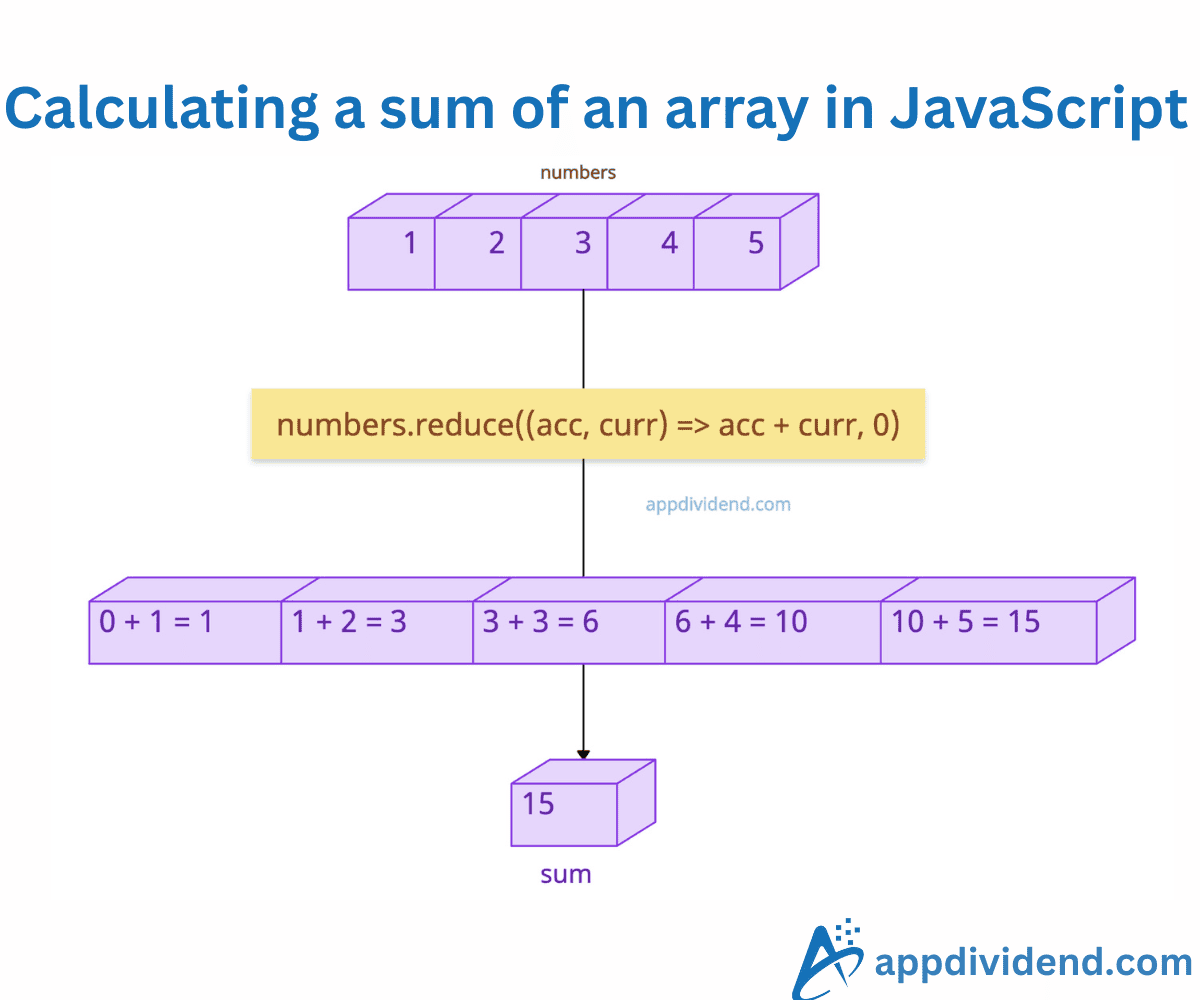
The most concise, functional, and idiomatic approach to find the sum of an array of numbers in JavaScript is to use the array.reduce() method. It iterates over the array indices, applies a reducer function, starting from an initial value (0 here), and accumulates the sum.
