The most common and efficient way to get a key with maximum value in a Python dictionary is to use the max() function with key=dict.get() argument. This method is helpful when you have numeric values in the dictionary.
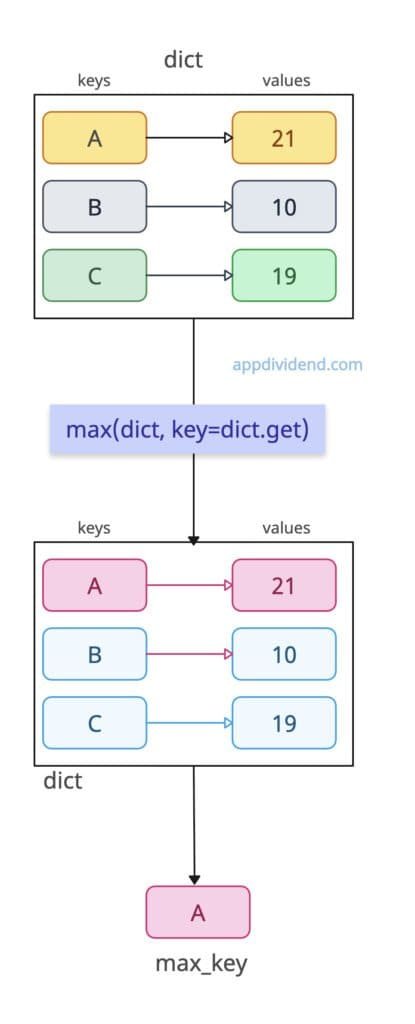
dict = {"A": 21, "B": 10, "C": 19}
max_key = max(dict, key=dict.get)
print(max_key)
# Output: A
In this code, key A has a maximum value of 21, which is why it is in the output. We only print the key of that max value. You can also print both the key and the value, depending on your requirements.
It is the cleanest and fastest O(n) Pythonic approach.
Empty dictionary
This happens often when your input dictionary is empty, and you apply the max() function to it. If you are not handling this scenario well, it will throw a ValueError.
empty_dict = {}
max_key = max(empty_dict, key=empty_dict.get)
# ❌ ValueError: max() arg is an empty sequence
To fix the ValueError: max() arg is an empty sequence error, pass default=None to the max() function.
empty_dict = {}
max_key = max(empty_dict, key=empty_dict.get, default=None)
print(max_key)
# Output: None
Multiple keys with the same maximum value
If there is a scenario where there are multiple keys with the same maximum value in a dictionary, the max() function will return the first encountered key.
dict = {"A": 10, "B": 25, "C": 25}
print(max(dict, key=dict.get))
# B (first with value 25)
But what if you want all the keys with maximum values? In that case, you need to use a list comprehension to get the list of keys.
dict = {"A": 10, "B": 25, "C": 25}
max_val = max(dict.values())
max_keys = [k for k, v in dict.items() if v == max_val]
print(max_keys)
# Output: ['B', 'C']
Uncomparable values
What if there is a dictionary with different value types? For example, the first key has an integer value, the second key has a string value, and the third key has a boolean value.
If you apply the max() function on that, it will return TypeError: ‘>’ not supported between instances of ‘str’ and ‘int’ because it cannot compare those values. After all, they are not of the same type.
dict = {"A": 10, "B": "hello", "C": False}
max_keys = max(dict.values())
print(max_keys)
# TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'int'
Alternate approaches
Approach 1: Using operator.itemgetter()
What if your dictionary is large and contains lots of key-value pairs? In that case, finding the maximum value becomes a lengthy process. That is why you should use the operator.itemgetter() method.
import random
from operator import itemgetter
random.seed(42) # ensures same values every run
large_dict = {f"key_{i}": random.randint(1, 1000000) for i in range(10000)}
max_key, max_val = max(large_dict.items(), key=itemgetter(1))
print("Max key:", max_key)
# Output: Max key: key_2077
print("Max value:", max_val)
# Output: Max value: 999915
In this code, we generated a dictionary containing 10,000 random numbers from a pool of 1,00,000 values. Each key gets a random number between 1 and 1,000,000 as its value.
Because of the seed, all numbers will be the same every time you run it.
When we run the code above, the largest random value from 1 to 1,00,000 is 99915. And its key is key_2077. Remember, there are only 10,000 key-value pairs from 1,00,000 numbers. So, the biggest value can be anything and does not have to be 1,00,000.
Approach 2: Using sorted()
What if your task involves sorting the values and then finding the maximum? That’s where you should use the built-in sorted() function.
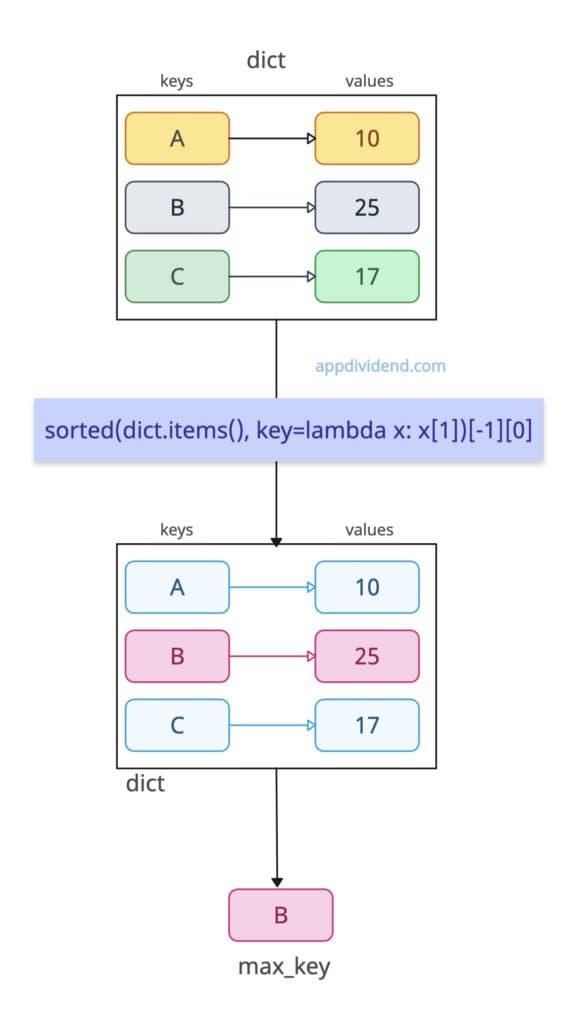
dict = {"A": 10, "B": 25, "C": 17}
max_key = sorted(dict.items(), key=lambda x: x[1])[-1][0]
print(max_key)
# Output: B
It gives you both sorted data and the max key.
Approach 3: Using a manual loop
The for loop provides complete control over the dictionary, and we can maintain full transparency into the data to find the maximum value. It is not memory-efficient, but yes, it works well with any data.
dict = {"A": 10, "B": 25, "C": 17}
max_key = None
max_value = float("-inf")
for key, value in dict.items():
if value > max_value:
max_value = value
max_key = key
print(max_key)
# Output: B
That’s all!