Whether you want to improve the readability of simple arrays or formatting for output to files or systems, sometimes you must present the array without brackets.
Here are two ways to print a Numpy array without brackets in Python:
- Using join(), map(), and str functions
- Using numpy.savetxt()
Method 1: Using join(), map(), and str functions
This approach requires conversion from a Numpy array to a string using map() and str. After converting it into a string, we can join the elements of a string with the desired separator using the join() function, which will print in the console.
Printing 1D numpy array
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([19, 21, 0, 1, 2])
print(" ".join(map(str, arr)))
# 19 21 0 1 2
Printing 2D numpy array
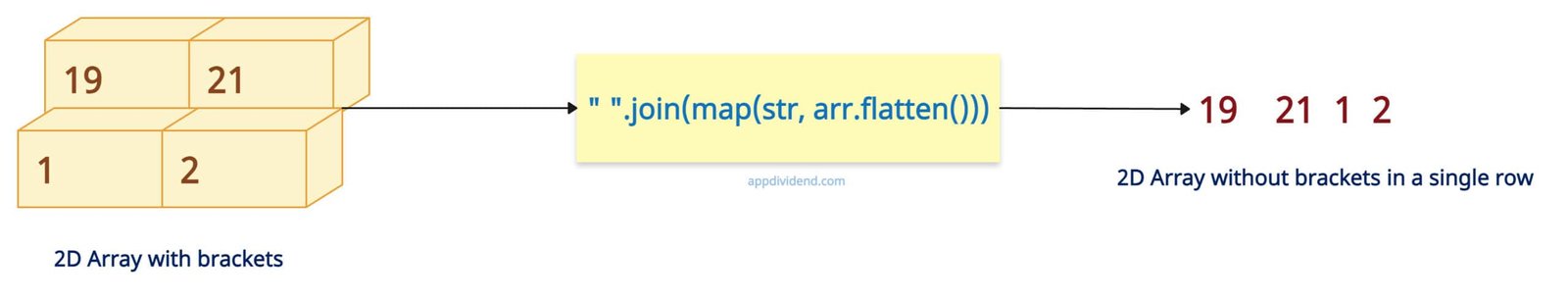
2D array is complex in structure and requires special attention. First, we must flatten the 2D array into a 1D array using the .flatten() method, and as we have done in the 1D array, use the join(), map(), and str functions.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[19, 21], [1, 2]])
print(" ".join(map(str, arr.flatten())))
# 19 21 1 2
If you want to print your array elements row-wise, you can do it using the code below:
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[19, 21], [1, 2]])
for row in arr:
print(" ".join(map(str, row)))
# 19 21
# 1 2
Pros
- Extremely lightweight and efficient for small to moderate array sizes.
- It works well with native Python types such as string and list.
Cons
- It lacks output formatting. Does not give much options.
- It becomes less performant when the dataset is large.
- Requires manual handling for multidimensional arrays.
Method 2: Using numpy.savetxt()
The numpy.savetxt() function saves an array to a text file, but we can use it for advanced formatting and output in the console.
Printing 1D array
import numpy as np import sys arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) np.savetxt(sys.stdout, arr.reshape(1, -1), fmt='%d', delimiter=' ') # 1 2 3 4 5
Printing 2D array
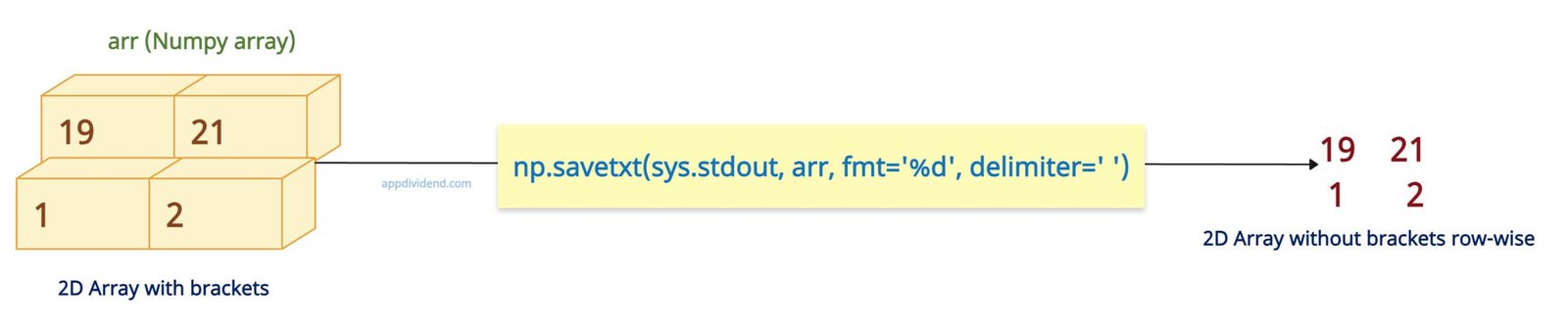
import numpy as np import sys arr = np.array([[19, 21], [1, 2]]) np.savetxt(sys.stdout, arr, fmt='%d', delimiter=' ') # 19 21 # 1 2
Pros
- Since np.savetxt() is a numpy method, it is optimized for large datasets, and it is highly efficient in complex tasks.
- It supports advanced formatting and delimiter control.
- It works excellently for tasks requiring file output.
Cons
- If you are working with small data, the np.savetxt() method is not recommended.
- The syntax is slightly more complicated than the join() method.
That’s all!