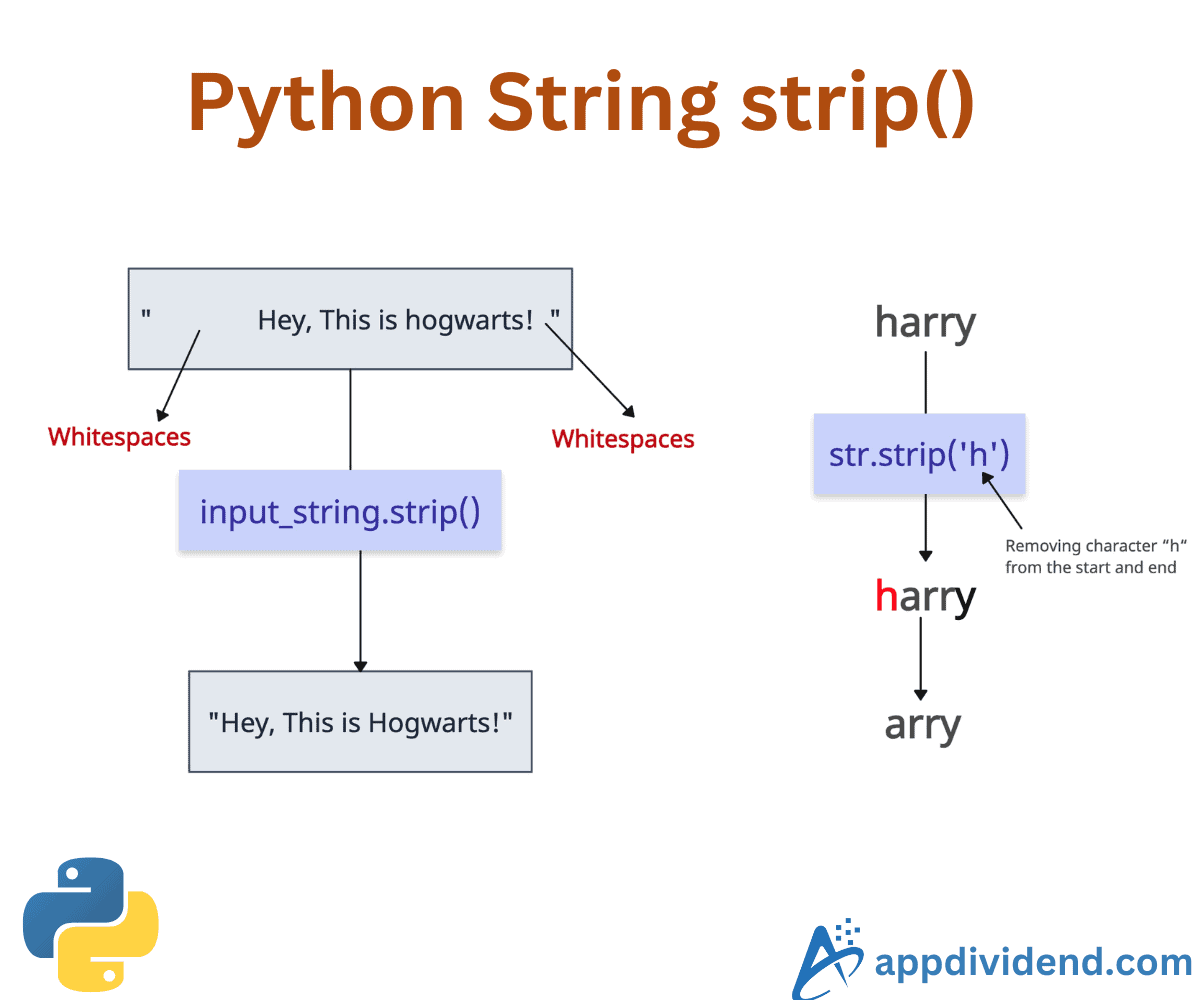
Python strip() is a built-in function that removes any specific characters from a string. By default, it removes any leading and trailing whitespaces to clean the string. The output is a new string with specified characters stripped.
input_string = " But, I am at Walmart! " print(input_string) # Output: " But, I am at Walmart! " stripped_output = input_string.strip() print(stripped_output) # Output: "But, I am at Walmart!"
In this code, all the leading and trailing spaces have been removed, and the result is a clean string.
It removes all whitespace types (including tabs and newlines by default).
