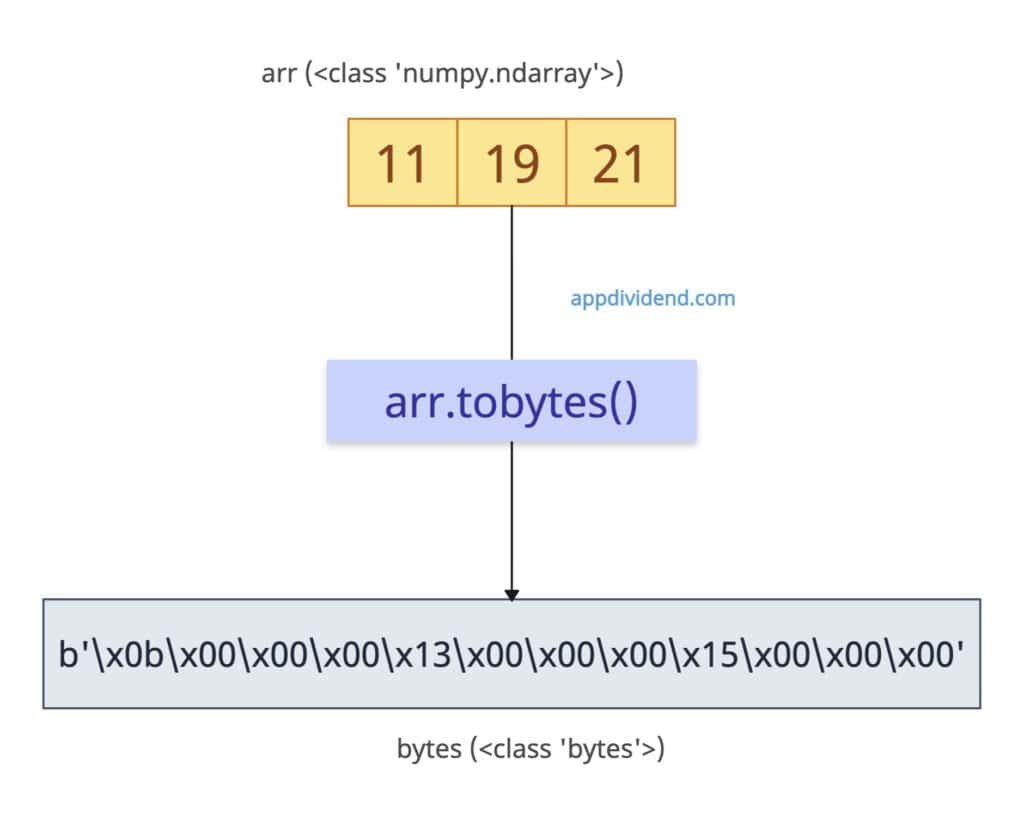
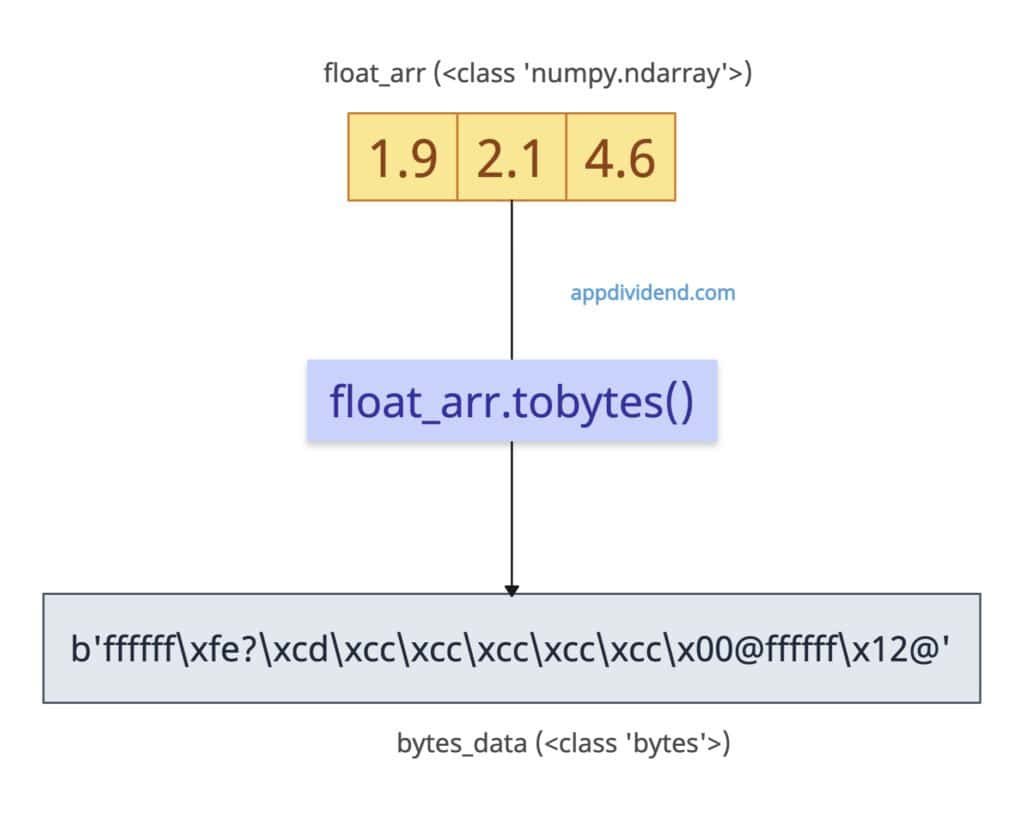
The most efficient and primary way to convert an input numpy array to Python bytes is to use the numpy.ndarray.tobytes() method. The np.ndarray.tobytes() extracts raw buffer contents as bytes.
import numpy as np arr = np.array([11, 19, 21], dtype=np.int32) bytes_data = arr.tobytes() print(bytes_data) # Output: b'\x0b\x00\x00\x00\x13\x00\x00\x00\x15\x00\x00\x00' print(len(bytes_data)) # Output: 12 (3 elements * 4 bytes)
In this code, we defined a 1D integer array, applied the tobytes() method to it, and printed the bytes and their lengths, which is 12. Each int32 takes 4 bytes.
Syntax
ndarray.tobytes(order='C')
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
|
order |
It controls memory layout.
(‘C’ for row-major/C-order, ‘F’ for column-major/Fortran-order, ‘A’ for preserving the original.) Default: ‘C’. |
1D float array
Let’s define an array of three floating values.
import numpy as np float_arr = np.array([1.9, 2.1, 4.6], dtype=np.float64) bytes_data = float_arr.tobytes() print(bytes_data) # Output: b'ffffff\xfe?\xcd\xcc\xcc\xcc\xcc\xcc\x00@ffffff\x12@' print(len(bytes_data)) # Output: 24
Different memory layouts
