What does it mean when you say you want to convert a string that represents a dictionary to a valid dictionary? It means you want to deserialize the data from a string to a dictionary. That string can be a simple literal, a JSON string, a human-readable YAML string, or a malformed/non-standard string.
For each type of input string, there are different methods. Each method serves a special purpose.
Here are four ways:
- Using ast.literal.eval()
- Using json.loads()
- Using yaml.safe_load()
- Using eval()
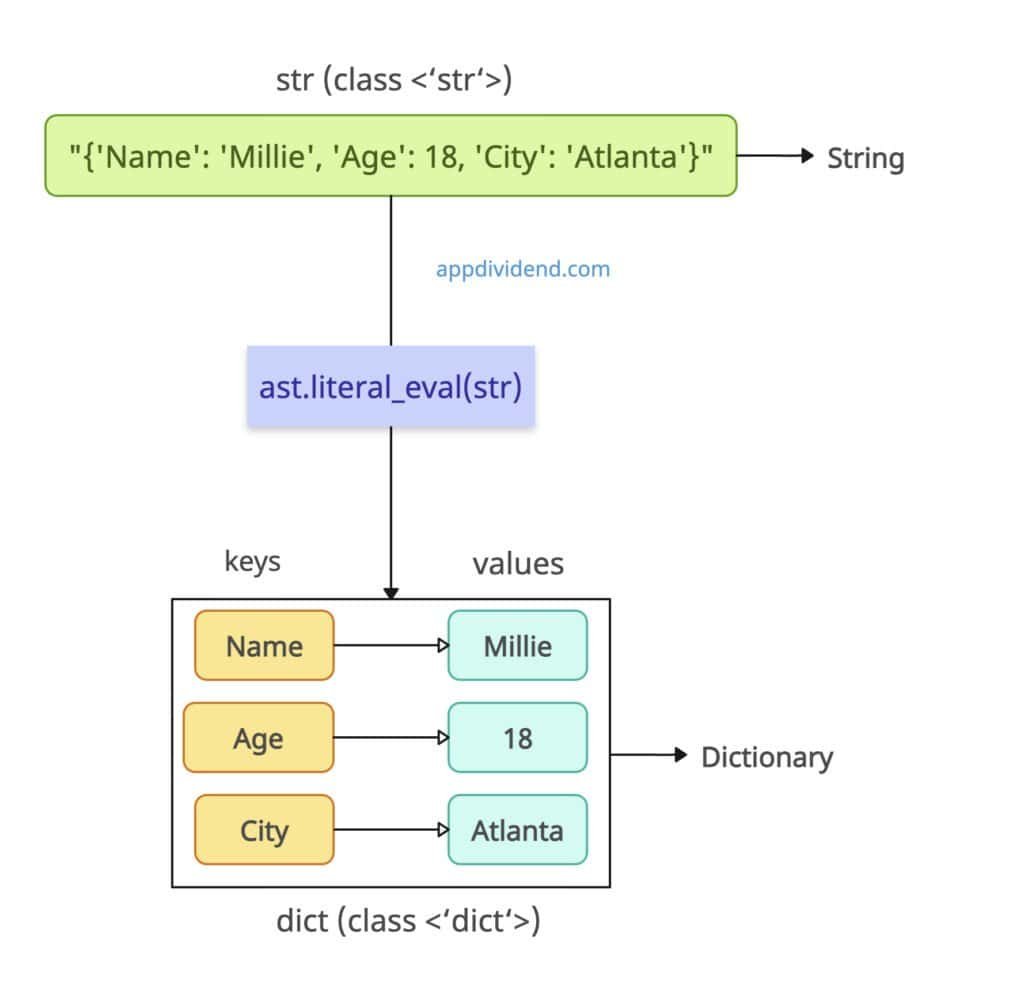
Method 1: ast.literal_eval()
The safest evaluation of strings as Python literals is to use the ast.literal_eval() function. It safely converts a string into a dictionary by evaluating literals and containers (such as dictionaries, lists, tuples, and strings), without executing arbitrary code.
It is ideal for native dict strings like “{‘key’: ‘value’}”. The standard dictionary has a proper key and its value without any syntax errors. If you wrap the dictionary with double quotes, it becomes a string.
import ast
str = "{'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}"
print(str)
# Output: {'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}
print(type(str))
# Output: <class 'str'>
dict = ast.literal_eval(str)
print(dict)
# Output: {'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}
print(type(dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
In this code, we passed a string literal to the ast.literal_eval() method, and it returns a dictionary. Further, we verified the data types using a built-in type() method.
