Emptying an array means removing all of its elements so that its length is 0.
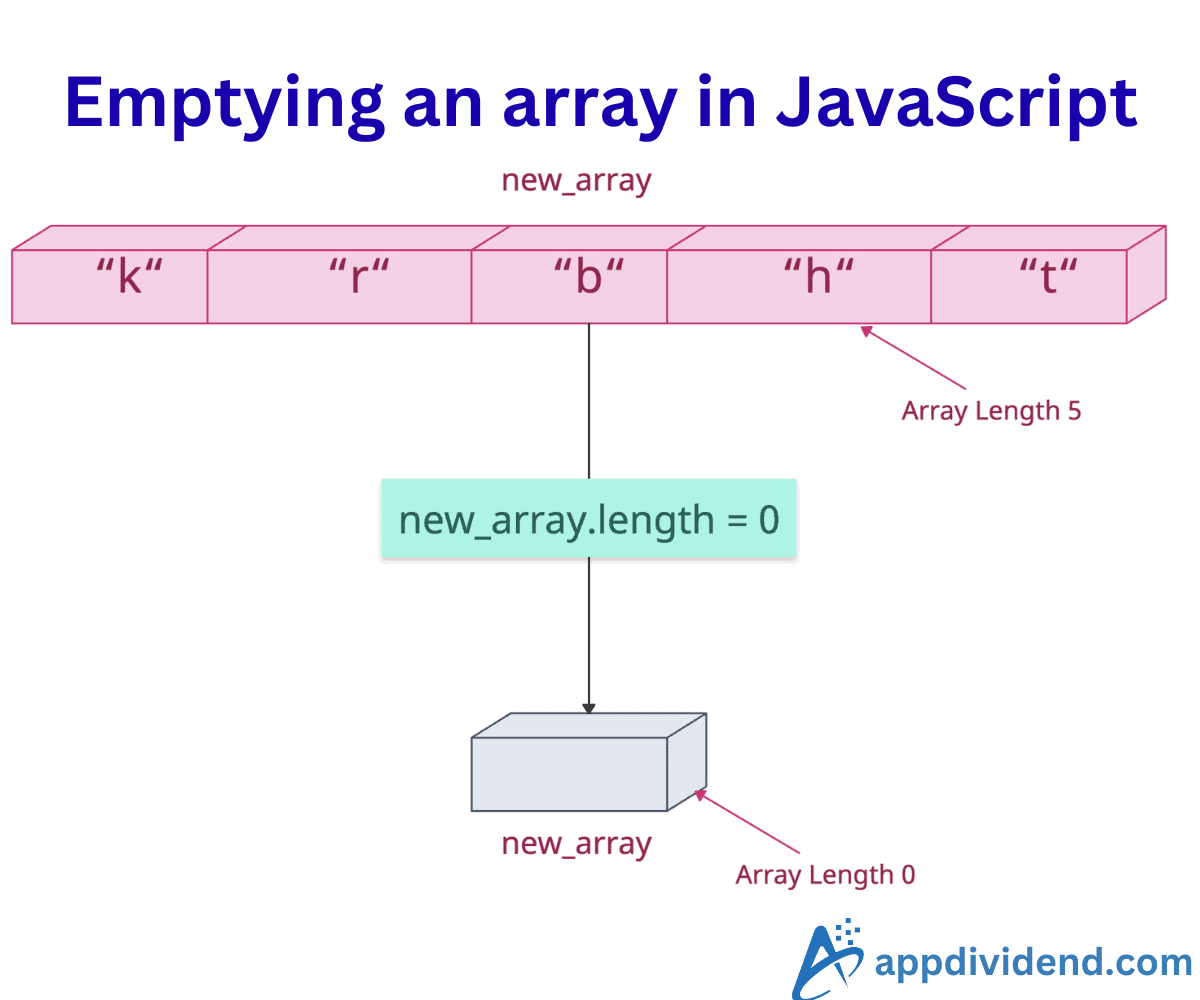
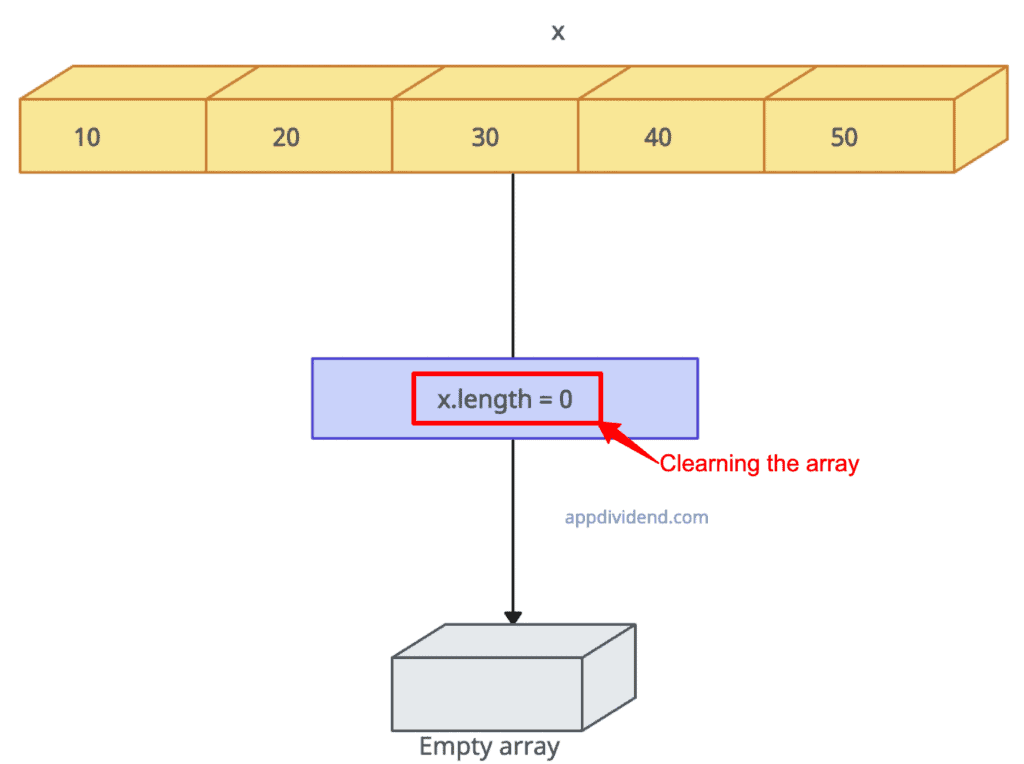
The most efficient and fastest way to empty an array is by setting the array length to 0, like this: array.legth = 0. All the elements will be cleared automatically.
const x = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
console.log("Before emptying: ", x)
// Output: Before emptying: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
x.length = 0;
console.log("After emptying: ", x)
// Output: After emptying: []
As you can see from the output that it cleared the array.
Already an empty array
If the array is already empty, it returns an empty array without throwing any error.
let arr = []; arr.length = 0; console.log(arr); // Output: []
Sparse Arrays (with Holes)
Let’s say we have an array with holes in it. If you clear that array, it will become empty too!
The length=0 removes holes; reassignment creates dense empty.
let arr = []; arr[5] = 'hole'; console.log(arr.length); // Output: 6 arr.length = 0; console.log(arr.length); // Output: 0 (holes gone)
Large Arrays (Performance)
If you have a large array filled with 0s, the fastest way to empty it is to set its length to 0. If you opt for a loop, it will cause a performance issue, and it is the slowest approach.
