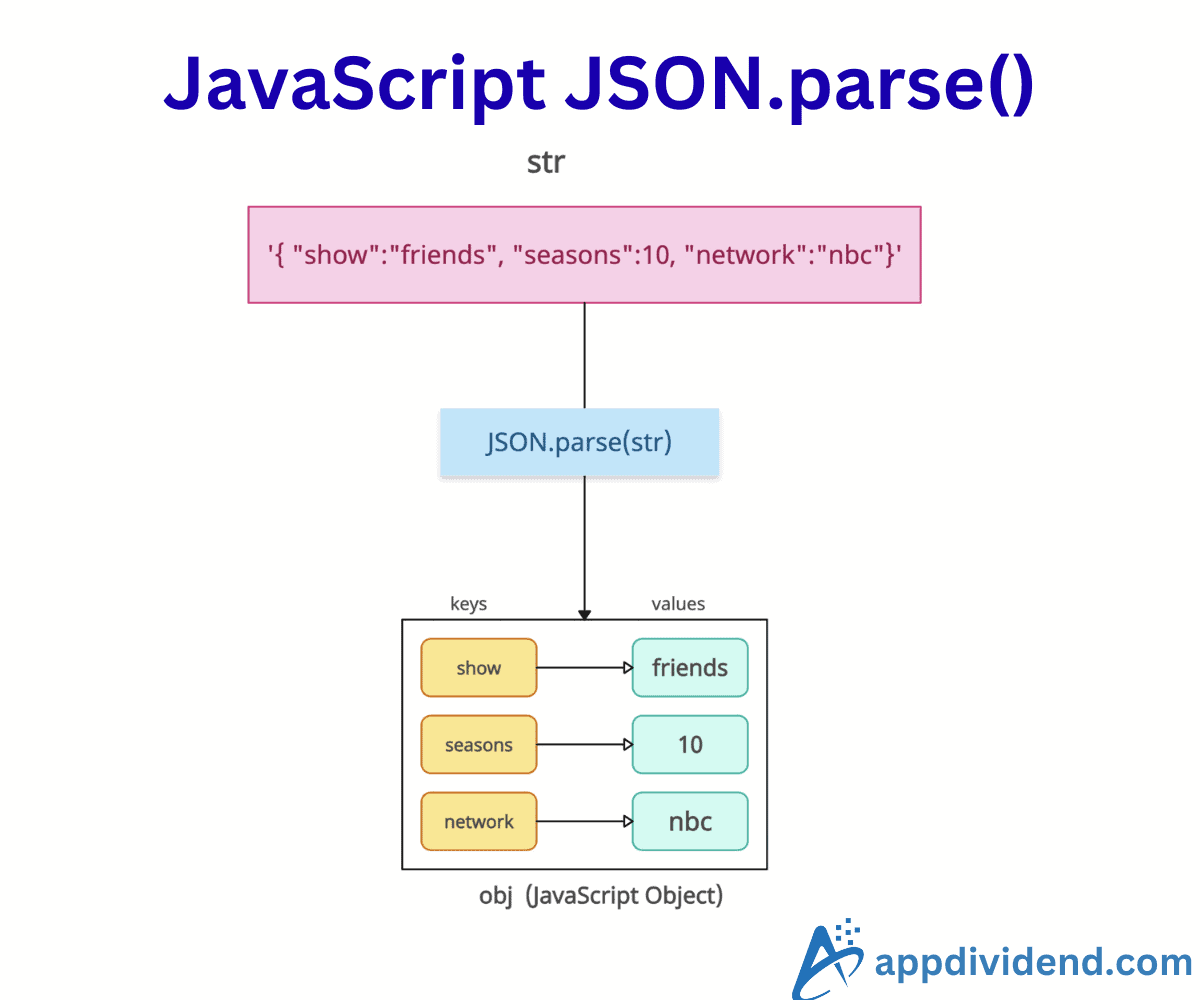
JavaScript JSON.parse() is a built-in static method that parses a JSON string, constructing the value (array, string, number, boolean, or null) or object described by the string.