A numpy store arrays in two different memory layouts:
| Order | Name | Meaning | Storage pattern |
|---|---|---|---|
'C' |
C-contiguous | Row-major (like Python, C) | Left-to-right, row by row |
'F' |
Fortran-contiguous | Column-major (like MATLAB, Fortran) | Top-to-bottom, column by column |
Let’s define a 2D array and apply two different memory layouts:
import numpy as np arr = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]], dtype=np.int8) c_bytes = arr.tobytes(order='C') print(c_bytes) # Output: b'\x01\x02\x03\x04' f_bytes = arr.tobytes(order='F') print(f_bytes) # Output: b'\x01\x03\x02\x04'
The c_bytes represent type order “C” and f_bytes represent type order “F”.
Boolean arrays
NumPy does not bit-pack boolean arrays by default when converting them to bytes with .tobytes(). It stores one full byte (0x00 or 0x01) per boolean, not 8 per byte.
import numpy as np bool_arr = np.array([True, False, True, True], dtype=bool) bytes_data = bool_arr.tobytes() print(bytes_data) # Output: b'\x01\x00\x01\x01'
Empty arrays
If the array is empty, the output is an empty byte array.
import numpy as np empty = np.array([], dtype=np.int32) print(empty.tobytes()) # Output: b''
That’s all!