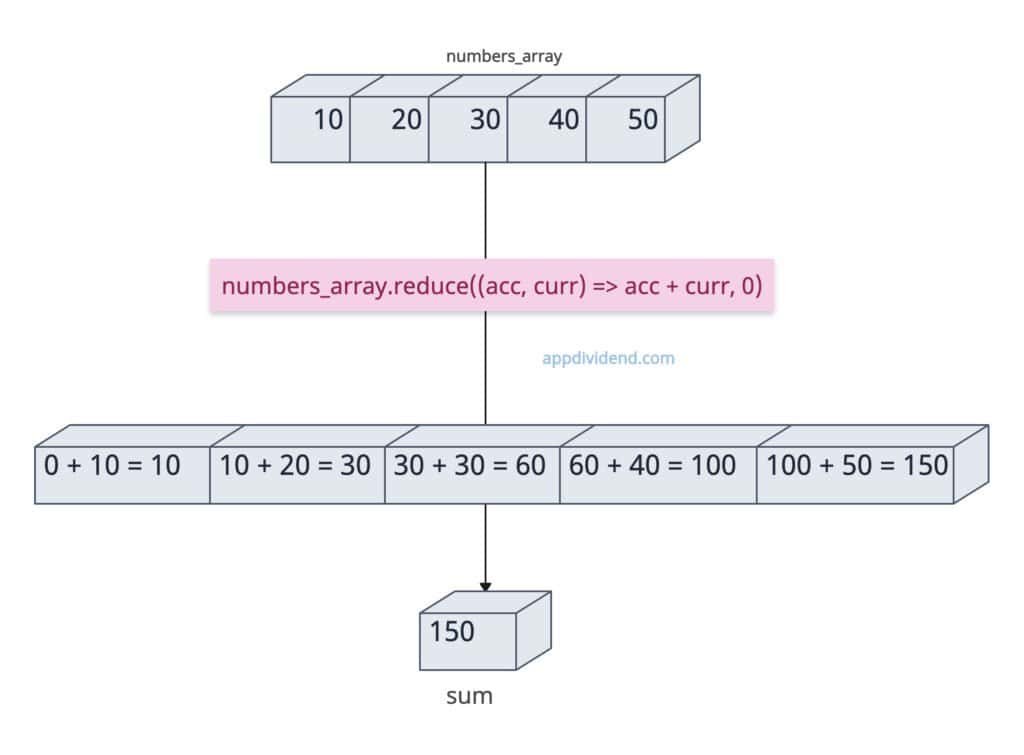
const numbers_array = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; const sum = numbers_array.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); console.log(sum); // Output: 150
In this code, 0 is the initial value. It then starts by adding 0 + 10 = 10, followed by 10 + 20 = 30, 30 + 30 = 60, 40 + 60 = 100, and finally, 50 + 100 = 150. Final sum is 150.