It is the inverse of JSON.stringify(), which converts JavaScript values to JSON strings.
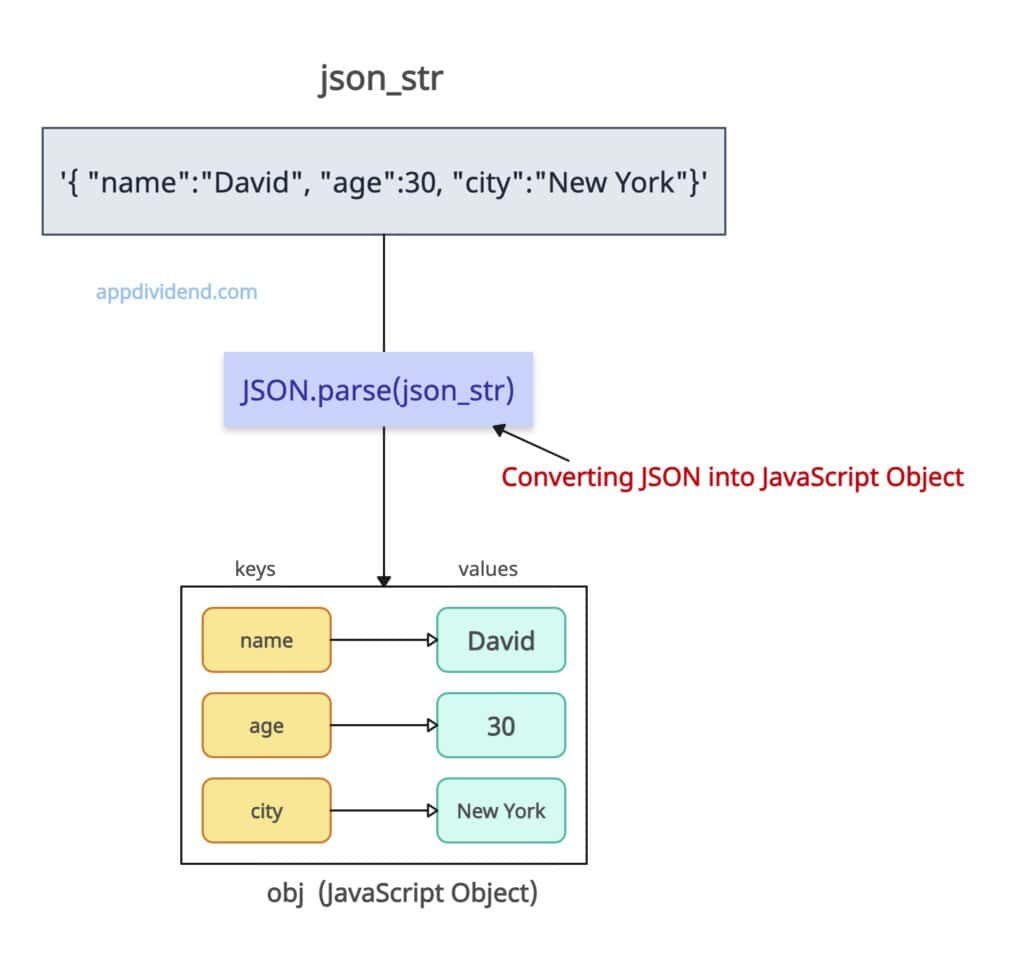
const json_str = '{ "name":"David", "age":30, "city":"New York"}';
const obj = JSON.parse(json_str);
console.log(obj);
// Output: { name: 'David', age: 30, city: 'New York' }
console.log(obj.name);
// Output: David
In the above figure and code, we defined a json string and passed it to the JSON.parse() method. The method converts the string into an appropriate object, which we then print along with its specific property (obj.name).
Syntax
JSON.parse(text, reviver)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| text (required, string) |
It represents a JSON-formatted string. It should contain valid json. If it is invalid, this method will throw an error. |
| reviver (optional, function) | It is a callback function that transforms the parsed value before returning it.
