Numpy.where() is a conditional selection function that returns elements from arrays based on conditions.
It operates in two distinct modes:
- Condition-only mode: It returns the tuple of indices where the condition is True.
- Condition + x, y mode: It returns elements chosen from x or y based on the condition.
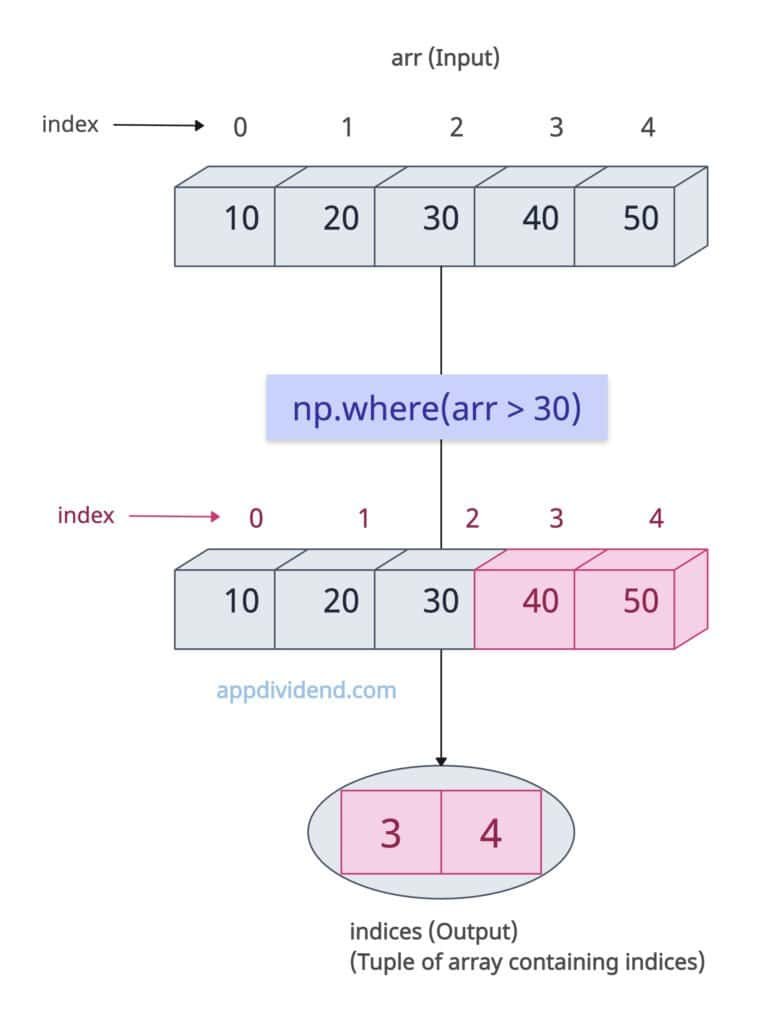
Finding indices where the condition is True (1D Array)
Let’s find the index of elements that satisfy our condition. The output array will be the indices of the input array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50]) indices = np.where(arr > 30) print(indices) # Output: (array([3, 4]),)
The above output shows that numpy.where() method returned a tuple with a single array of indices (0-based).
Use result[0] to access the index array.
Syntax
For finding indices: numpy.where(condition) For conditional selection: numpy.where(condition, x, y)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| condition (array_like, bool) | It represents a Boolean array or an expression. |
