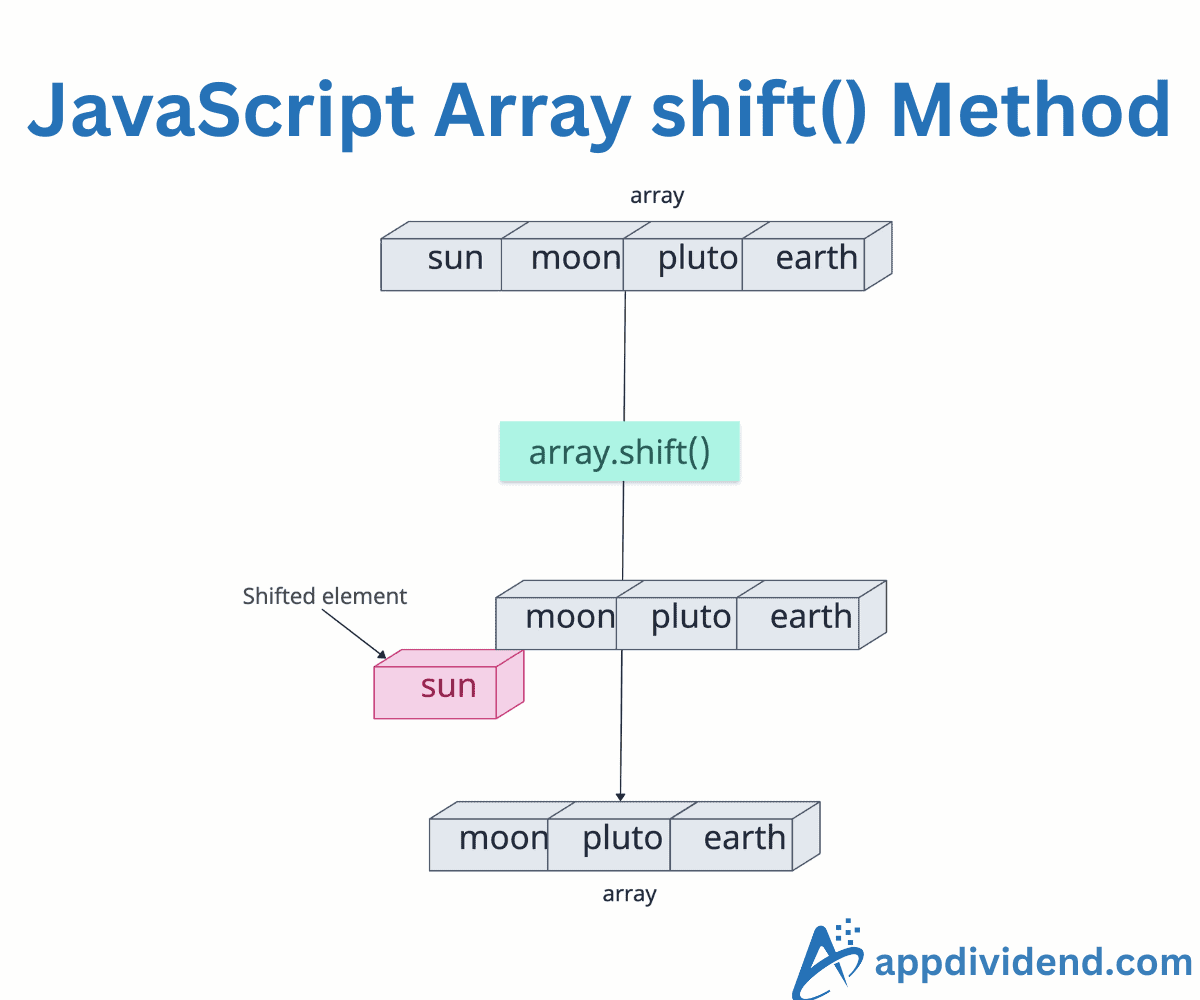
JavaScript Array shift() method removes the first element from the array and returns that removed element. It modifies the original array by decreasing its length by one.