Syntax
string.strip(characters)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| characters (str or None) |
It represents a string specifying the set of characters to remove from both ends of the string. It is a set of individual characters, not a substring. If omitted or None, all whitespace characters are removed (‘ ‘, \t, \n, \r, \x0b, \x0c). |
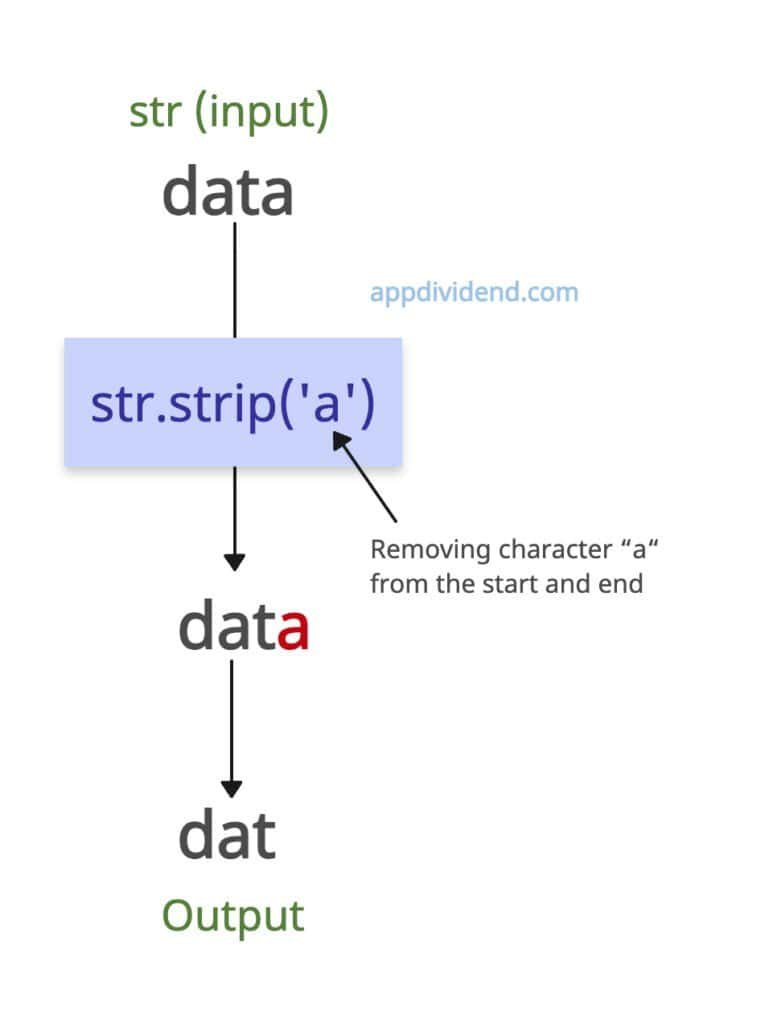
Removing a specific character
Let’s remove the specific character from a string from either the start or the end.
str = "data"
print(str.strip('a'))
# Output: dat
In the above code, we removed the “a” at the end of the string. The output is just “dat”.
Removing newlines and tabs
If the string contains “\t” and “\n” characters, you don’t need to specify them to remove them. They are whitespace characters, and they will be stripped by default.
new_tab = "\n\tHello AppDividend\t\n" print(new_tab) # Output: # Hello AppDividend stripped_input = new_tab.strip() print(stripped_input) # Output: # Hello AppDividend
Removing multiple characters from the start and end
Using the strip() function, we can remove multiple specific characters from a string at the start and end points, but cannot remove them from the middle of the string.
multi_str = "...Hello. World!!!"
print(multi_str.strip('.!'))
# Output: Hello. World
In this code, we removed the three “.” (dots) from the start of the string, but were unable to remove the dot (.) from the middle of the string. It also stripped “!” from the end of the string.
Remember, the argument is a character, which means the method matches any character, not substrings.
Empty string
When the string is empty, the output string will be empty too, since there are no characters.
empty_str = "" print(empty_str.strip()) # Output: ""
No chars Match → Original string returned.
If no characters match, it will return the original string without any modification. The output is the same as the input.
str = "data"
print(str.strip('me'))
# Output: data
Removing the whole string
What if the character(s) you want to remove are that whole string? Meaning, let’s say, you want to remove “z” from “zzz”? Well, in this case, the entire string “zzz” will be removed.
str = "zzz"
print(str.strip('z'))
# Output: ""
The above output shows that it returns an empty string, meaning everything is removed.
Removing Substrings vs. Characters
The string strip() method is not about substring removal; it is about removing special characters, such as whitespaces, from the string at the start and end points.
It cannot remove the characters from the middle of the string.
For proper substring removal, use str.replace() or re.sub() method.
str = "Google"
print(str.strip("Goo"))
# Output: gle
In the above code, we are stripping three characters: G, o, and o. Since all three characters appear at the start of the string, they were removed. Here, “Goo” is removed, not as a substring, but as individual characters.
But why did it not remove “g”? Well, the strip() function is case-sensitive. So, the “G” is not the same as “g” and hence, it did not strip it from the string.







Bilbo
my precious