let large = new Array(1e6).fill(0); large.length = 0; // Instant while (large.length) large.pop(); // Slow, O(n)
Alternate approaches
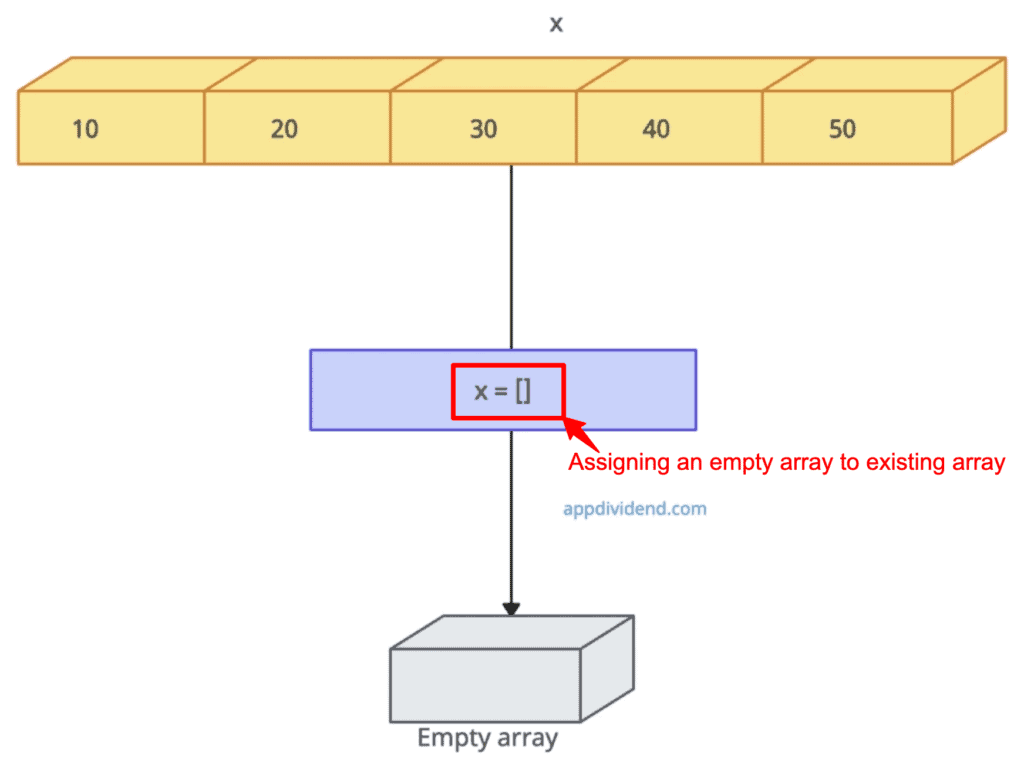
Approach 1: Assigning an empty array to an existing array
If you don’t need to maintain references to the original array, you can simply assign a new empty array to the existing array, and it becomes an empty.
let x = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
console.log(x)
// Output: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
x = []
console.log("Empty array: ", x)
// Output: Empty array: []
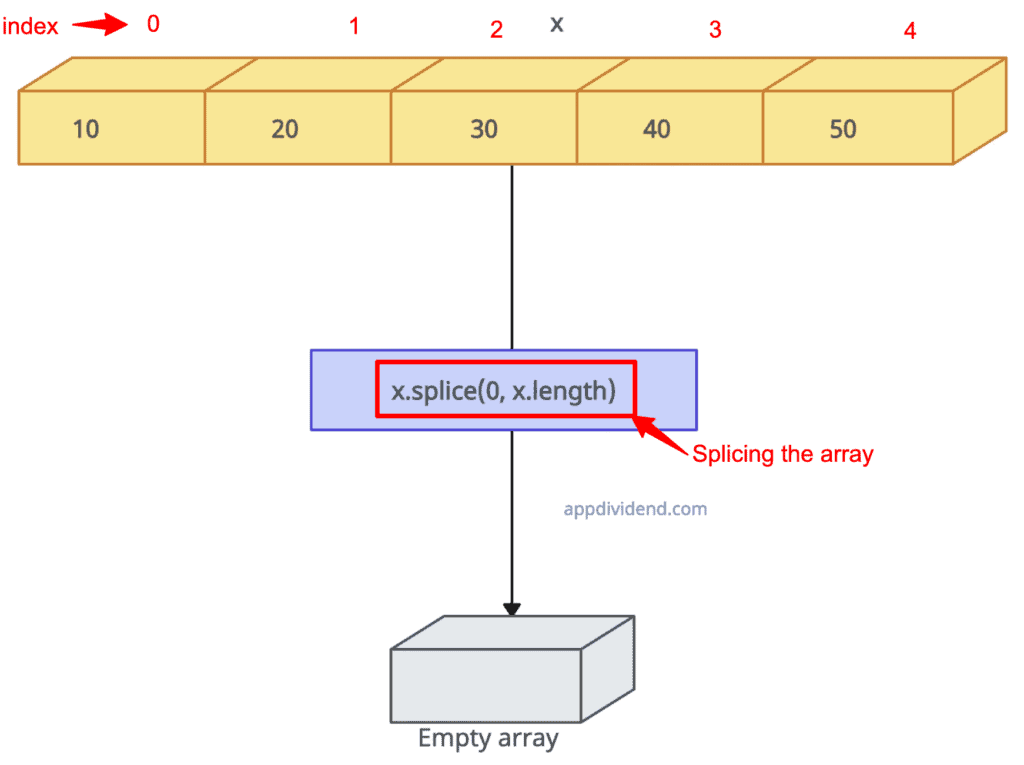
Approach 2: Using the splice() function
You can use the array.splice() method to set the starting 0 and delete count to the array’s length, which means from the starting point, we are clearing the whole array, no matter how many elements are in it.