It receives two arguments:
|
Parsing rules
- JSON strings must use double quotes (” “). Single quotes cause errors.
- It supports primitives (string, number, boolean, null), objects, and arrays.
- It does not allow trailing commas or unquoted keys.
- Dates, functions, undefined, and other non-JSON types are not natively supported.
Using the Reviver Function
With the help of the reviver function, we can transform the input as needed.
For example, we can create a condition that removes a specific property based on its value when converting to an object.
const json_str = '{ "name":"David", "age":30, "city":"New York"}';
let obj = JSON.parse(json_str, (key, value) => {
if (key === "age") {
return undefined // Remove the "age" property
}
return value;
});
console.log(obj);
// Output: { name: 'David', city: 'New York' }
In this code, we removed the age property while converting the JSON string into a JavaScript object using a reviver function. The output object is transformed by removing a property.
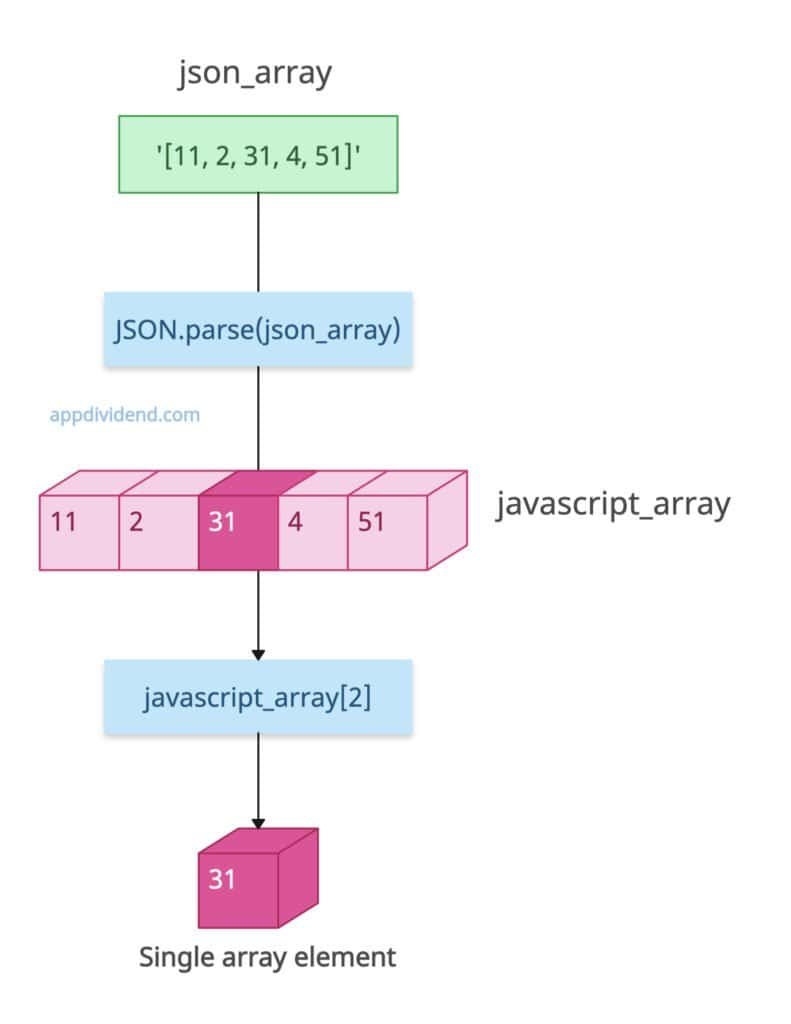
Parsing Arrays
What if the input JSON string is an array underneath? In that case, after json parsing, the output will be a JavaScript array.
const json_array = '[11, 2, 31, 4, 51]'; const javascript_array = JSON.parse(json_array); console.log(javascript_array[2]); // Output: 31
That’s all!


Cristiano De Vinni
Really nice tutorial dude !