Removing HTML tags prevents cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks and ensures consistent formatting. If you are performing a word count, your text must be cleaned of all the scripting tags; otherwise, the word count will be inaccurate.
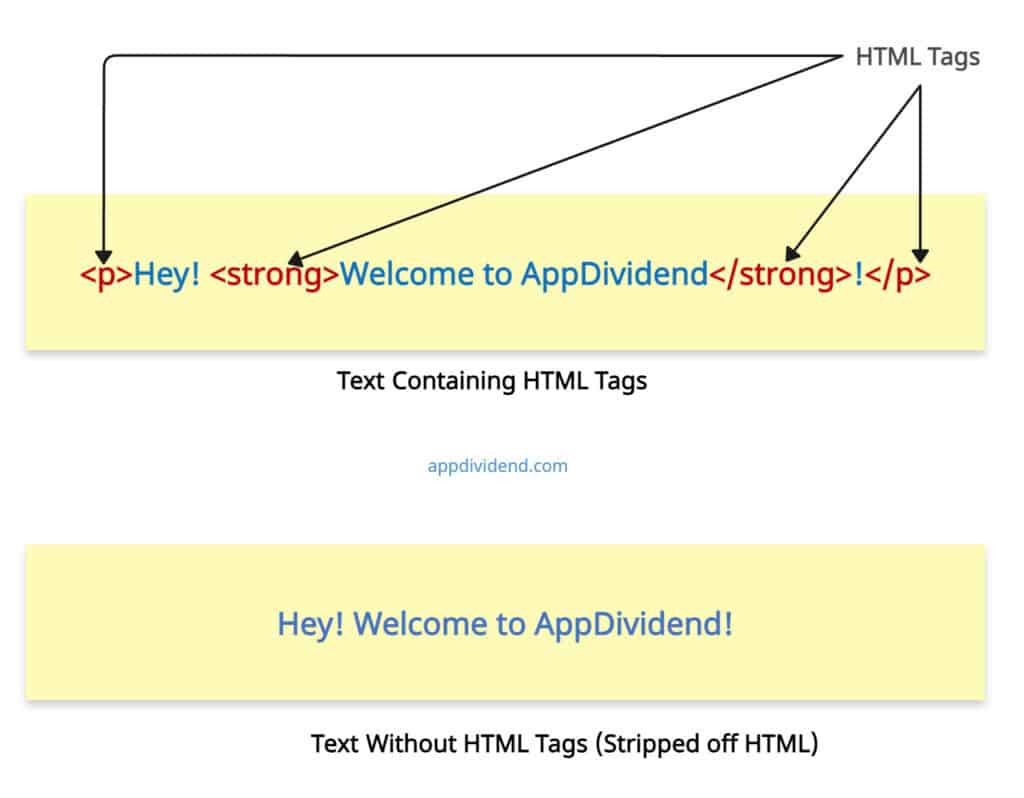
But how do you distinguish HTML tags in standard text? HTML is a markup language, and you can identify each tag by its opening bracket (“<“) and a closing bracket (“>”). Everything in between these brackets is a tag.
Here is the pictorial representation:
Here are three ways to strip HTML tags from a string in JavaScript:
- Using string.replace() (Regular Expression)
- Using the DOM Parser
- Using .textContent or .innerHTML
Method 1: Using a string.replace() (Regular Expression)
The string.replace() method uses patterns in the form of regular expressions to identify and replace tags within a text. This is not a browser-specific method, and you can use it on the “Node.js” platform as well.
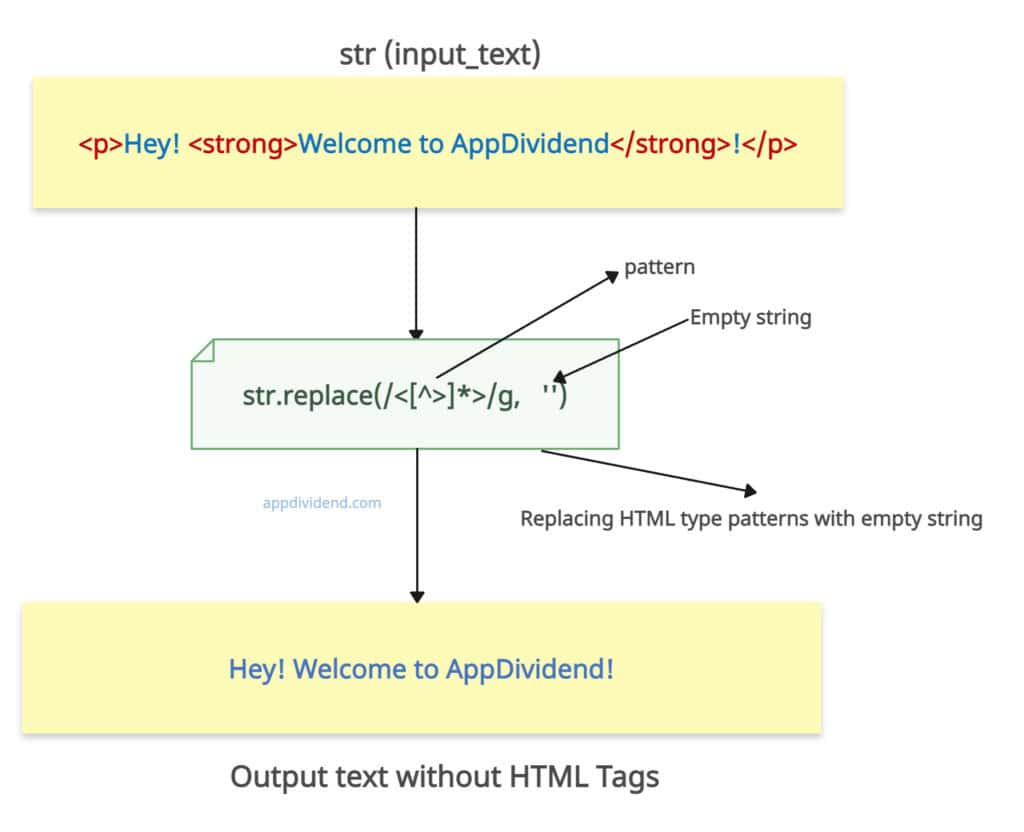
function stripHtmlTags(str) {
// Identifying and removing HTML Tags
return str.replace(/<[^>]*>/g, '');
}
// Example usage:
const input_text = "<p>Hey! <strong>Welcome to AppDividend</strong>!</p>";
console.log("Before stripping: ", input_text)
console.log("After stripping: ", stripHtmlTags(input_text));
Output
Before stripping: <p>Hey! <strong>Welcome to AppDividend</strong>!</p> After stripping: Hey! Welcome to AppDividend!
This approach is basic and works well with most basic HTML structures.
