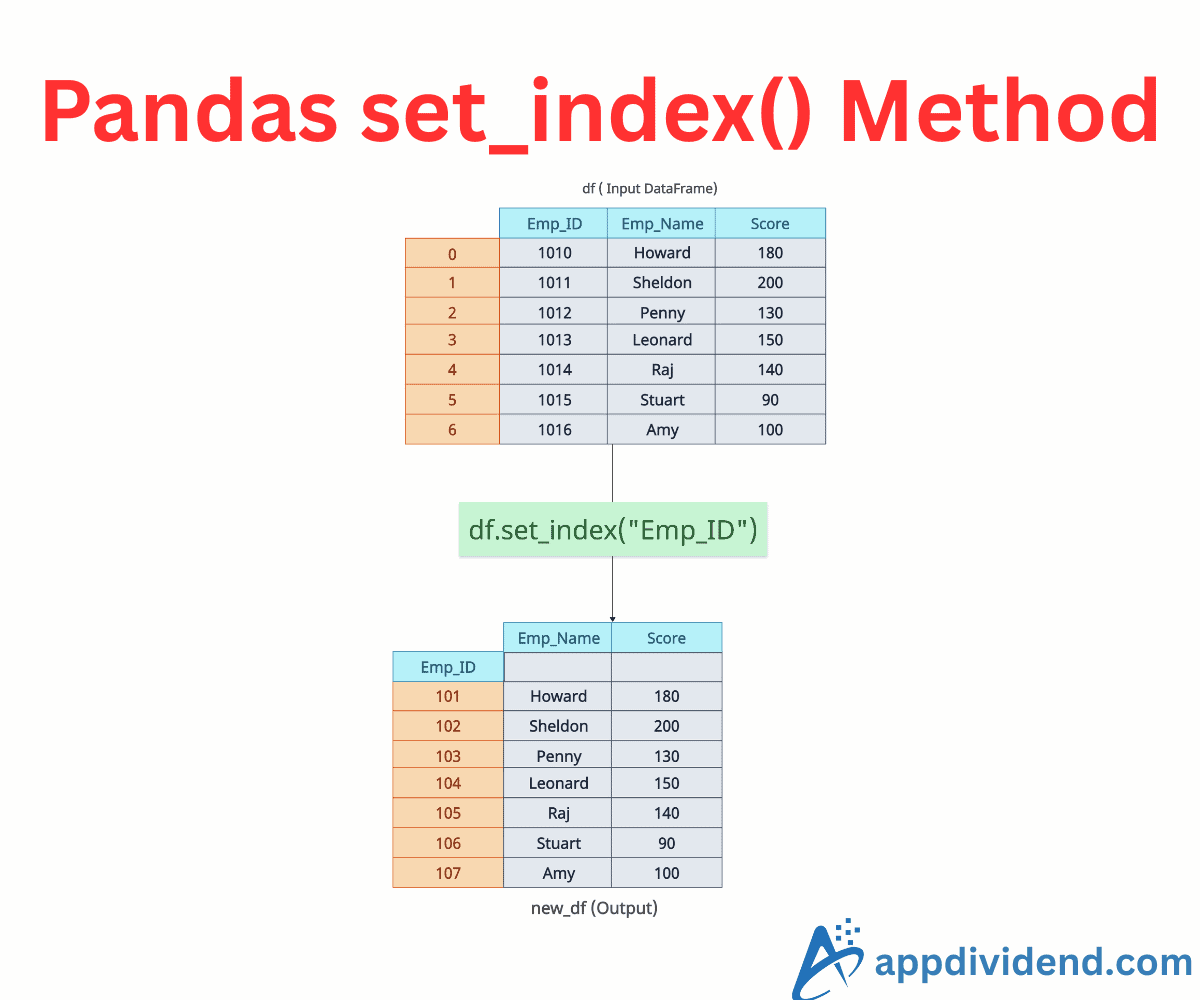
The set_index() method in Pandas sets one or more existing columns of a DataFrame as its index (row labels). It restructures the DataFrame by promoting specified columns to the index.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107],
'Team_Name': ["Lakers", "Patriots", "Yankees", "Lakers", "Red Sox", "Warriors", "Patriots"],
'Wins': [12, 10, 14, 12, 13, 15, 18]
}
)
print(df)
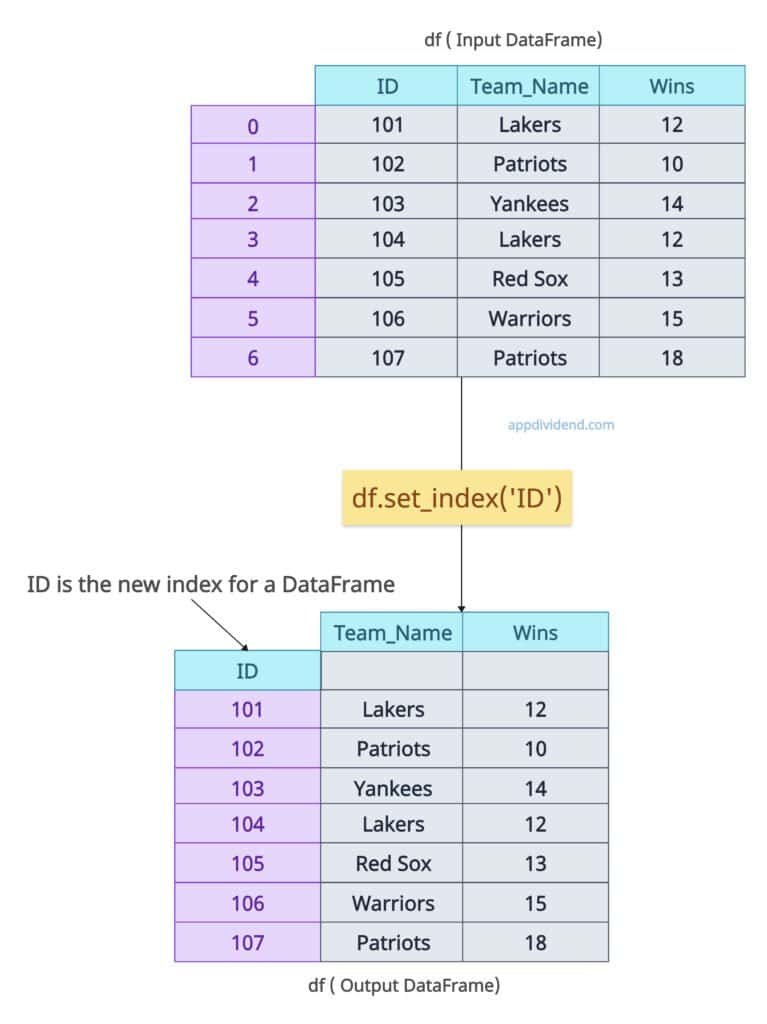
df = df.set_index('ID')
print(df)
In the above output figure, we are setting the “ID” column as the index of the DataFrame. After setting the index, the structure of the output DataFrame differs from that of the input DataFrame.
By default, the DataFrame has indexes, but if you have a requirement to set any unique column as an index, you can use this method.
Syntax
DataFrame.set_index(keys,
drop=True,
append=False,
inplace=False,
verify_integrity=False)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| keys (label or array-like or list of labels/arrays, required) |
It represents the column label(s) to use as the new index. It can be a single string/column name, a list for a multi-index. |
| drop (bool, default True) |
If it is True, it removes the column(s) specified in keys from the DataFrame’s columns after setting them as the index. If False, it retains them as regular columns. |
| append (bool, default False) |
If it is True, it appends the specified keys to the existing index (creating or extending a multi-index) instead of replacing it. |
| inplace (bool, default False) | If it is True, it modifies the DataFrame in place and returns None.
If False, it returns a new DataFrame with the changes. |
| verify_integrity bool, default False) | If it is True, it checks for duplicates in the new index and raises a ValueError if any are found, ensuring uniqueness. |
Setting multiple columns as a multi-index
We can set multiple columns as indexes for a DataFrame. Just pass the array of columns to the set_index() method, and it is done.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107],
'Team_Name': ["Lakers", "Patriots", "Yankees", "Lakers", "Red Sox", "Warriors", "Patriots"],
'Wins': [12, 10, 14, 12, 13, 15, 18]
}
)
print(df)
multi_indexes_df = df.set_index(['ID', 'Team_Name'])
print(multi_indexes_df)
In this code, we are setting two columns as indices: ID and Team_Name.