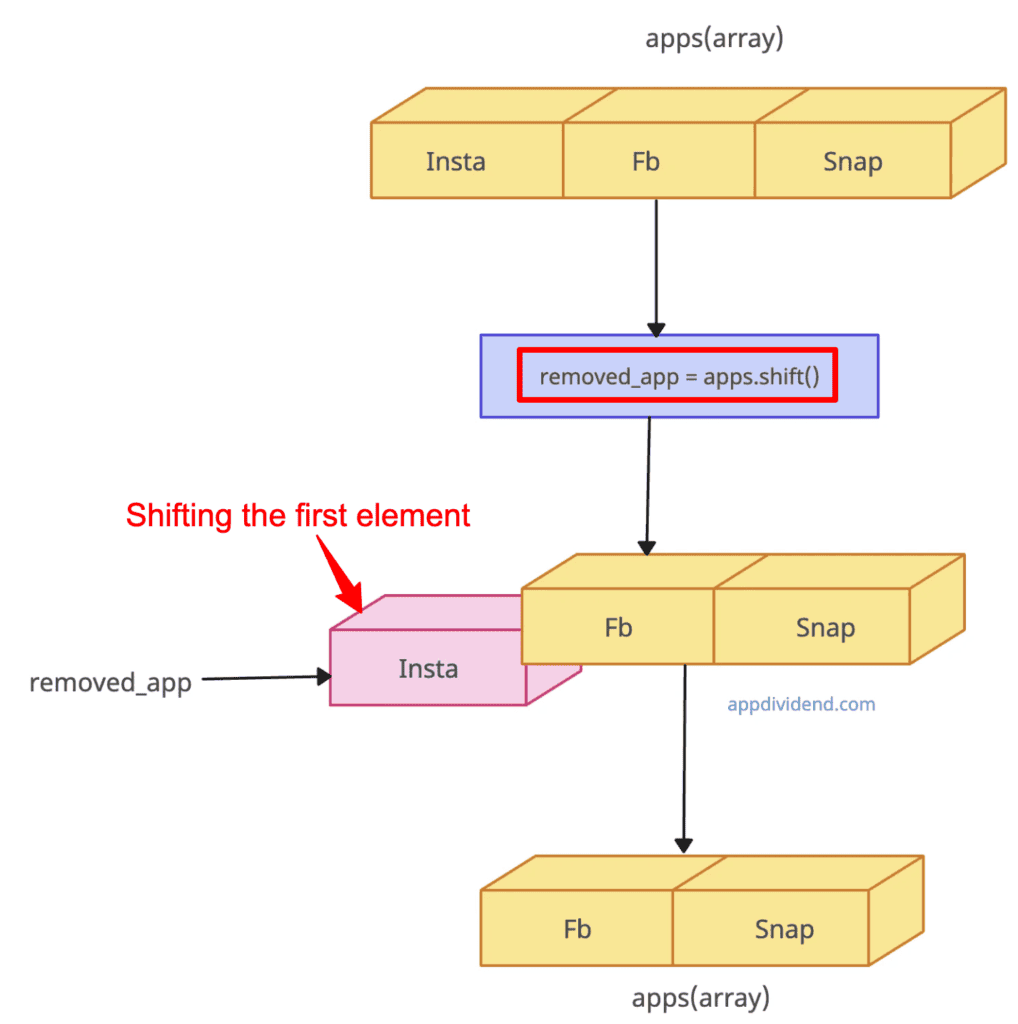
const apps = ["Insta", "Fb", "Snap"]; console.log(apps); // Output: ["Insta", "Fb", "Snap"] removed_app = apps.shift(); console.log(removed_app); // Output: "Insta" console.log(apps); // Output: ["Fb", "Snap"]
Syntax
array.shift()
Parameters
None.
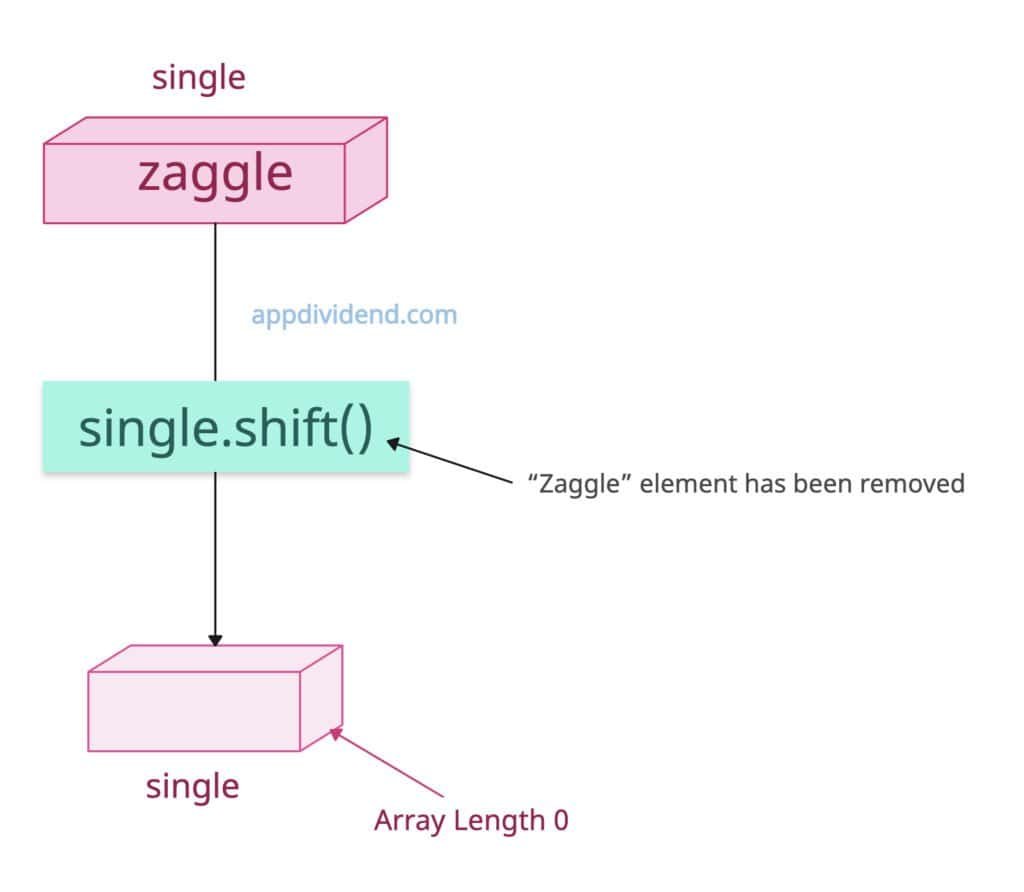
An array with a single element
If you apply a shift() function to an array with one element, it makes the array empty since the first element is the only element.