However, if you are dealing with nested html tags or malformed HTML tags, it may not handle all these edge cases very well. Furthermore, it can be slower for larger strings.
Method 2: Using DOMParser
The DOMParser() constructor, available in browsers, creates a new DOMParser object that has a parseFromString() method for parsing a string using either the HTML parser or the XML parser.
The .textContent property contains all the text inside the HTML <body> tag, strips the tags, and returns the clean textual output.
The DOMParser() constructor is only available in the browser and not available in the “Node.js” environment. Therefore, you must execute your program in the browser.
Here is the implementation code in the form of an HTML file:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Removing HTML Tags</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function stripHtmlTagsDOM(html) {
// Identifying and extracting text from html
const doc = new DOMParser().parseFromString(html, "text/html");
return doc.body.textContent || "";
}
// Example usage:
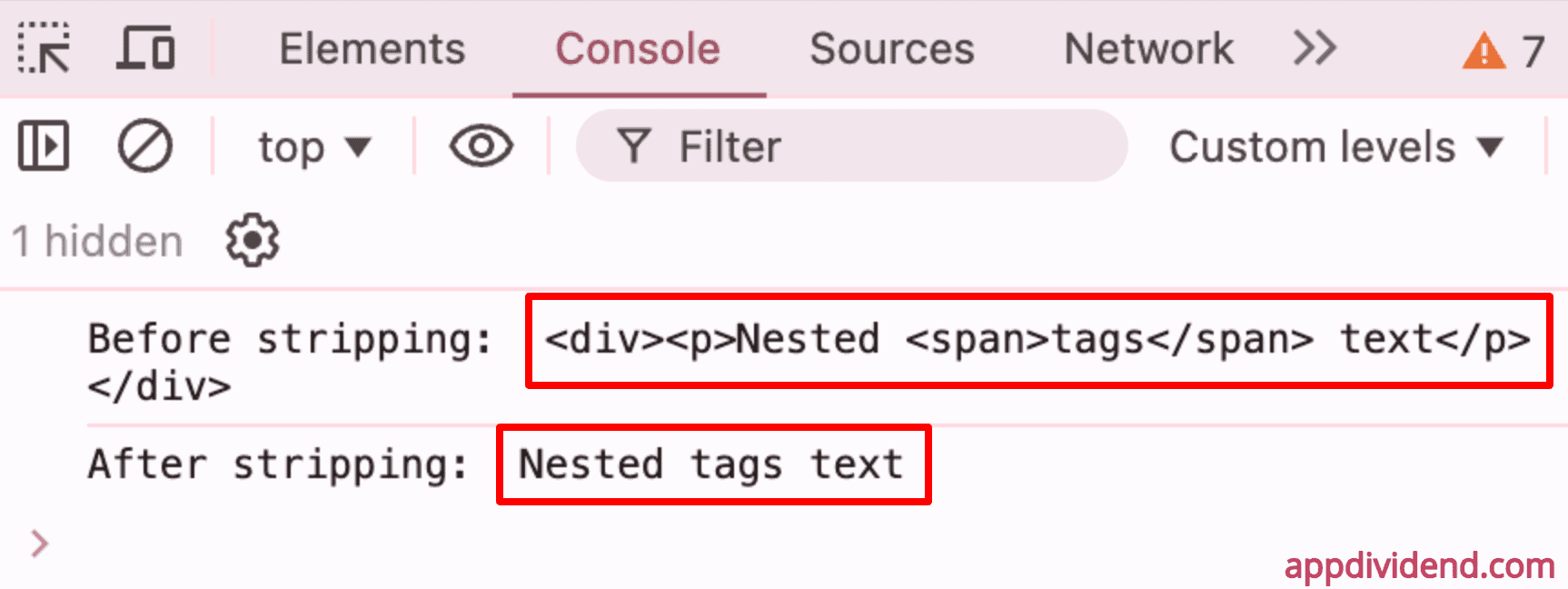
const input_text = "<div><p>Nested <span>tags</span> text</p></div>";
console.log("Before stripping: ", input_text);
console.log("After stripping: ", stripHtmlTagsDOM(input_text));
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
I would highly recommend the DOMParser approach because it handles complex HTML structures and correctly interprets HTML entities.