It created a hierarchical MultiIndex. You can access via multi_indexes_df.loc[(104, ‘Lakers’)].
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107],
'Team_Name': ["Lakers", "Patriots", "Yankees", "Lakers", "Red Sox", "Warriors", "Patriots"],
'Wins': [12, 10, 14, 12, 13, 15, 10]
}
)
multi_indexes_df = df.set_index(['ID', 'Team_Name'])
print(multi_indexes_df.loc[(104, 'Lakers')])
# Output:
# Wins 12
# Name: (104, Lakers), dtype: int64
Retaining columns with drop=False
By default, drop=True because when you set a column as an index, that specific regular column will be gone, because otherwise, there would be a duplicate column. One acts as an index and the other acts as a normal.
Let’s set drop=False and have a duplicate column to see what that DataFrame structure looks like:
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107],
'Team_Name': ["Lakers", "Patriots", "Yankees", "Lakers", "Red Sox", "Warriors", "Patriots"],
'Wins': [12, 10, 14, 12, 13, 15, 18]
}
)
df_duplicate = df.set_index("ID", drop=False)
print(df_duplicate)
Here is the output:
Appending to existing index with append=True
What if we set a column as an index, and now we want to add another column as an index? Can we do it programmatically? The answer is YES. You can append another column as an index to the existing index column by setting the append=True argument.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107],
'Team_Name': ["Lakers", "Patriots", "Yankees", "Lakers", "Red Sox", "Warriors", "Patriots"],
'Wins': [12, 10, 14, 12, 13, 15, 18]
}
)
df = df.set_index("ID")
appended_index_df = df.set_index('Team_Name', append=True)
print(appended_index_df)
In this code, first, we set an “ID” column as an index, and then we appended another column, “Team_Name” as an index. So, we now have two index columns.
In-Place modification
If you don’t want a new DataFrame after setting an index and modifying the existing one, pass inplace=True as an argument to the method.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame(
{
'ID': [101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107],
'Team_Name': ["Lakers", "Patriots", "Yankees", "Lakers", "Red Sox", "Warriors", "Patriots"],
'Wins': [12, 10, 14, 12, 13, 15, 18]
}
)
df.set_index("ID", inplace=True)
print(df)
That’s all!






Kareem Morkve
Great share! very immpreive article