Converting a list to a dictionary in Python demands the type of input data you have and what your dictionary looks like.
For example, if you have two lists as input, you can create a dictionary from them, where the first list serves as the keys and the second list serves as the values. That way, it would become a meaningful dictionary.
It is also possible that you have a list or tuple of tuples and you want to convert it to a meaningful dictionary. In that case, the approach will be different.
Another case is that you have only one list and use the list indices as keys, with the list values serving as the dictionary values.
So, you have multiple approaches, each tailored for separate use cases.
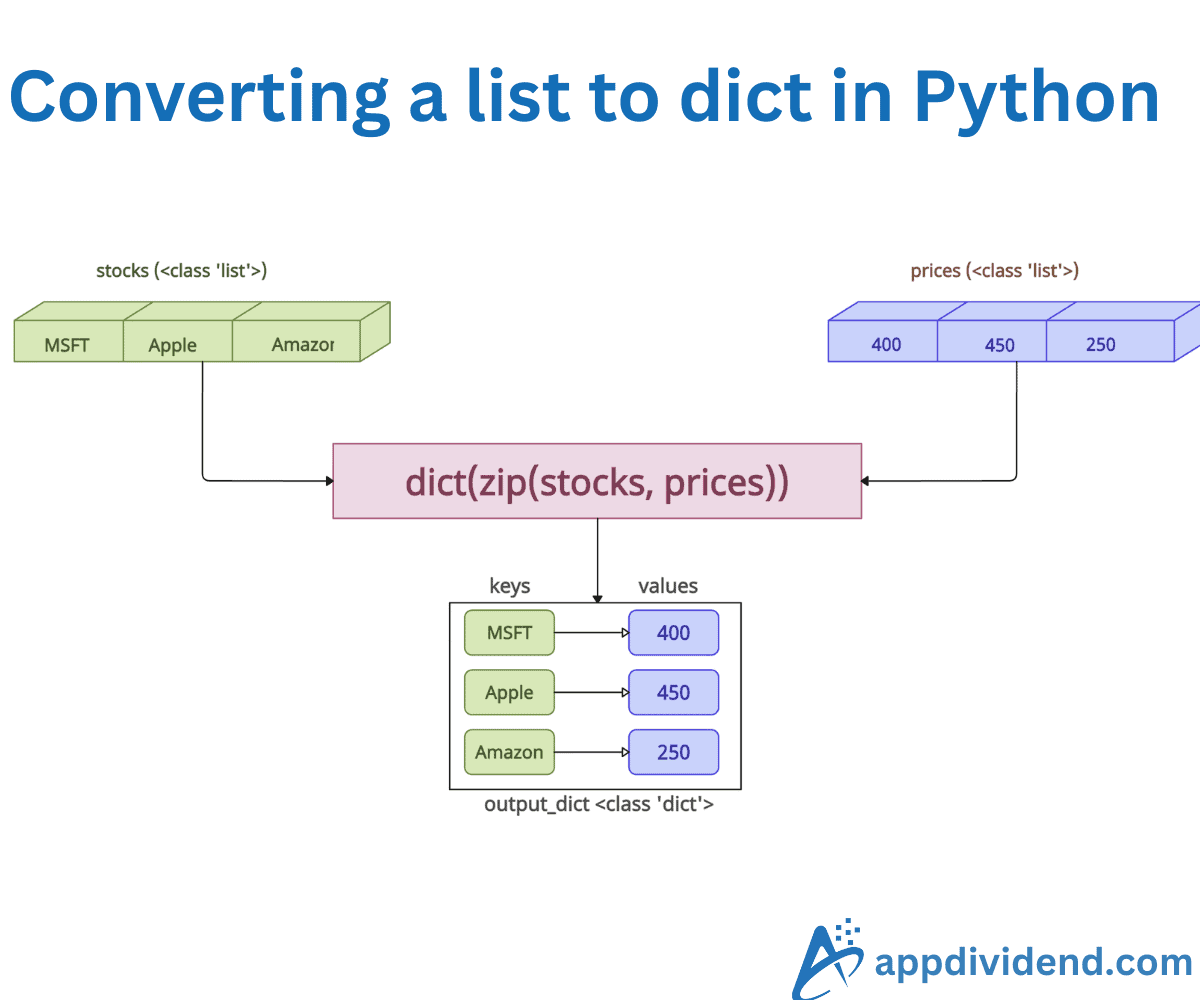
Method 1: Using dict() and zip() methods
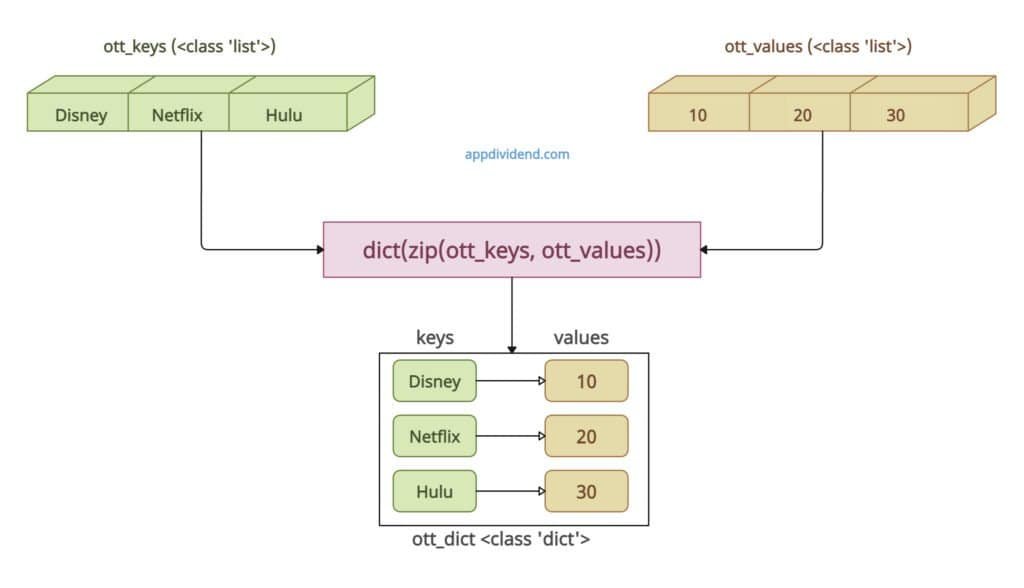
Imagine that you have two parallel lists, one for dict keys and another for dict values. The fastest way to convert them into a dictionary is to use the zip() method in combination with the dict() method.
I highly recommend this approach if you are working with two lists.
The zip() method combines both lists to create an iterator and then converts that iterator to a dictionary using the dict() method.
ott_keys = ['Disney', 'Netflix', 'Hulu']
print(type(ott_keys))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_values = [10, 20, 30]
print(type(ott_keys))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_dict = dict(zip(ott_keys, ott_values))
print(ott_dict)
# Output: {'Disney': 10, 'Netflix': 20, 'Hulu': 30}
print(type(ott_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
In this code, the zip() function pairs elements (like (‘Disney’, 10)). The dict() method then converts pairs into a dictionary. It is a clean and Pythonic approach.