| x or y (An optional array-like object or scalar) |
It represents arrays (or scalars) with the same shape as the condition (or that can be broadcast to it). If both are provided, elements are chosen from x when the condition is True, else from y. If omitted, returns indices where the condition is True. |
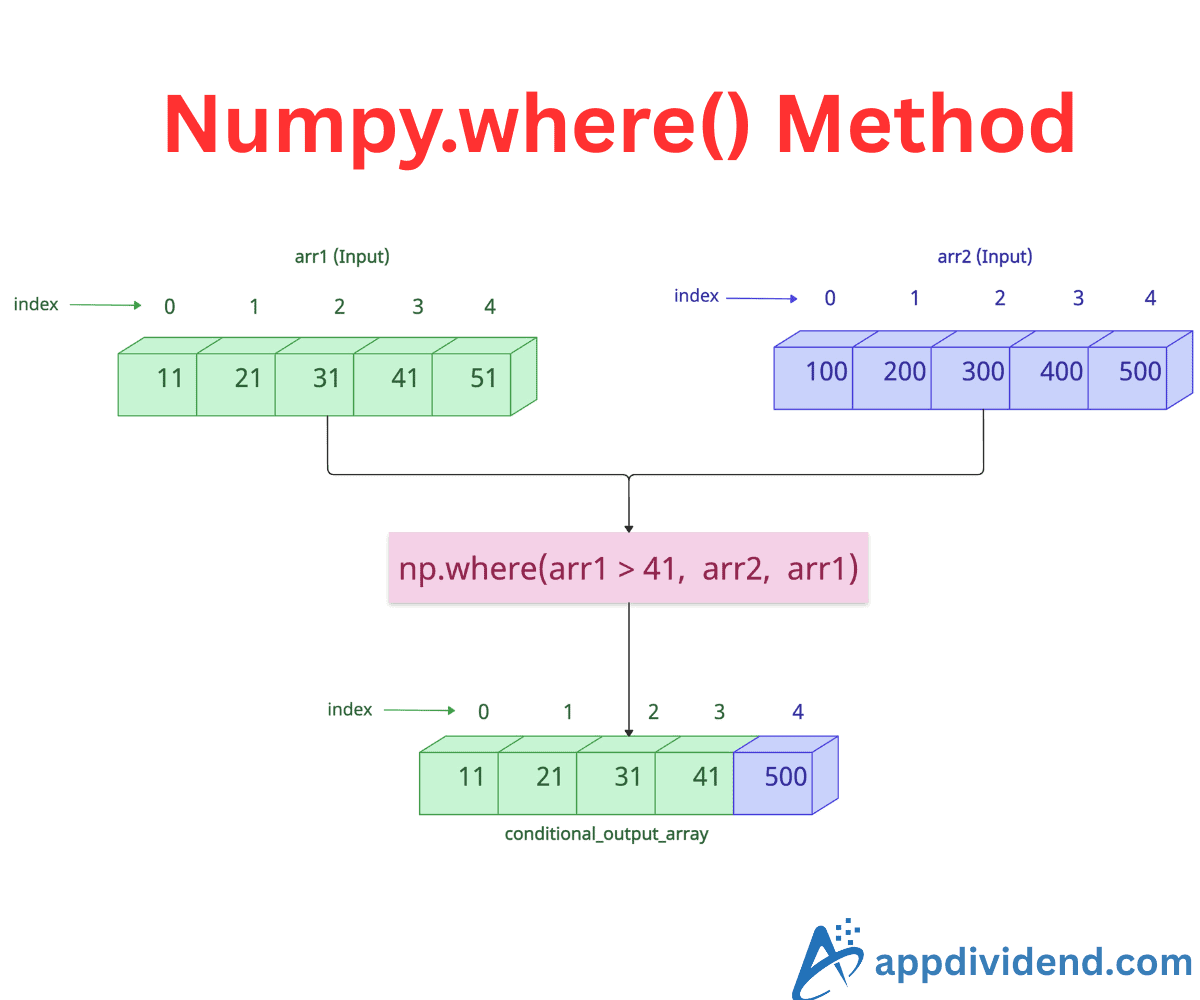
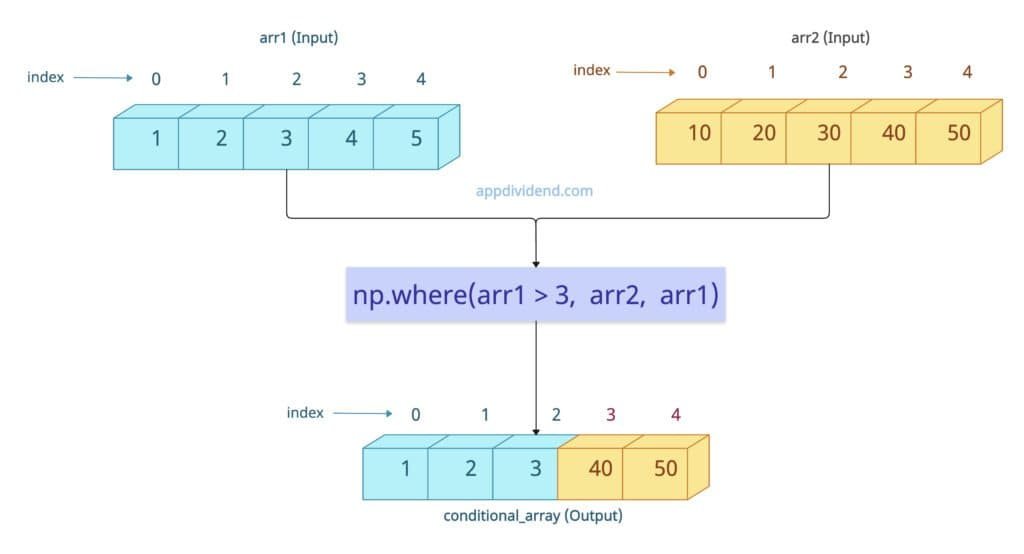
Conditional selection from two arrays
The np.where() method replaces elements based on a condition using values from another array.
import numpy as np arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) arr2 = np.array([10, 20, 30, 40, 50]) conditional_array = np.where(arr1 > 3, arr2, arr1) print(conditional_array) # [ 1 2 3 40 50]
In this code, for elements where the condition arr1 > 3 is True, the corresponding element from arr2 is selected. Otherwise, the element from arr1 is selected.