However, it might be slightly complex and can be overkill for simple markup removal.
If you are working with user-generated content where comments or related text are filled with malformed html, then you can use this method.
Method 3: Using .textContent or .innerHTML
The .textContent fetches the text content between the HTML tags, effectively removing the tags.
However, we also use the .innerHTML property as a fallback due to older versions of browsers. If neither of the props is available to the browsers, then an empty string will be returned as a final resort.
Again, this approach is browser-based and would not work directly in a Node.js environment without additional libraries.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Stripping HTML Tags</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function stripHtmlTagsTextContent(html) {
const temp = document.createElement("div");
temp.innerHTML = html;
return temp.textContent || temp.innerText || "";
}
// Example usage:
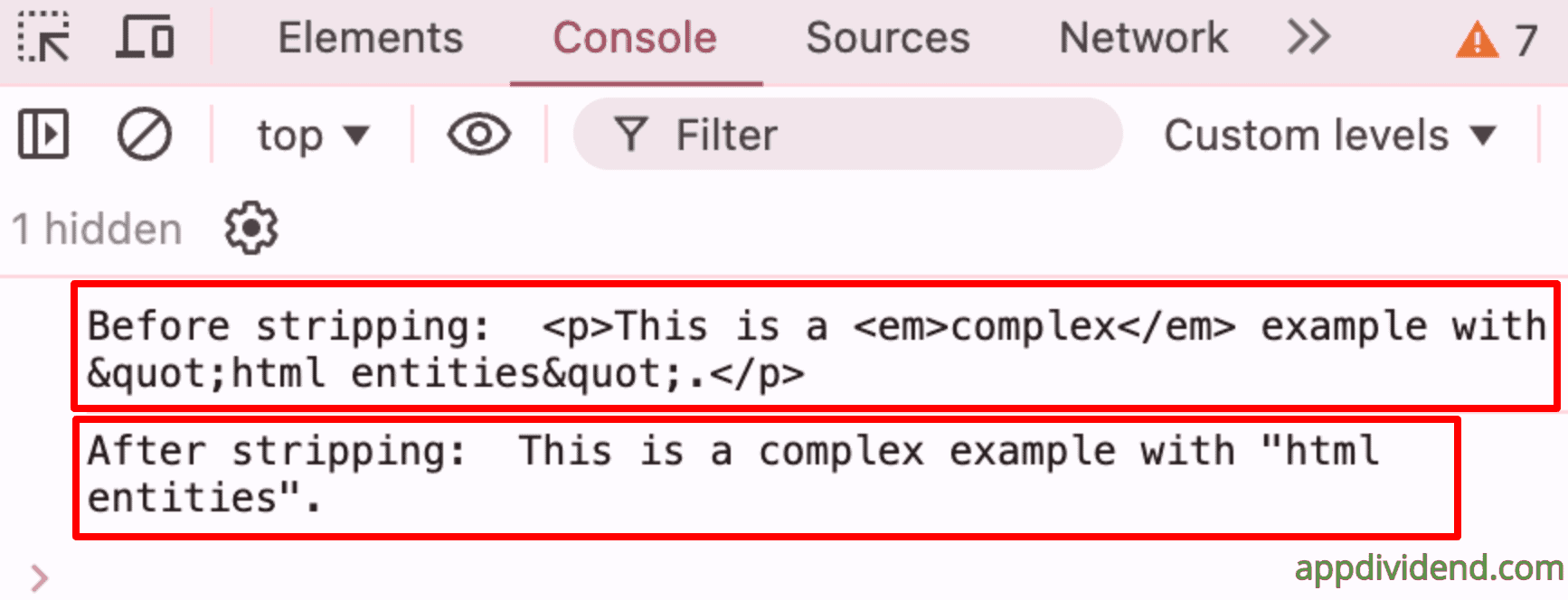
const input_text =
"<p>This is a <em>complex</em> example with "html entities".</p>";
console.log("Before stripping: ", input_text);
console.log("After stripping: ", stripHtmlTagsTextContent(input_text));
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output
That’s all!