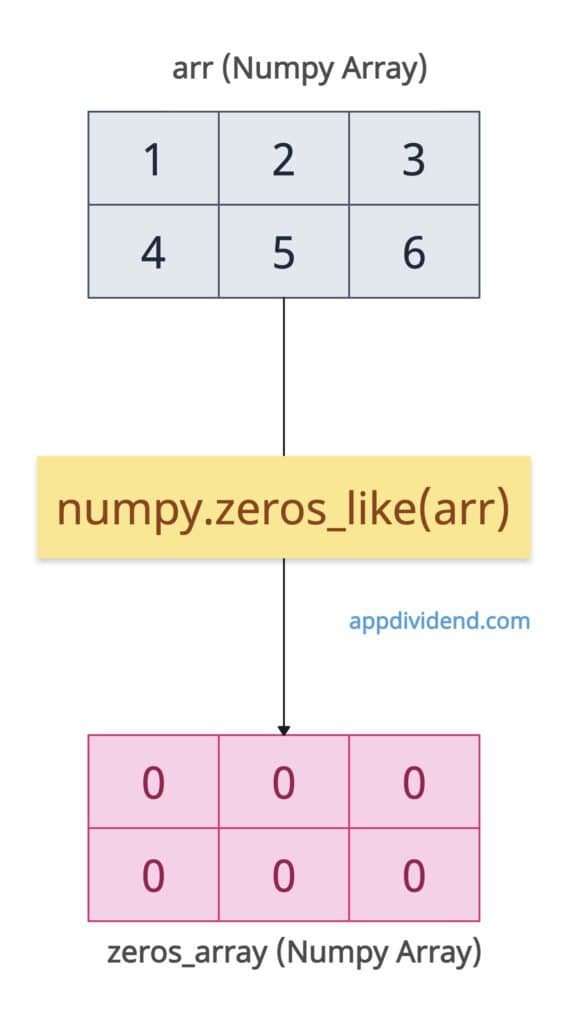
The numpy.zeros_like() method creates a new array of zeros with the same shape and type as a given input array or array-like object.
import numpy as np
arr = np.array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
zeros_array = np.zeros_like(arr)
print(zeros_array)
# Output:
# [[0 0 0]
# [0 0 0]]
We created a 2D array of 0s from the input array with the same shape (2×3) and matching int64 dtype (the default on most systems).
Syntax
numpy.zeros_like(arr,
dtype=None,
order='K',
subok=True,
shape=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| arr (required, array_like) | It represents an array or array-like object.
You can take it as a reference array from which the zeros_like() method will create a new array filled with 0s with the same shape and size as arr. |
| dtype (data-type, optional) | It overrides the dtype of the resulting array. By default, it is an int64, but you can override it as needed. |
| order ({‘C’, ‘F’, ‘A’, ‘K’}, optional) | It controls the memory layout of the output array. By default, it is “k”. |
| subok (bool, optional) |
If True (default), they are subclasses of ndarray. If False, the output is always a base ndarray. |
