When it comes to converting a Pandas DataFrame to a Python List, it depends on what type of output you want. For example, you can convert a whole DataFrame to a List of Lists (Row-Wise, Preserves Order), a single column to a flat list, or a DataFrame to a list of dicts.
Converting a full DataFrame to a List
The df.values.tolist() method converts the whole DataFrame into a list of lists, where each row becomes a list, and it keeps order (row-wise). This approach is fast and memory-efficient, but it loses column names.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [11, 21, 31],
'B': ['x', 'y', 'z'],
'C': [True, False, True]
})
print(df.values.tolist())
# Output: [[11, 'x', True], [21, 'y', False], [31, 'z', True]]
In the DataFrame df, we defined 3 columns, each containing three values.
The output list had three rows, each containing 3 values. The first row has [11, ‘x’, True]. The second row is [21, ‘y’, False]. The third row is [31, ‘z’, True].
Empty DataFrame
If the input DataFrame is empty, the output list will be empty too!
import pandas as pd empty_df = pd.DataFrame() empty_list = empty_df.values.tolist() print(empty_list) # Output: []
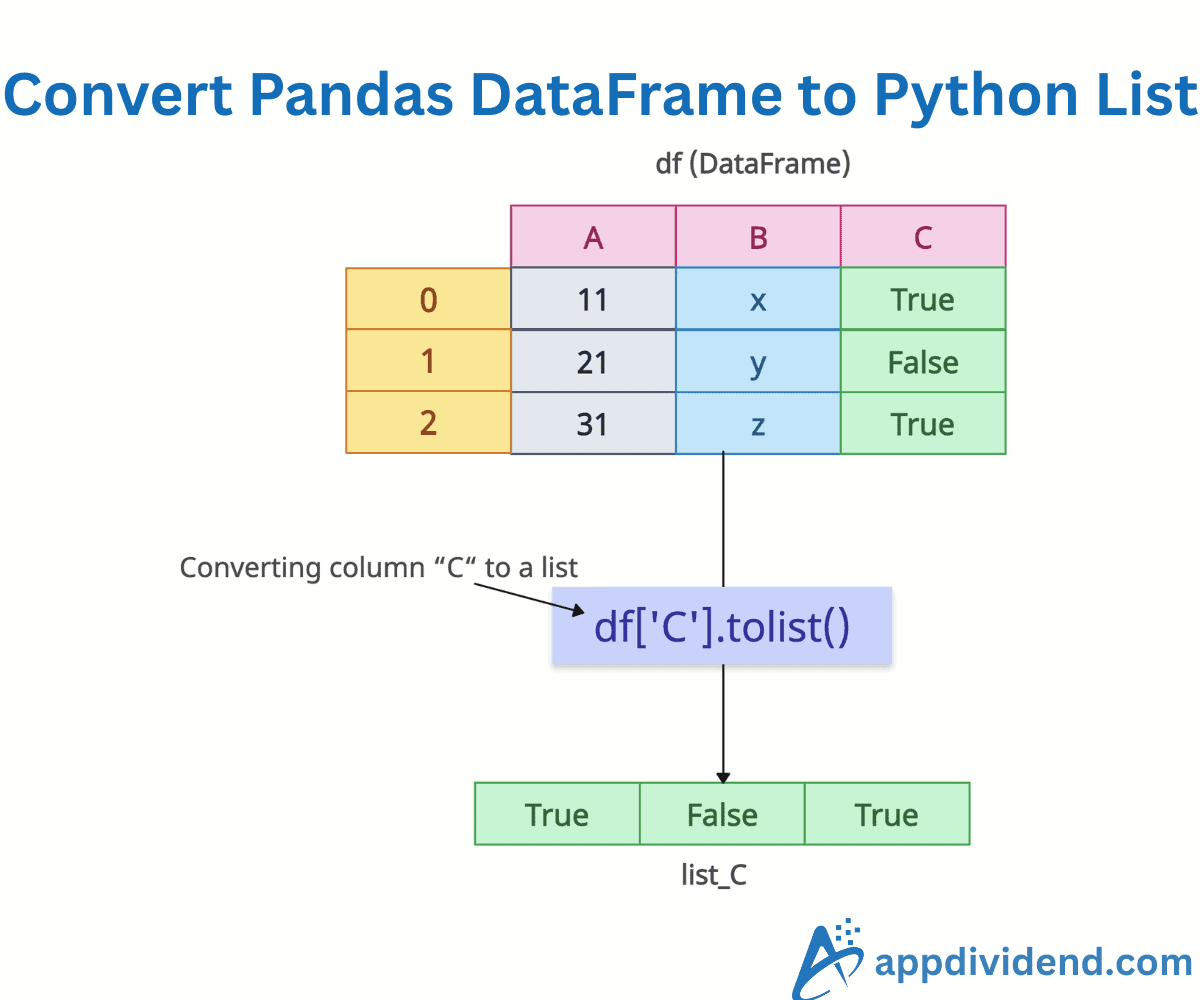
Converting a DataFrame column to a list
The df[‘col_name’].tolist() method selects by column label (name) and converts it to a list. This method is for a specific column. If you want a list of specific column values, you can use this approach.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [11, 21, 31],
'B': ['x', 'y', 'z'],
'C': [True, False, True]
})
list_B = df['B'].tolist()
print(list_B)
# Output: ['x', 'y', 'z']
In this code, I want to fetch the column “B”‘s values as a list, so we used df[‘B’] to select that column and converted all the values to a list using the tolist() method.
Converting a DataFrame to a List of dicts
Use the df.to_dict(‘records’) method when you want an output as a list of dictionaries. It is feasible for REST APIs, NoSQL, JSON dumps, and readable output.
The main advantage of this approach is that it retains column names as keys. However, it is slightly slower than a list of lists, as dictionaries use more memory.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [11, 21, 31],
'B': ['x', 'y', 'z'],
'C': [True, False, True]
})
list_of_dicts = df.to_dict('records')
print(list_of_dicts)
# Output: [{'A': 11, 'B': 'x', 'C': True}, {'A': 21, 'B': 'y', 'C': False}, {'A': 31, 'B': 'z', 'C': True}]
That’s all!




R A
Thanks a lot Sir, you are genius
threadsGuy
This is a great post! I was wondering how to do the same thing with my dataframe.