Here are four different ways to extract text from XML files in Python:
- Using “xml.etree.ElementTree” built-in module
- Using “lxml” (third-party library)
- Using “xmltodict” (for converting XML text into a dictionary)
- Using the “re” module (Regular Expressions)
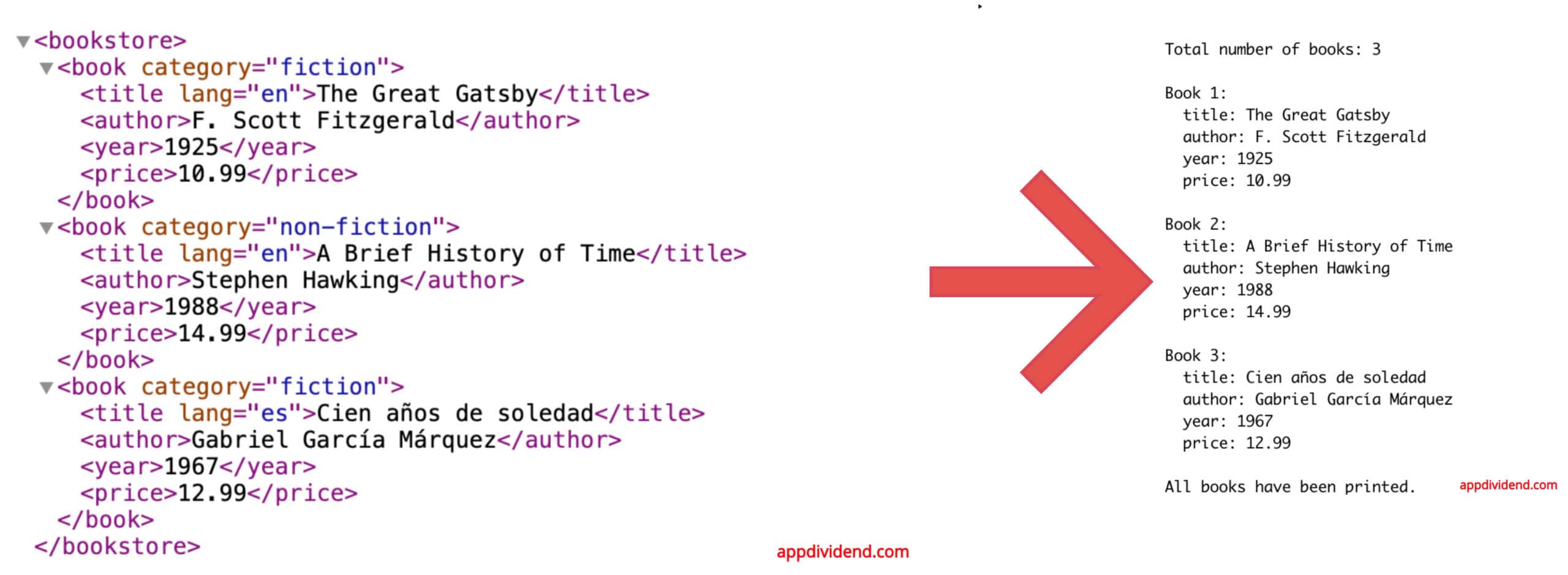
To extract the data, we need a proper “XML” file. For this project, we will use the “books.xml” file that looks like the image below:
The above file has a valid XML structure.
Method 1: Using the “xml.etree.ElementTree” module
The “xml.etree.ElementTree” is a built-in module that provides a parse() function that will accept an “XML” file, and you can get the text from that file using the iter() function.
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse('books.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
for element in root.iter():
print(element.text)
Output
The Great Gatsby F. Scott Fitzgerald 1925 10.99 A Brief History of Time Stephen Hawking 1988 14.99 Cien años de soledad Gabriel García Márquez 1967 12.99
As expected, we obtained the exact output we wanted. Just DATA!
Method 2: Using “lxml”
If you are looking for a third-party solution, then I would highly recommend using the “lxml” library. It provides etree.parse() method that accepts an XML file, use the .getroot() method to get the root of the file, and finally, use the .iter() and .text() methods to extract the content.
You can install the “lxml” library using the command below:
pip install lxml
Here is the code:
from lxml import etree
tree = etree.parse('books.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
for element in root.iter():
print(element.text)
Output
The Great Gatsby F. Scott Fitzgerald 1925 10.99 A Brief History of Time Stephen Hawking 1988 14.99 Cien años de soledad Gabriel García Márquez 1967 12.99
Method 3: Using “xmltodict”
The “xmltodict” is a third-party library specifically used when you want your extracted data to be represented as a Python dictionary. It provides a parse () method that reads the XML file and returns the dictionary.
import xmltodict
with open('books.xml', 'r') as file:
data = xmltodict.parse(file.read())
print(data)
Output
{'bookstore': {'book': [{'@category': 'fiction', 'title': {'@lang': 'en', '#text': 'The Great Gatsby'}, 'author': 'F. Scott Fitzgerald', 'year': '1925', 'price': '10.99'}, {'@category': 'non-fiction', 'title': {'@lang': 'en', '#text': 'A Brief History of Time'}, 'author': 'Stephen Hawking', 'year': '1988', 'price': '14.99'}, {'@category': 'fiction', 'title': {'@lang': 'es', '#text': 'Cien años de soledad'}, 'author': 'Gabriel García Márquez', 'year': '1967', 'price': '12.99'}]}}
Method 4: Using the “re” module (regex)
Regular expressions are a de facto standard for finding and extracting elements from a file, string, or any other object. You can use the re.findall() method to get the exact data you are looking for in an XML file.
If you are looking to extract specific pieces of data from a large XML file without parsing the entire structure, I recommend using the “regular expression” approach.
import re
def parse_xml_with_regex(file_path):
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
# Updated regex pattern to capture entire book elements
book_pattern = r'<book.*?>(.*?)</book>'
books_raw = re.findall(book_pattern, content, re.DOTALL)
# Process each book
books = []
for book_content in books_raw:
book = {}
# Parse individual fields within each book
fields = re.findall(r'<(\w+).*?>(.*?)</\1>', book_content, re.DOTALL)
for tag, value in fields:
book[tag] = value.strip()
books.append(book)
return books
# Use the function
books = parse_xml_with_regex('books.xml')
# Print all books
print(f"Total number of books: {len(books)}")
for i, book in enumerate(books, 1):
print(f"\nBook {i}:")
for key, value in book.items():
print(f" {key}: {value}")
print("\nAll books have been printed.")
Output
That’s all!