Python statements usually end with a newline. However, if you are writing a lengthy statement or code that requires multiple lines, you need to use multiple lines without any errors.
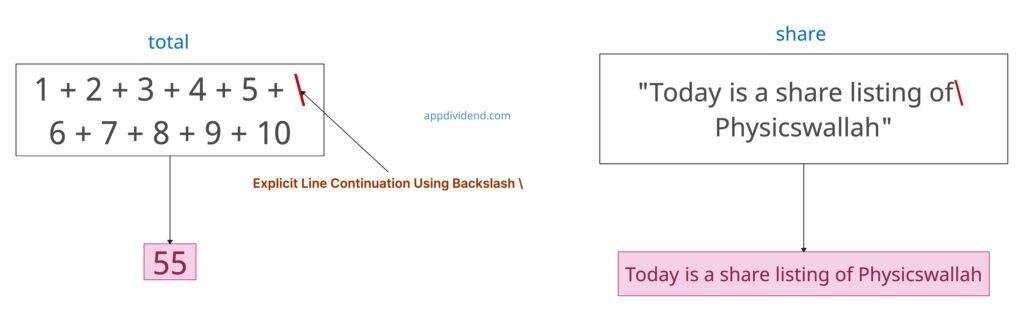
Method 1: Explicit Line Continuation Using Backslash \
You can use the explicit line continuation using backlash (\) at the end of a line to indicate that the line should continue on the next line.
The main advantage of using backlash is that it works with or without brackets, and its intent is clearly visible.
total = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + \
6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10
print(total)
# Output: 55
share = "Today is a share listing of\
Physicswallah"
print(share)
# Output: Today is a share listing of Physicswallah
In this code, the interpreter treats an entire sequence of numbers as a single assignment statement: total = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10? But why? Because of the backlash (\) sign that tells the interpreter that it is the continuation, even though some digits are on the second line. Hence, it totals 55.
In the second part of our code example, the backslash (\text) within the double quotes allows you to break the string definition across multiple physical lines.
When an interpreter processes the string, the backslash and the newline character immediately following it are ignored.
Disadvantages and Warnings
The backlash approach is very error-prone. How can you tell? Well, any whitespace after \ causes SyntaxError.
bad = "hello" + \ # space after \ SyntaxError
"world"
print(bad)
# SyntaxError: unexpected character after line continuation character
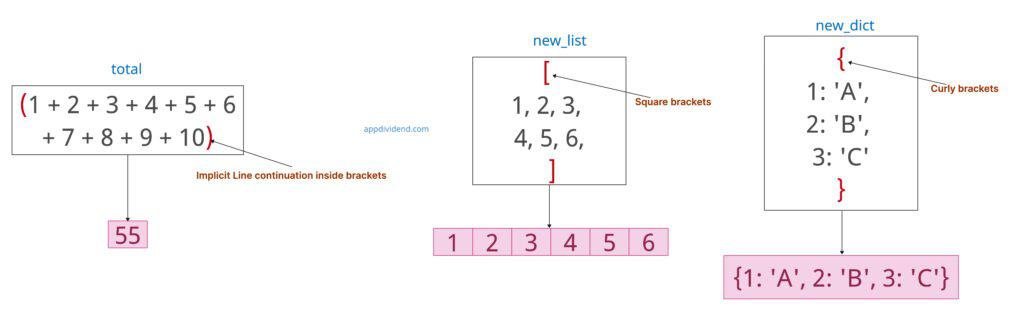
Method 2: Implicit Line continuation inside brackets
You can also continue a line onto the next one by enclosing your expression in parentheses (), brackets [], or braces {}.
This is a more Pythonic way and is often used for long function calls, lists, tuples, dictionaries, or sets.
total = (1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 +
6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10)
print(total)
# Output: 55
new_list = [
1, 2, 3,
4, 5, 6,
]
print(new_list)
# Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
new_dict = {1: 'A',
2: 'B',
3: 'C'}
print(new_dict)
# Output: {1: 'A', 2: 'B', 3: 'C'}
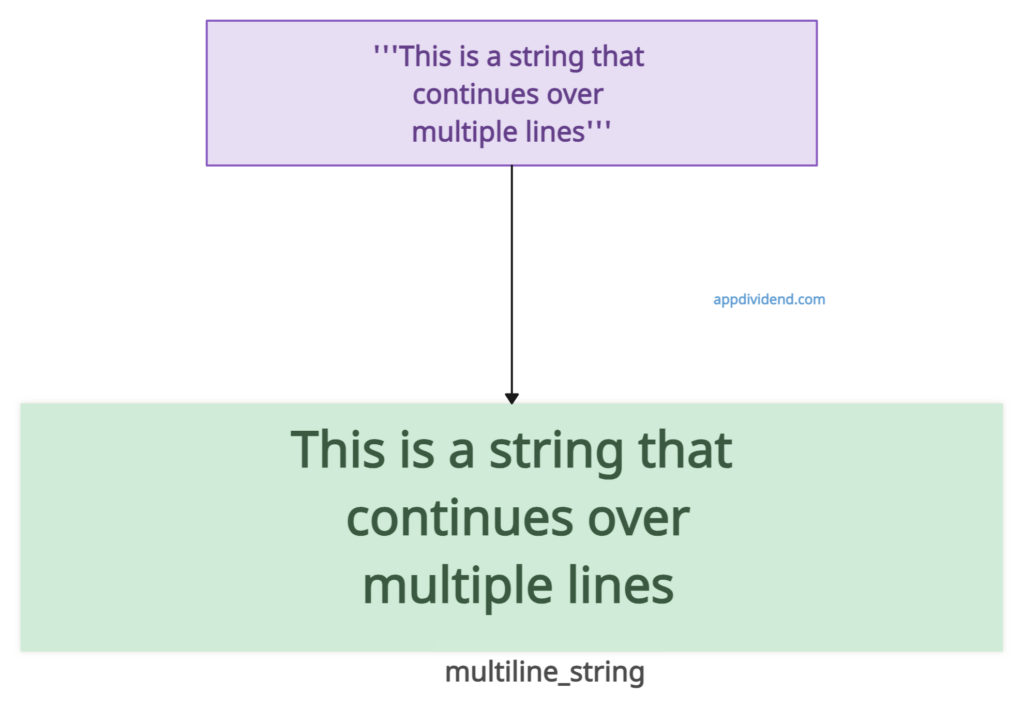
Method 3: Multi-line Strings (Triple Quotes)
For strings, you can use triple single quotes (”’) or triple double quotes (“””) triple quotes to continue over multiple lines.
multiline_string = '''This is a string that continues over multiple lines''' print(multiline_string) # Output: # This is a string that # continues over # multiple lines
That’s all!