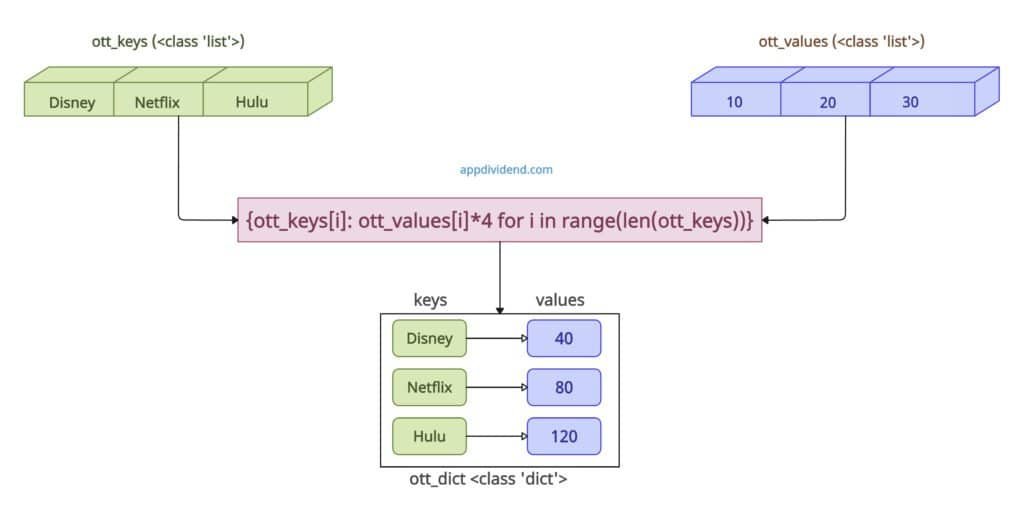
Method 2: Using Dictionary Comprehension
Another easy way is dictionary comprehension for two separate input lists. It iterates over the indices of the keys list.
For each iteration, it takes an element from the keys list as the key and the corresponding element from the values list as the value.
The main advantage of dictionary comprehension is that it helps us in custom conversion logic.
ott_keys = ['Disney', 'Netflix', 'Hulu']
print(type(ott_keys))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_values = [10, 20, 30]
print(type(ott_keys))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_dict = {ott_keys[i]: ott_values[i]*4 for i in range(len(ott_keys))}
print(ott_dict)
# Output: {'Disney': 40, 'Netflix': 80, 'Hulu': 120}
print(type(ott_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
In this code, while transforming to a dictionary, we multiplied the value by 4 for each key in the output dictionary.
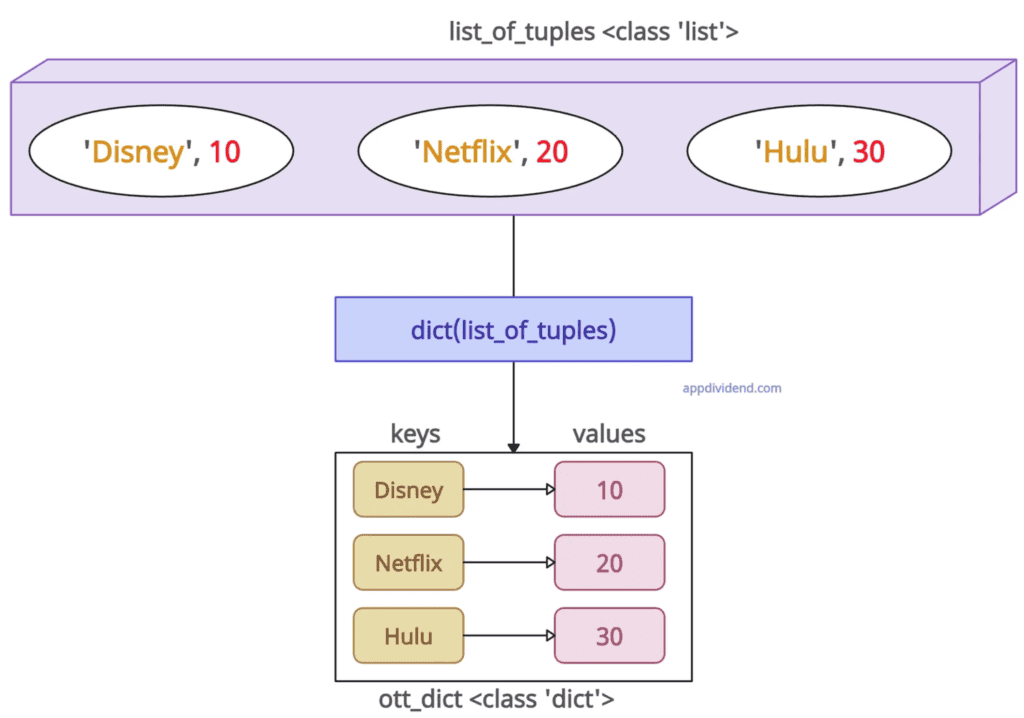
Method 3: Using dict() with list of tuples or lists
If you have a list of tuples, where each tuple contains two elements (key, value), you can directly convert it into a dictionary using dict().
