JavaScript Object.values() is a static method that returns an array of a given object’s own enumerable property values, in the same order as provided by a for…in loop (excluding prototype chain properties).
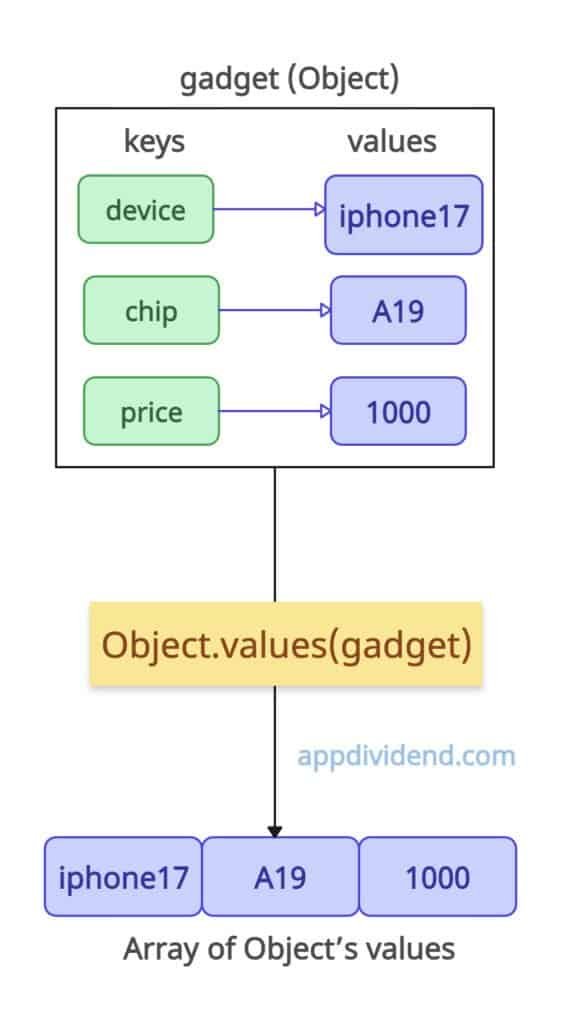
const gadget = { device: "iPhone17", chip: "A19", price: 1000 };
console.log(Object.values(gadget));
// Output: [ 'iPhone17', 'A19', 1000 ]
In this code, we log the values of a “gadget” object in an array. For fetching an array of keys, use Object.keys() method.
One thing to note is that only properties with the enumerable attribute set to true are included in the output values array.
Syntax
Object.values(obj)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| obj (required) | It represents an object from which to extract the enumerable own property values. |
Non-enumerable properties
Let’s create an Object with an enumerable property set to false and see if it appears in the output values array.
const obj = {};
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'hidden', {
value: 'secret',
enumerable: false
});
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'visible', {
value: 'data',
enumerable: true
});
console.log(Object.values(obj));
// Output: [ 'data' ]
In this code, we defined a property “hidden” for the object, but we set enumerable to false. Then, we added another property to the obj and set the enumerable to true. By default, for each property, enumerable is set to true if you add a property using dot (.) notation.
If you examine the output values array, it displays only the “data” value because its enumerable property value is set to true; however, the “hidden” property has an enumerable value of false. So, it was not included in the output array.
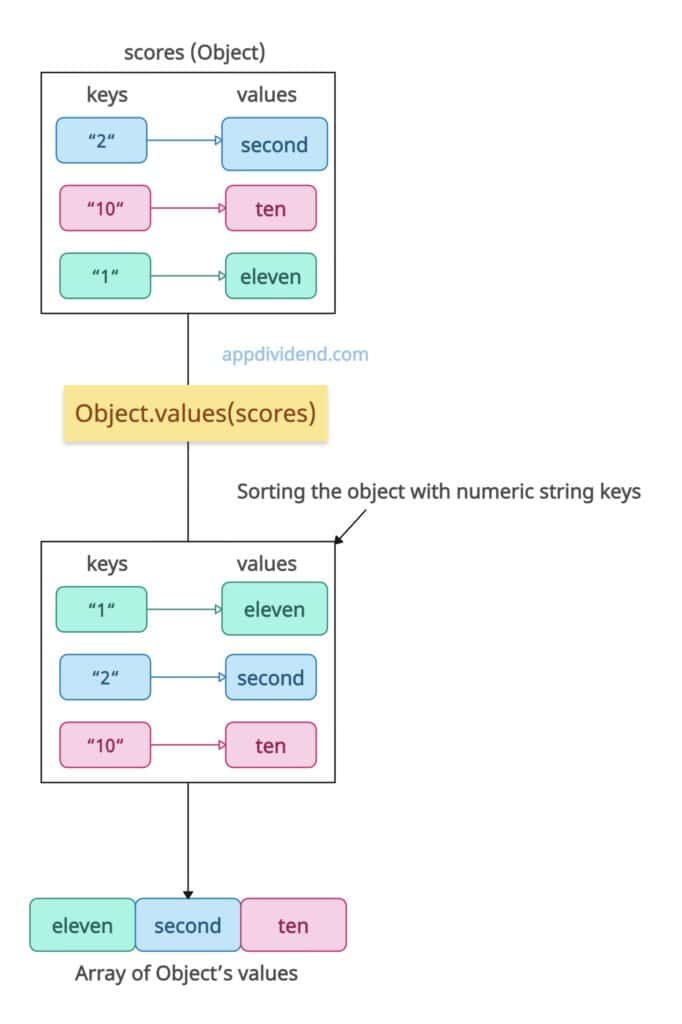
Numeric keys ordering
Numeric keys are treated as indices and sorted in ascending order, regardless of insertion order.