Empty array
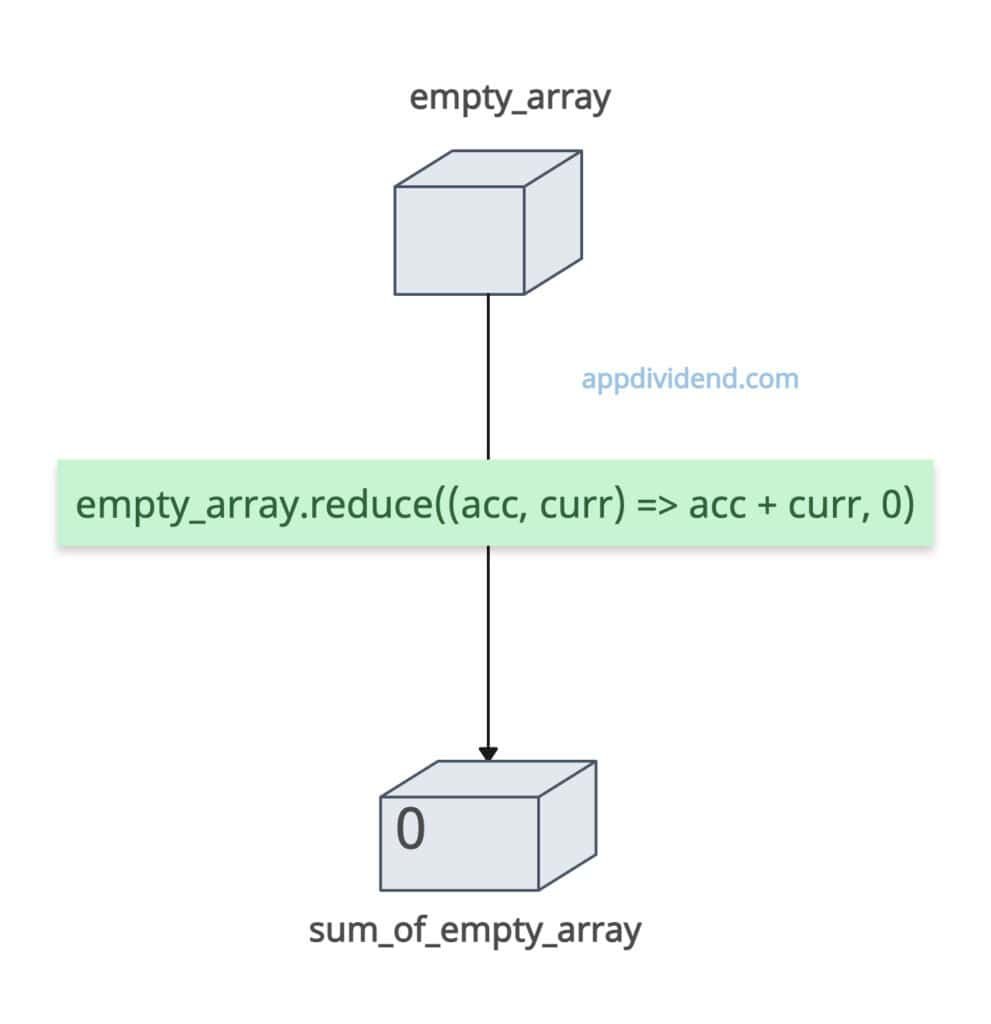
If the array is empty, the sum is 0 (Assuming that the initial value is 0).
const empty_array = []; const sum_of_empty_array = empty_array.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); console.log(sum_of_empty_array); // Output: 0
Single-element array
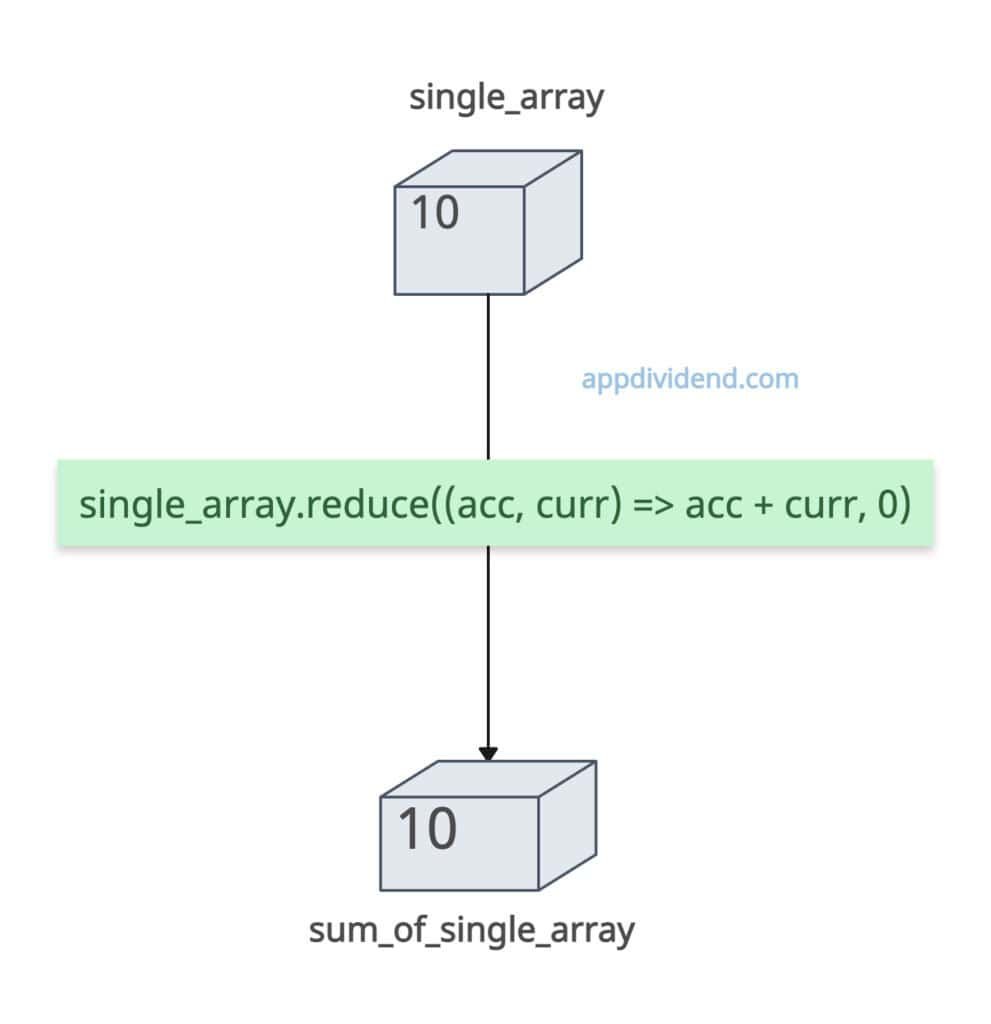
If the array contains a single element, the reduce() method returns that element itself as an output.
const single_array = [10]; const sum_of_single_array = single_array.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); console.log(sum_of_single_array); // Output: 10
Since the accumulator starts at 0, it adds the single value. So, 0 + 10 = 10, and hence the sum is 10.
An array with negative numbers
If the array contains negative integers, the reduce() method handles subtraction gracefully.
const array_with_negatives = [-10, 10, -20, -50, 30]; const sum_of_negatives = array_with_negatives.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); console.log(sum_of_negatives); // Output: -40
Array with floating-point numbers
If the array contains floating-point values, it returns a floating-point value as a sum.
const array_of_floating = [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4]; const sum_of_floating_point = array_of_floating.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); console.log(sum_of_floating_point); // Output: 11
Non-Numeric elements
If the array does not contain purely numeric values, coercion occurs (e.g. ‘2’ becomes 2, but booleans true become 1, and false becomes 0). What about if it encounters a string like this, “krunal”?
If it is a pure string, it will concatenate with other elements as the “+” operator does the concatenation with string elements.
const mixed_array = [1.1, true, "Krunal", false]; const sum_of_mixed_array = mixed_array.reduce((acc, curr) => acc + curr, 0); console.log(sum_of_mixed_array); // Output: 2.1Krunalfalse
As you can see from the output, the entire output becomes a string containing both numeric and alphabetic values.
Other approaches
Using forEach() Method
The array.forEach() method applies a callback to each element, accumulating the sum inside.
const numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]; let sum = 0; numbers.forEach(num => sum += num); console.log(sum); // Output: 150
The above approach is more functional than loops and easier to understand.
Using for…of Loop (Modern Iteration)
Using a for…of loop, you don’t need indices to iterate over each loop, and that is the difference between a regular for loop and this loop. It is more readable.
const numbers = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50];
function sumArray(arr) {
let sum = 0;
for (const num of arr) {
sum += num;
}
return sum;
}
console.log(sumArray(numbers));
// Output: 150
That’s all!