let x = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
console.log(x)
// Output: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
x.splice(0, x.length)
console.log("Empty array: ", x)
// Output: Empty array: []
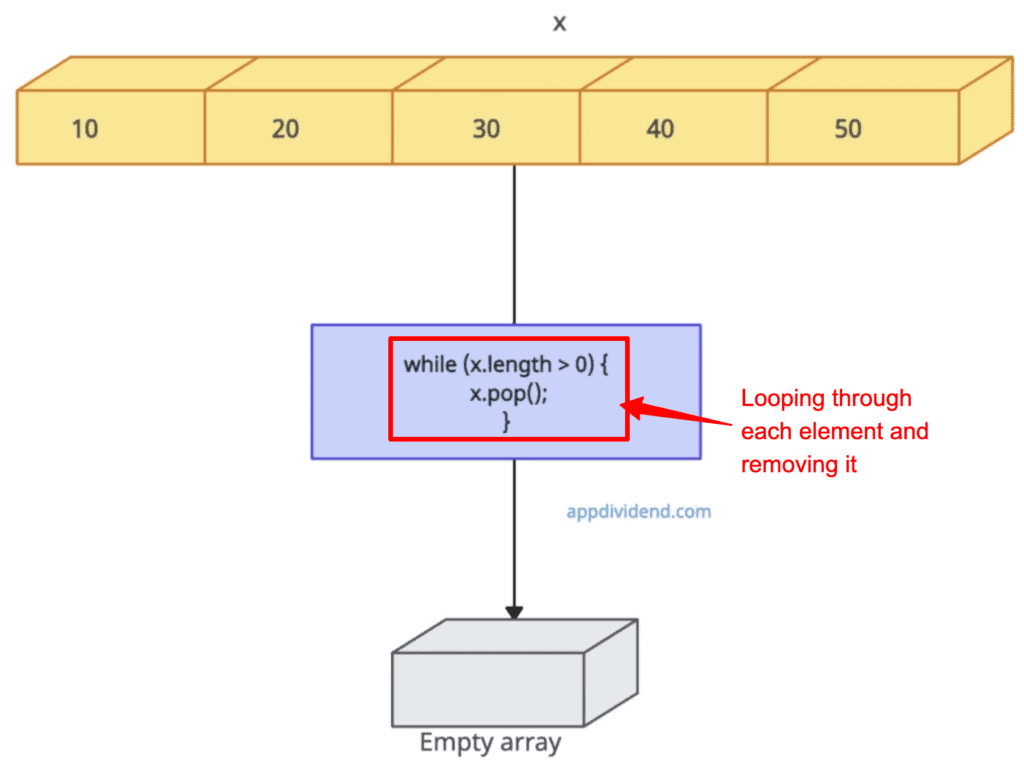
Approach 3: Using pop() in a Loop
While less efficient, you can also empty an array by repeatedly calling pop() until the array is empty.
let x = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
console.log("Original array: ", x)
// Output: Original array: [ 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 ]
while (x.length > 0) {
x.pop();
}
console.log("Empty array: ", x)
// Output: Empty array: []
That’s all!