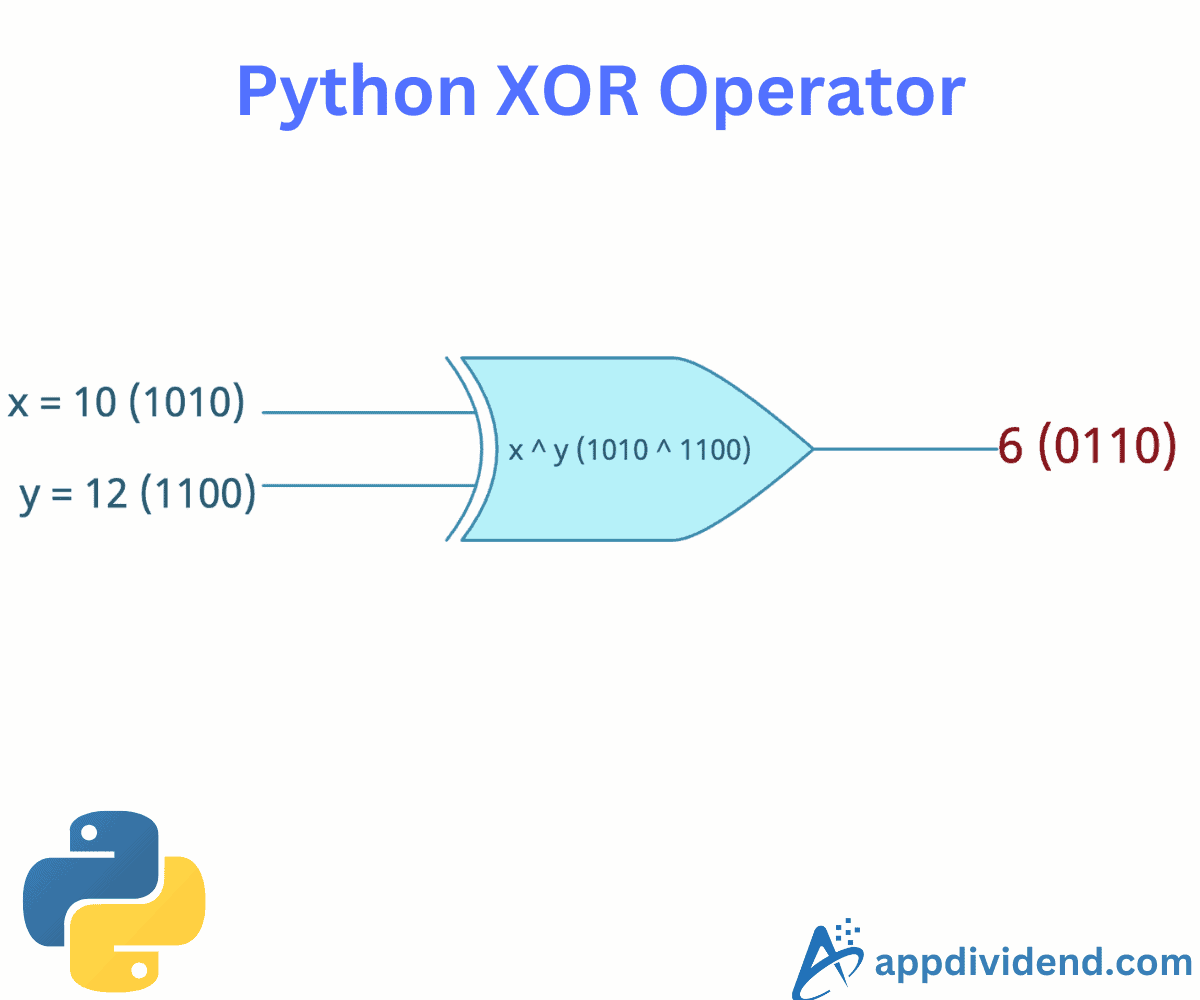
The XOR (Exclusive OR) operator in Python, represented by ^ (carat), performs a bitwise exclusive OR operation on two integers.
It returns True if exactly one operand is True. If both operands are either True or False, it returns False.
If input operands are integers and if both operands are either 0 or 1, it returns 0. If operand 1 is 0 and the other operand is 1, it returns 1.
Here is the truth table for more clarity:
XOR Truth Table
| Input A | Input B | Input A ⊕ Input B |
| 0 (False) | 0 (False) | 0 (False) |
| 0 (False) | 1 (True) | 1 (True) |
| 1 (True) | 0 (False) | 1 (True) |
| 1 (True) | 1 (True) | 0 (False) |
Syntax
result = operand1 ^ operand2
Here, operand1 represents the value, which can be either an integer or a boolean.
The operand2 also represents the value, which can be either an integer or a boolean.
If the operands are of other types (like string, float, etc), it will raise a TypeError.
Boolean XOR
Let’s test the truth table for boolean values and see if it returns True for one value that is True and the other is False.