const scores = { '2': "second", '10': "ten", '1': "eleven" };
console.log(Object.values(scores));
// Output: [ 'eleven', 'second', 'ten' ]
The output array is based on the numeric string keys. It is sorted in ascending order based on the keys.
This mimics array behavior but applies to objects.
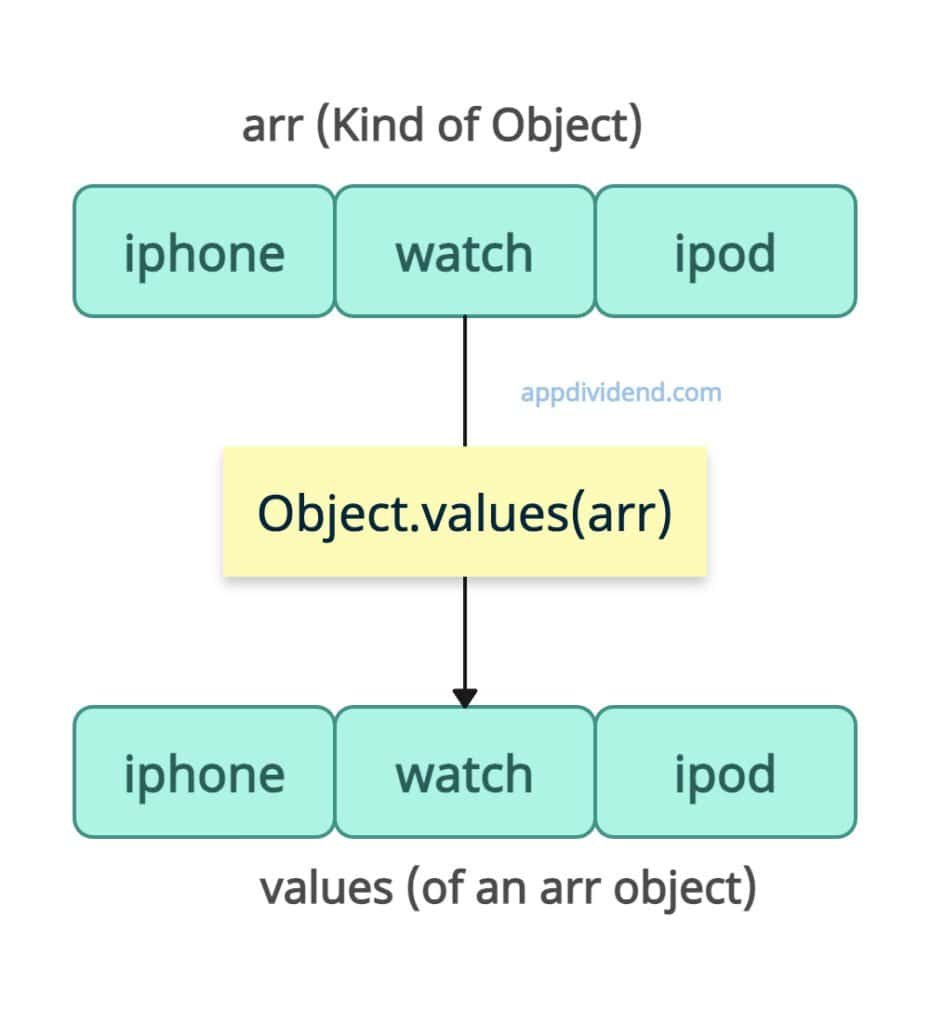
Arrays (Special case of objects)
Arrays are also objects, and their keys are numeric keys (0, 1, 2), which are enumerable.
If the input is an array, the Object.values() method returns the elements in index order.
const arr = ['iphone', 'watch', 'ipod']; console.log(Object.values(arr)); // Output: [ 'iphone', 'watch', 'ipod' ]
Inherited Properties
The .values() method ignores inherited properties and only counts its own properties.
const parent = { inherited: 'from parent' };
const child = Object.create(parent);
child.own = 'from child';
console.log(Object.values(child));
// Output: ['from child']
That’s all!


Azmi
This was helpful. Thanks 🙂