Similarly, if you have a list of lists, where each inner list contains two elements (key, value), you can use this method.
list_of_tuples = [('Disney', 10), ('Netflix', 20), ('Hulu', 30)]
print(list_of_tuples)
# Output: [('Disney', 10), ('Netflix', 20), ('Hulu', 30)]
print(type(list_of_tuples))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_dict = dict(list_of_tuples)
print(ott_dict)
# Output: {'Disney': 10, 'Netflix': 20, 'Hulu': 30}
print(type(ott_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
This approach is best when each element already has a key-value structure, and it is speedy.
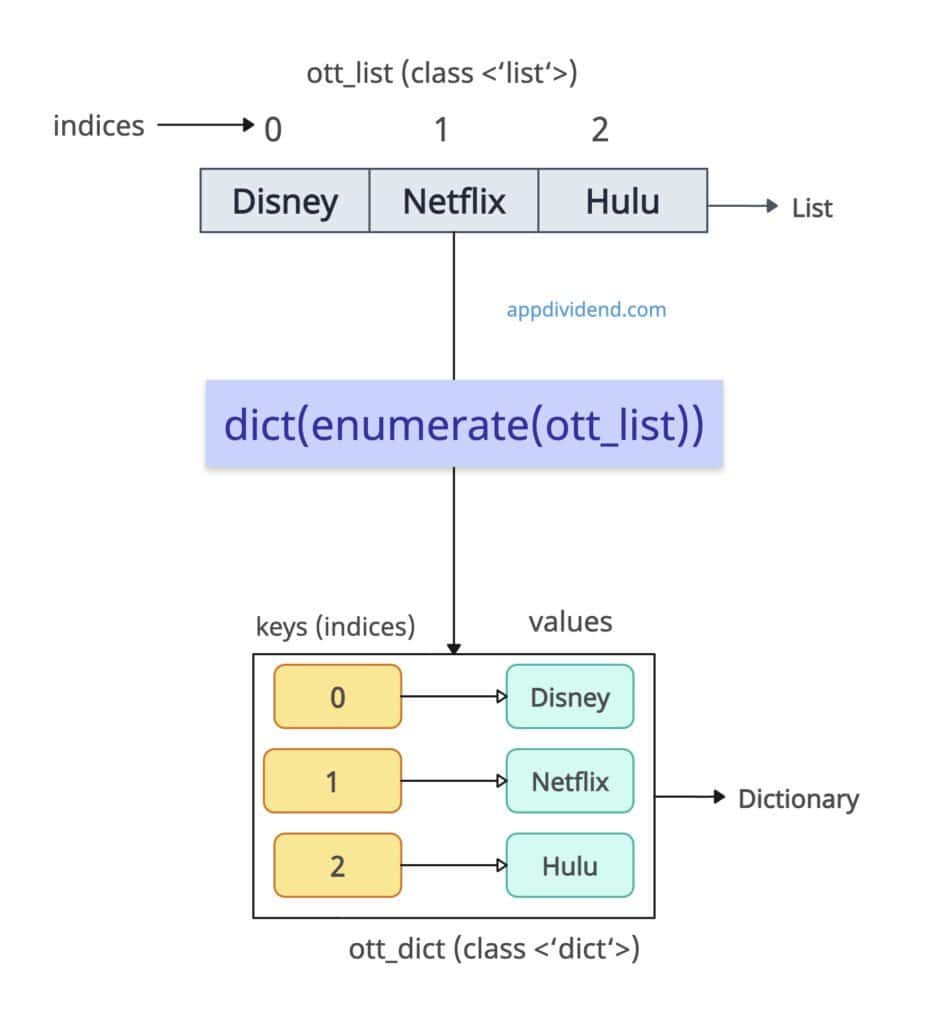
Method 4: Using enumerate() — List Index as Key
What if you have only a single list and need to convert it to a dictionary? Since a list only has values for the dictionary, how will we create keys for the dict? That’s when you need to map list indices to values.