const single = ['Zaggle']; const removed = single.shift(); console.log(removed); // Output: 'Zaggle' console.log(single); // Output: []
If you further call the shift() method, it will return undefined, as the input array is now empty.
With a while loop
Let’s clear the whole array with the help of the shift() method using a while loop.
const apps = ["Insta", "Fb", "Snap", "x"];
while ((i = apps.shift()) !== undefined) {
console.log(apps);
}
// Output:
// [ 'Fb', 'Snap', 'x' ]
// [ 'Snap', 'x' ]
// [ 'x' ]
// []
Until the undefined value is found, it will remove each element of the array.
Empty array
If the array is empty before the call, it returns undefined.
let apps = []; removed_app = apps.shift(); console.log(removed_app); // Output: undefined (since the array is empty) console.log(apps); // Output: [] (the array remains empty)
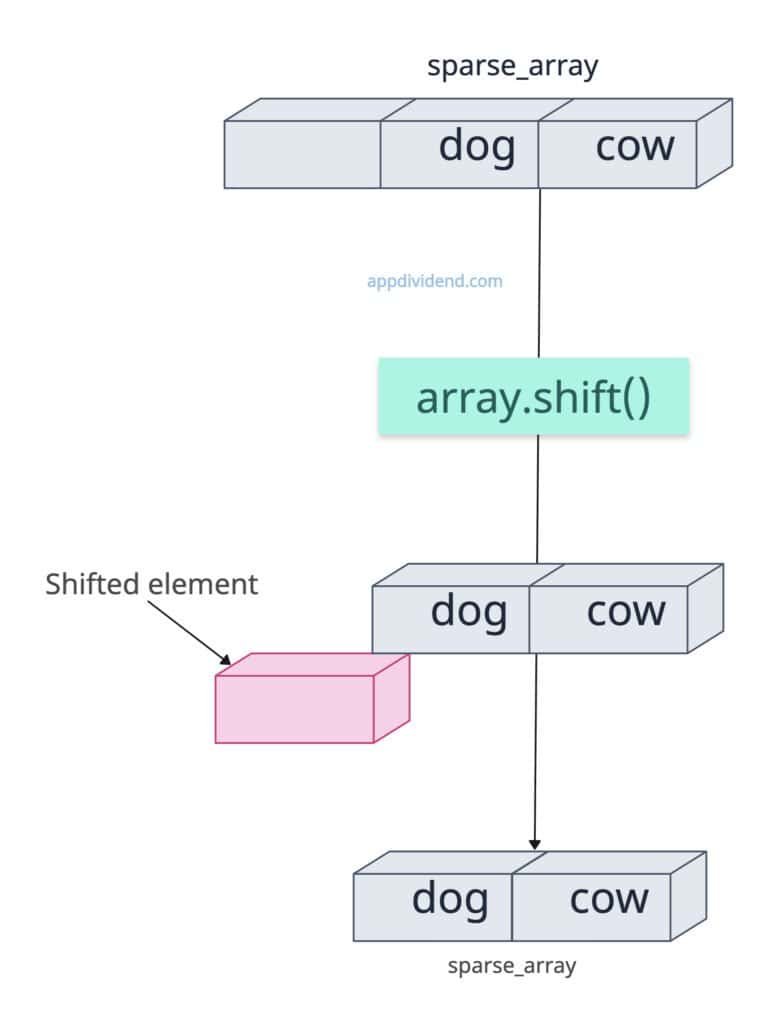
Sparse Arrays
If the first element is an empty slot, it will remove that element and return undefined as the hole element from the sparse array.
const sparse_array = [, 'dog', 'cow']; // Index 0 is a empty slot const removed = sparse_array.shift(); console.log(removed); // undefined (empty slot treated as undefined) console.log(sparse_array); // ['apple', 'banana'] (shifts left, empty slot removed)
That’s all!



Post
It works really well for me
Alan
Suits!!