The main advantage of this approach is that it rejects non-literal code and handles Python-specific code. Also, it does not require any third-party library.
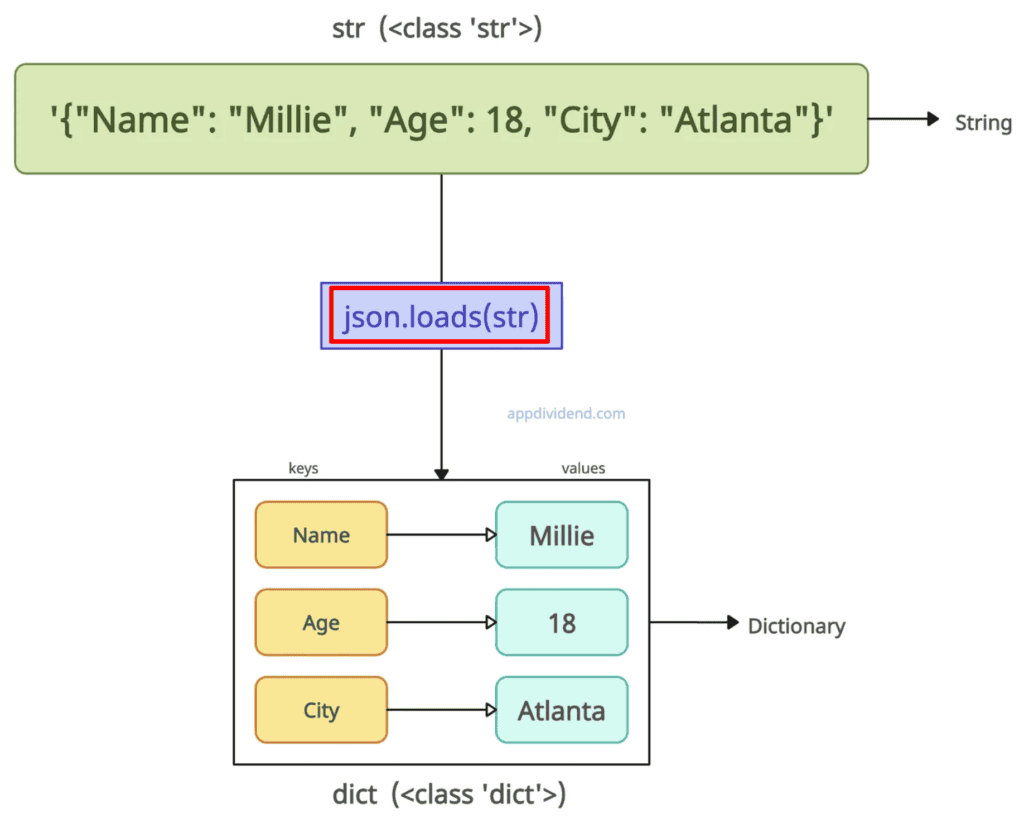
Method 2: Using json.loads()
What if you have a JSON string as an input? In that case, always use the json.loads() method.
The json.loads() method parses a string conforming to JSON standards (double quotes, no trailing commas, escaped specials) and converts to a native dict (keys as strings).
import json
str = '{"Name": "Millie", "Age": 18, "City": "Atlanta"}'
print(str)
# Output: {"Name": "Millie", "Age": 18, "City": "Atlanta"}
print(type(str))
# Output: <class 'str'>
# Usage of json.loads() method
dict = json.loads(str)
print(dict)
# Output: {'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}
print(type(dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
Method 3: Using yaml.safe_load()
The yaml.safe_load() method from the PyYAML (install via pip if needed, but assume available) package parses YAML strings and converts an input string to a dict. For security, use the “safe_load” argument.
import yaml
# Basic conversion (YAML allows single quotes, comments)
str = """
a: 1
b: 'two' # This is a comment
"""
print(str)
# Output:
# a: 1
# b: 'two' # This is a comment
dict = yaml.safe_load(str)
print(dict)
# Output: {'a': 1, 'b': 'two'}
print(type(dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
Method 4: Using eval()
If you are working in a trusted environment and don’t mind executing arbitrary code, the eval() method is helpful. This approach is your last resort for the conversion because it opens up potential threats against our system. Always use in controlled environments.
str = "{'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}"
print(str)
# Output: {'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}
print(type(str))
# Output: <class 'str'>
# Usage of eval() to convert string to dictionary
dict = eval(str)
print(dict)
# Output: {'Name': 'Millie', 'Age': 18, 'City': 'Atlanta'}
print(type(dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
That’s it!