ott_list = ["Disney", "Netflix", "Hulu"]
print(ott_list)
# Output: ['Disney', 'Netflix', 'Hulu']
print(type(ott_list))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_dict = dict(enumerate(ott_list))
print(ott_dict)
# Output: {0: 'Disney', 1: 'Netflix', 2: 'Hulu'}
print(type(ott_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
In the above output, you can see that it automatically generates index-based keys, and values are list elements.
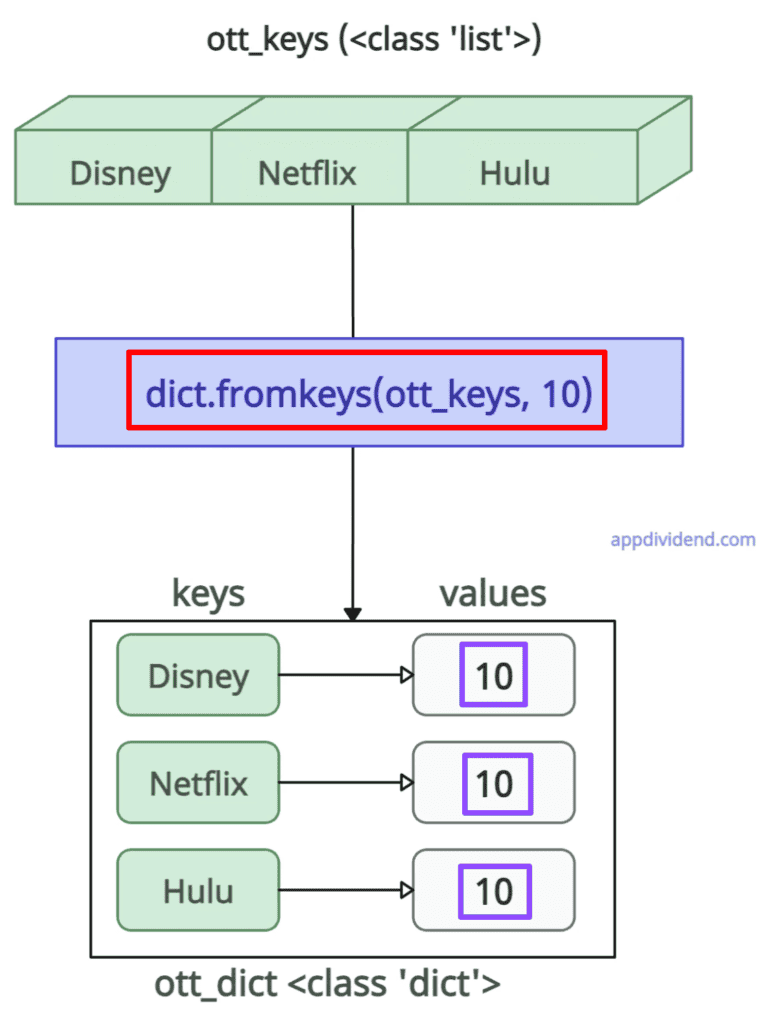
Method 5: Using dict.fromKeys()
If you have a list of keys and want to assign the same value to each key, you can use the dict.fromkeys() method. This approach is helpful when you want the same default value for all keys.
ott_keys = ["Disney", "Netflix", "Hulu"]
print(ott_keys)
# Output: ['Disney', 'Netflix', 'Hulu']
print(type(ott_keys))
# Output: <class 'list'>
ott_values = 10
ott_dict = dict.fromkeys(ott_keys, ott_values)
print(ott_dict)
# Output: {'Disney': 10, 'Netflix': 10, 'Hulu': 10}
print(type(ott_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
That’s all!