Here are three ways to delete pages from a PDF using Python:
- Using pymupdf
- Using pypdf2
- Using pdfrw
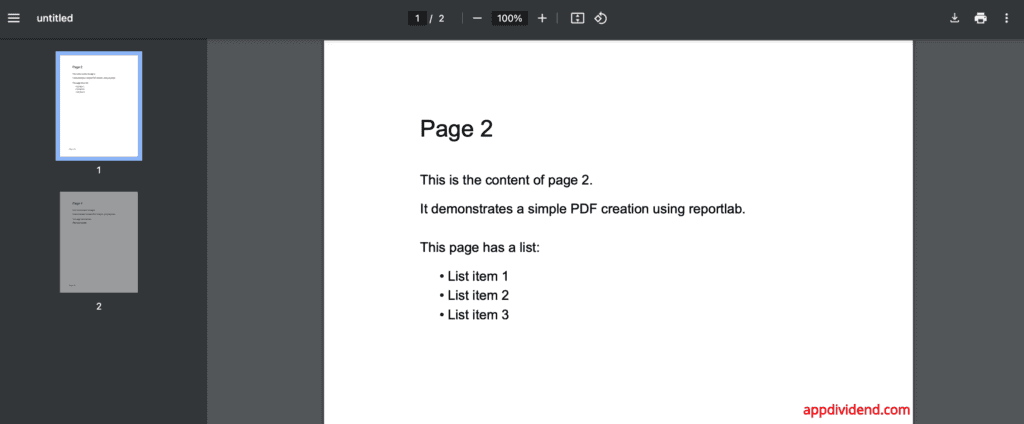
For this practical implementation, we will use the five-page PDF like this:
We will remove some of the pages from the above PDF for the demonstration.
Here is the file: sample_5_pages.
Method 1: Using PyMuPDF
If you are looking for a memory-efficient solution among many PDF libraries, then I highly recommend using the PyMuPDF library. It provides a .delete_page() function that accepts the index as a page number and removes it.
You can install it using the “pip”:
pip install pymupdf
You can import it as “fitz” like this code:
import fitz
Here is the complete code:
import fitz
def delete_pages(input_path, output_path, pages_to_delete):
doc = fitz.open(input_path)
pages_to_delete.sort(reverse=True)
for page_num in pages_to_delete:
doc.delete_page(page_num - 1) # 0-indexed
doc.save(output_path)
doc.close()
# Usage
input_path = 'sample_5_pages.pdf'
output_path = 'reduced.pdf'
pages_to_delete = [1, 3, 5] # Page numbers to delete (1-indexed)
delete_pages(input_path, output_path, pages_to_delete)
print("Pages no 1, 3, and 5 deleted successfully")
Output
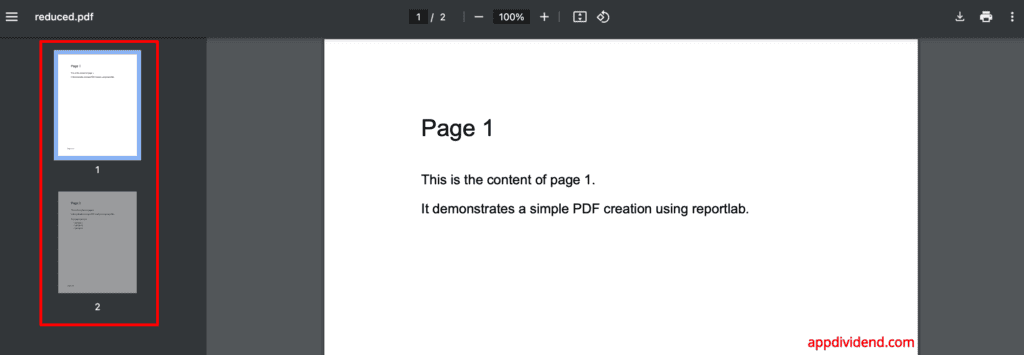
As illustrated in the screenshot above, our output PDF has only two pages, numbered 2 and 4. Page numbers 1, 3, and 5 have been deleted successfully.
Method 2: Using PyPDF2
The most popular library to use for simple operations is PyPDF2. If you need to remove specific pages rather than a range, this is the approach to take.
import PyPDF2
# Custom function to delete pages
def delete_pages(input_path, output_path, pages_to_delete):
with open(input_path, 'rb') as file:
pdf_reader = PyPDF2.PdfReader(file)
pdf_writer = PyPDF2.PdfWriter()
for page_num in range(len(pdf_reader.pages)):
if page_num + 1 not in pages_to_delete:
page = pdf_reader.pages[page_num]
pdf_writer.add_page(page)
with open(output_path, 'wb') as output_file:
pdf_writer.write(output_file)
# Calling the custom function
input_path = 'sample_5_pages.pdf'
output_path = 'reduced.pdf'
pages_to_delete = [1, 2, 3, 5] # Page numbers to delete (1-indexed)
delete_pages(input_path, output_path, pages_to_delete)
print("Pages number 1, 2, 3, and 5 have been deleted")
Output
From the image above, it’s clear that we removed four pages from the PDF, and only one page remains, which is page 4.
Method 3: Using pdfrw
The pdfrw is a third-party PDF library that has a unique use case. When you want to preserve the original PDF structure while operating, you should use this library.
You can install the pdfrw library using the command below:
pip install pdfrw
Here is the complete Python code:
from pdfrw import PdfReader, PdfWriter
def delete_pages(input_path, output_path, pages_to_delete):
reader = PdfReader(input_path)
writer = PdfWriter()
for page_num, page in enumerate(reader.pages, 1):
if page_num not in pages_to_delete:
writer.addpage(page)
writer.write(output_path)
# Calling the custom function
input_path = 'sample_5_pages.pdf'
output_path = 'reduced.pdf'
pages_to_delete = [3, 4, 5] # Page numbers to delete (1-indexed)
delete_pages(input_path, output_path, pages_to_delete)
print("Pages number 3, 4, and 5 have been deleted")
Output
You can see from the above screenshot that we generated a new PDF, but the last three pages are missing.
Final analysis
Which library to choose always depends on which type of requirement you have.
- If performance and speed are priorities, use PyMuPDF.
- For small to medium-sized PDFs with simple structures, use the “PyPDF2” or “pdfr2” library.