Joining two (or more) lists involves combining the elements of two or more lists into a single, unified sequence.
Here are different ways based on various scenarios:
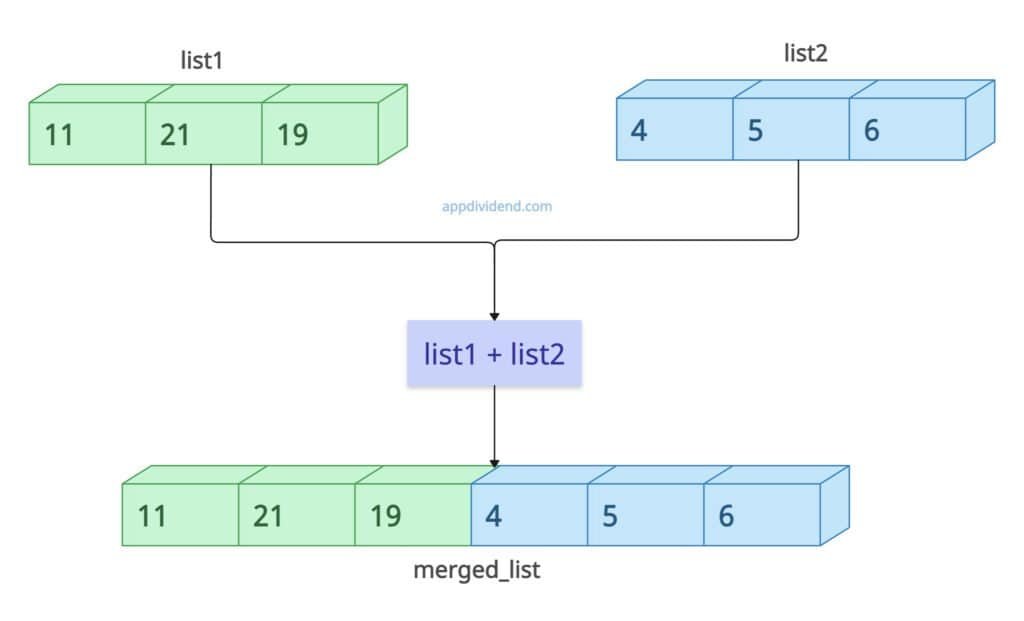
Method 1: Using the standard operator (+)
The most intuitive method for concatenating two lists is the + operator in Python. It creates a new list containing the elements of the first list, followed by those of the second.
Here is the basic syntax:
new_list = list1 + list2
It does not modify the original lists. It allocates new memory for the result.
list1 = [11, 21, 19] list2 = [4, 5, 6] # Creates a completely new object merged_list = list1 + list2 print(merged_list) # Output: [11, 21, 19, 4, 5, 6] print(list1) # Output: [11, 21, 19] (remains unchanged)
If the memory usage is not your primary concern, you can opt for this approach. However, it only works for lists and not for other types.
list1 = [11, 21, 19] merged_list = list1 + (4, 5, 6) print(merged_list) # TypeError: can only concatenate list (not "tuple") to list
Handling None
If one of your variables is None rather than an empty list [], concatenation will crash.
a = [1, 2] b = None result = a + b # Raises TypeError print(result) # TypeError: can only concatenate list (not "NoneType") to list
For safe concatenation, you can use a list comprehension.
a = [1, 2] b = None result = a + (b if b is not None else []) print(result) # Output: [1, 2]
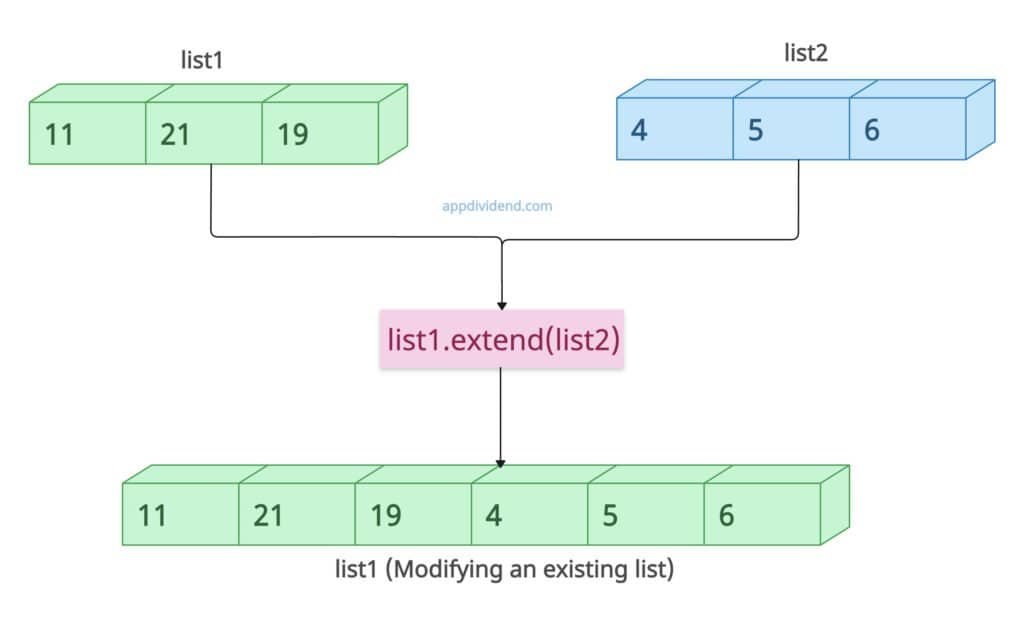
Method 2: Using a list.extend()
If you want to modify an existing list and do not care for a new list, use the built-in list.extend() method. It is the most efficient method for in-place concatenation.
The extend() method adds the second list to the tail end of the first list.
list1 = [11, 21, 19] list2 = [4, 5, 6] list1.extend(list2) # This modifies list1 in place and returns None print(list1) # Output: [11, 21, 19, 4, 5, 6]
The return value of the extend() method is None because it extends an existing list. In our case, we added three elements of list2 at the end of list1 and printed list1.
Method 3: Using itertools.chain()
What if you are working with massive lists (datasets) and you want to merge those efficiently? That’s where the itertools built-in package comes into the picture.
To efficiently merge two large lists in Python, use the itertools.chain() method to combine them.
The itertools.chain() method returns an iterator, and we need to convert back to a list using the list() constructor.
import itertools list1 = range(100000) # Large list list2 = range(100000) # Large list merged_iterator = itertools.chain(list1, list2) merged_list = list(merged_iterator) print(merged_list) # Output: [0, 1, 2, ..., 99999, 0, 1, 2, ..., 99999]
That’s all!