To write a dictionary to a file in Python, you can serialize the data to json using json.dump() or json.dumps() method or serialize it to a string by converting it into a string using str(), then writing it using write().
Method 1: Using json.dump()
The json.dump() is a built-in function that directly writes a dictionary as a JSON object to a file. After you write it, you can open the file and read it easily or manipulate it as needed.
import json
shares = {'Name': "Netweb Tech", 'Price': 4051}
# writing dictionary to a file as JSON
with open('data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(shares, f)
print("Data has been written to data.json file")
# Output: Data has been written to data.json file
In your current working directory, you will find a new file called “data.json” with the above content.
Method 2: Using json.dumps()
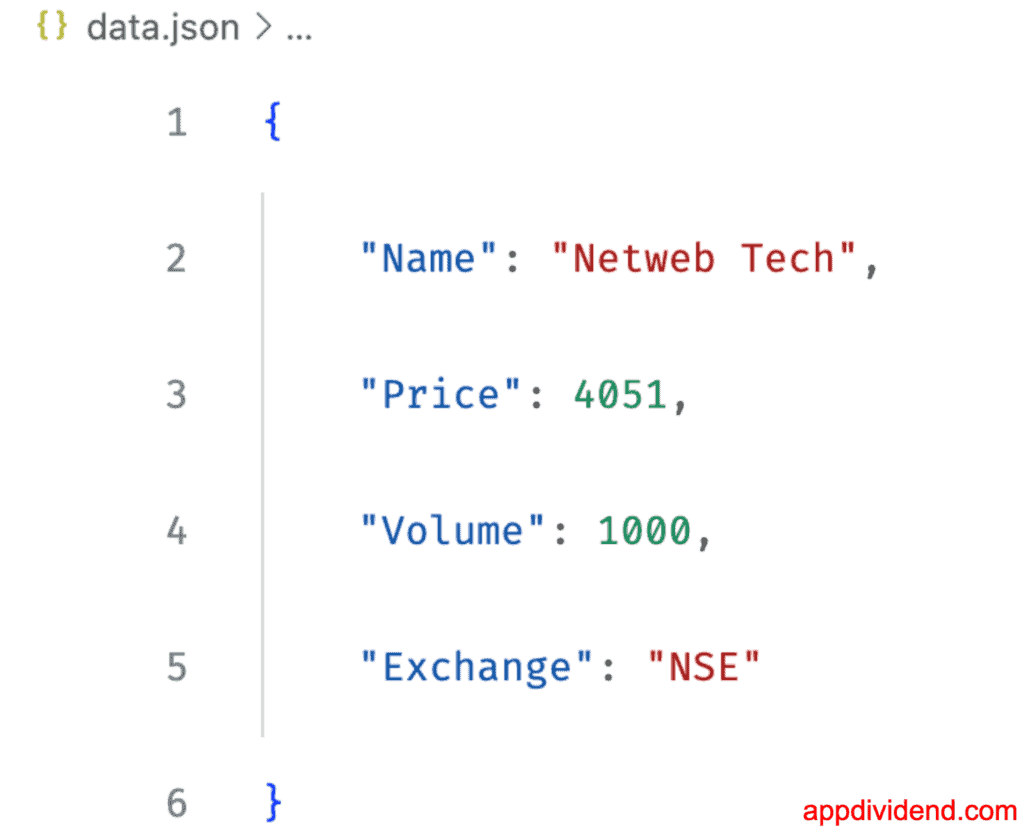
The json.dumps() method does not write a dictionary to a file; instead, it converts the dictionary to a JSON string. You then need to write that JSON string to a file using the write() method. It allows us to add options like formatting and indentation.
import json
shares = {'Name': "Netweb Tech", 'Price': 4051, 'Volume': 1000, "Exchange": "NSE"}
with open('data.json', 'w') as file:
file.write(json.dumps(shares, indent=4))
Method 3: Using str()
Another simple method is to use the str() method to convert a dictionary to a string, and then write the string to a file using the write() method.
shares = {'Name': "Netweb Tech", 'Price': 4051,
'Volume': 1000, "Exchange": "NSE"}
with open('data.txt', 'w') as file:
file.write(str(shares))
Method 4: Using pickle.dump()
What if you want to save a dictionary in a binary file? Well, in that case, you should use the pickle module and use its pickle.dump() method. We will use the with open() statement to create a binary file in write mode and write a dictionary into it.
import pickle
shares = {'Name': "Netweb Tech", 'Price': 4051,
'Volume': 1000, "Exchange": "NSE"}
with open('binary_data.pkl', 'wb') as file:
pickle.dump(shares, file)
That’s all!