operand_true = True operand_false = False output = operand_true ^ operand_false print(output) # Output: True (one True) print(operand_true ^ operand_true) # Output: False (both True) print(operand_false ^ operand_false) # Output: False (both False) print(operand_false ^ operand_true) # Output: True (one True)
Bitwise XOR on Integers
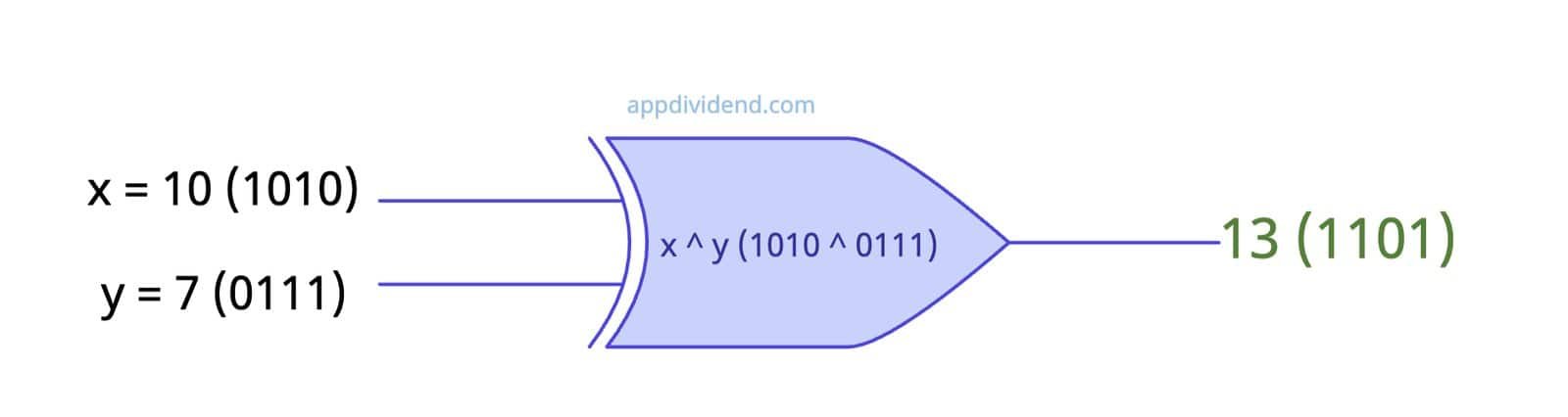
Let’s perform bitwise XOR on integers. Behind the scenes, operands’ binary values are performed bitwise XOR.
x = 10 # In binary: 1010 y = 7 # In binary: 0111 output = x ^ y # 1010 ^ 0111 = 1101 print(output) # Output: 13 (1101) in binary
You can see that the actual operation takes place between binary values of two operands. The output binary value is 1101, which corresponds to a decimal value of 13.
What if the operands are strings
If your input operands are strings, how can you apply the XOR operator? Well, if you directly apply XOR on strings, it will raise TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for ^: ‘str’ and ‘str.
string = "Kaynes Technology" empty_string = "" output = string ^ empty_string print(output) # Output: TypeError: unsupported operand type(s) for ^: 'str' and 'str'
To fix the error, we need to convert the input operands to a boolean value using the bool() method. So, the first string becomes True and empty_string becomes False.
string = "Kaynes Technology" empty_string = "" output = bool(string) ^ bool(empty_string) print(output) # Output: True
True ^ False returns True, and that’s what we got in the output.
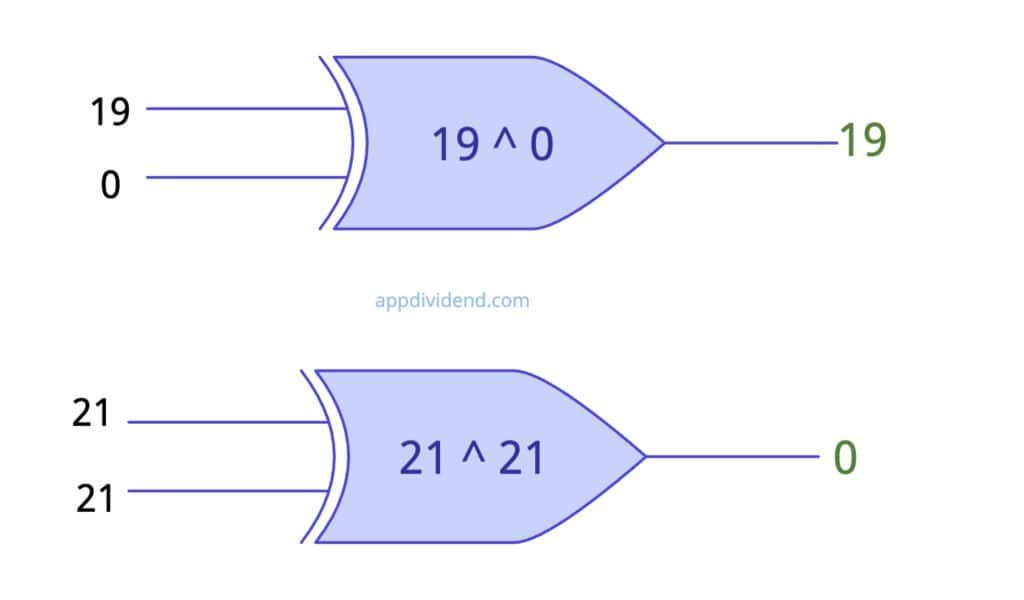
Zero and Self
XOR with 0 returns the original number; XOR with itself returns 0.
print(19 ^ 0) # Output: 19 print(21 ^ 21) # Output: 0
Swapping Two Variables
You can swap two variables without using a third variable using the XOR operator, but it is not as readable as the normal way.
x = 10
y = 7
print('Before swapping: ')
print('The value of x is: ', x)
print('The value of y is: ', y)
x = x ^ y
y = x ^ y
x = x ^ y
print('After swapping: ')
print('The value of x is: ', x)
print('The value of y is: ', y)
# Output:
# Before swapping:
# The value of x is: 10
# The value of y is: 7
# After swapping:
# The value of x is: 7
# The value of y is: 10
What is the difference between XOR and OR?
The main difference between XOR and OR operators is that XOR returns True if exactly one of the inputs is 1, whereas OR returns 1 (True) if at least one of the inputs is 1.
Here’s a comparison in tabular format:
| Input A | Input B | XOR (A ^ B) | OR (A | B) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
The other difference is that XOR is an exclusive operator, whereas OR is an inclusive operator.