In short, where arr1 > 3 is True, where() method starts taking elements from arr2; else from arr1.
Conditional selection with Scalars
When you pass scalars instead of arrays for the x and y arguments in np.where(condition, x, y), NumPy applies uniform replacement across the entire array.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]) uniform_replacement = np.where(arr > 3, 100, -100) print(uniform_replacement) # Output: [-100 -100 -100 100 100]
In this code, it replaced an entire array with x and y values. The elements that passed the condition are replaced by 100, and those that did not pass are replaced by -100.
np.where() with Multiple Conditions
By default, the np.where() method accepts only a single condition, but you can add multiple conditions by using bitwise operators like AND(&), OR(|), and NOT(~).
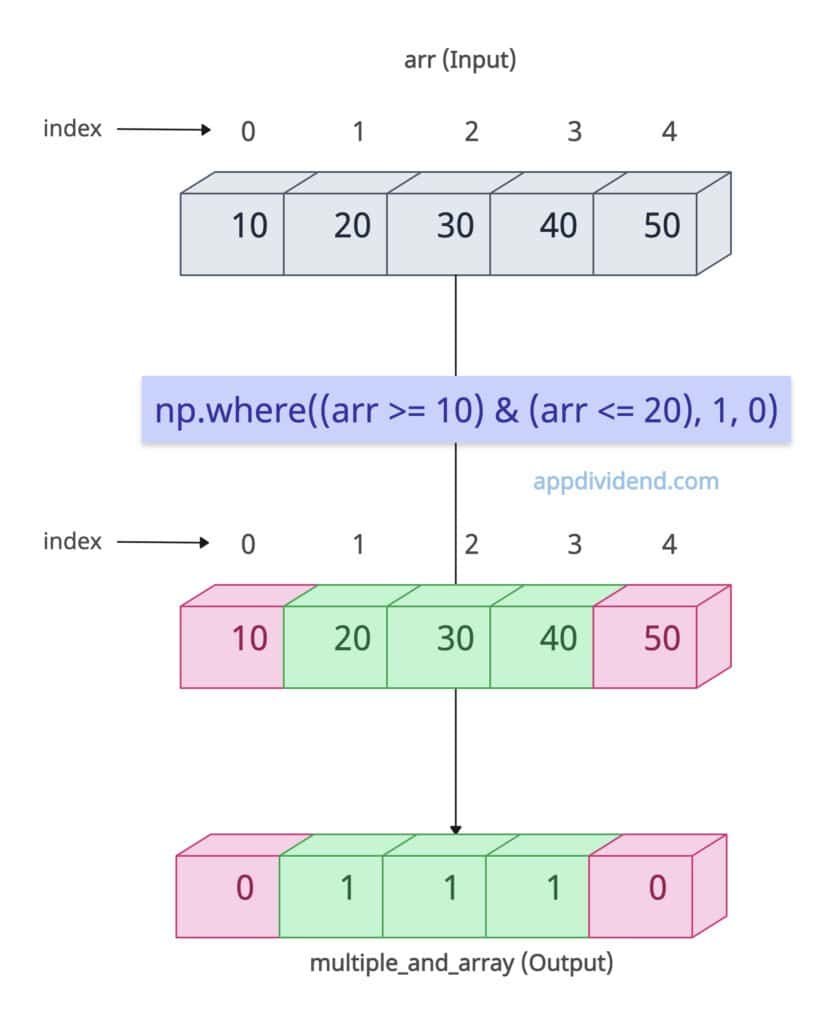
AND (&) condition
import numpy as np arr = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20, 25]) # Select elements between 10 and 20 (inclusive) multiple_and_array = np.where((arr >= 10) & (arr <= 20), 1, 0) print(multiple_and_array) # Output: [0 1 1 1 0]
In the above code, we used the & operator to apply two conditions: >= and <=.
Only numbers in the range [10, 20] are replaced with 1; others are replaced with 0.
OR (|) condition
import numpy as np arr = np.array([5, 10, 15, 20, 25]) # Select elements less than 10 OR greater than 20 result = np.where((arr < 10) | (arr > 20), 1, 0) print(result) # Output: [1 0 0 0 1]
In the above code, we used the | operator to apply two conditions: < and >.
Elements outside the [10, 20] range get 1, other elements get 0.
That’s all!