| shape (int or sequence of ints, optional) |
It overrides the shape of the resulting array. |
Overriding dtype
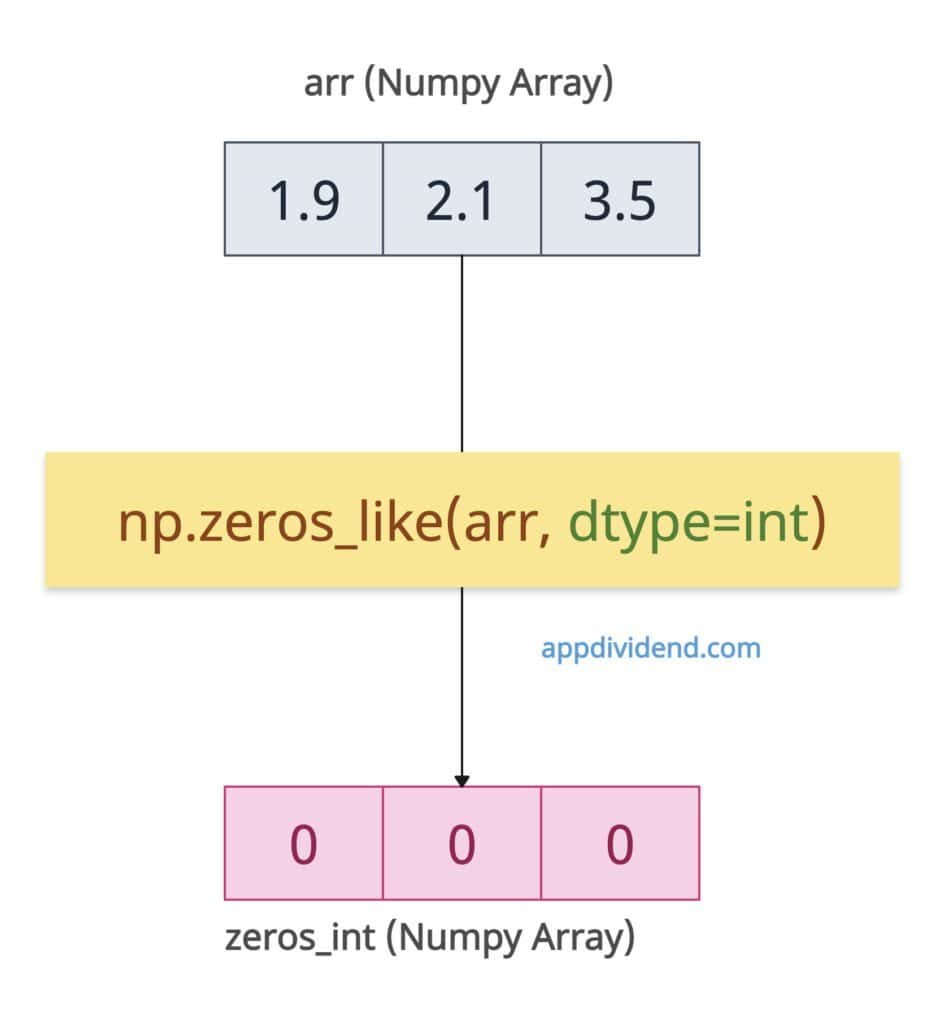
Change the output array’s type to int64 by passing the dtype=int argument, even if the input array contains float values.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1.9, 2.1, 3.5]) zeros_int = np.zeros_like(arr, dtype=int) print(zeros_int) # Output: [0 0 0]
Specifying memory order
The ‘order’ control defines the layout; ‘K’ preserves the input’s order for optimal memory access.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]], order='F') # Fortran-contiguous z_c = np.zeros_like(arr, order='C') # Force C-order print(z_c) # Output: [[0 0] [0 0]], C-contiguous z_k = np.zeros_like(arr) print(z_k) # Output: [[0 0] [0 0]], K-contiguous # Default 'K' preserves 'F'
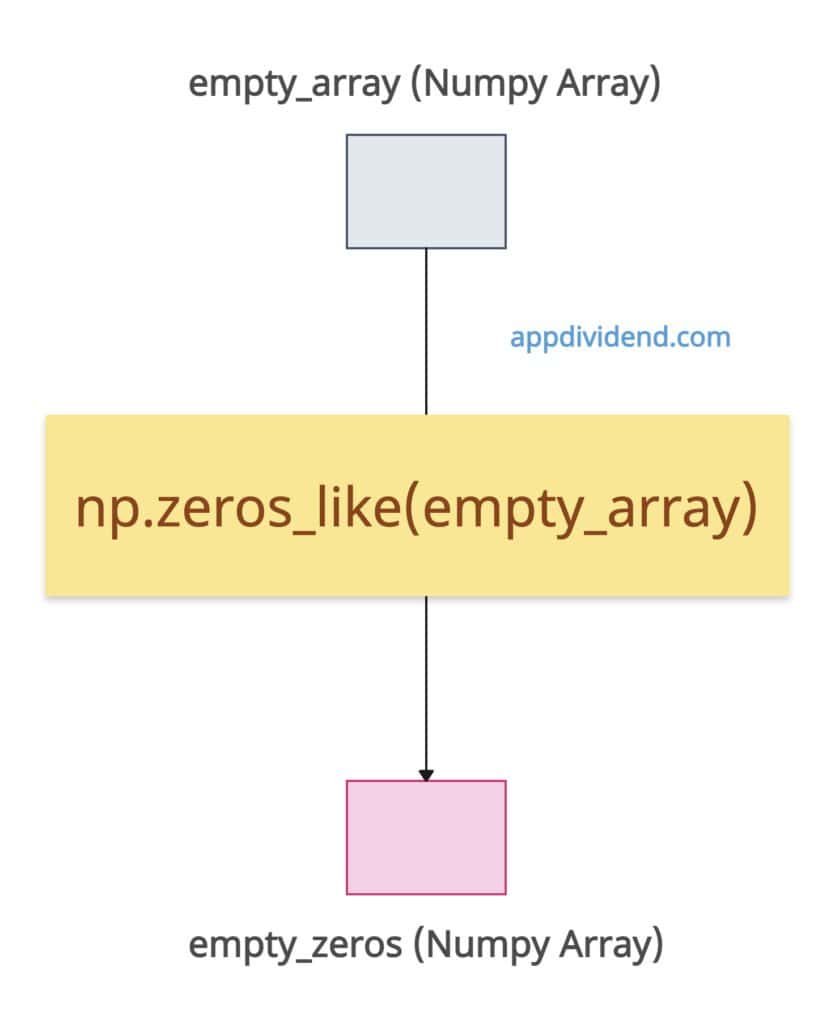
Empty array input
The np.zeros_like() method handles empty shapes correctly, producing an array of zeros.
import numpy as np empty_array = np.array([]) # Shape (0,) empty_zeros = np.zeros_like(empty_array) print(empty_zeros) # Output: []
That’s all!