You need to create a list of numbers within a given range to iterate over sequences, simulate data series, initialize arrays for algorithms, or prepare inputs for numerical computations.
The range has a starting point, and the end point is the point before the endpoint.
Method 1: Using range() + list()
To efficiently create an integer-based list within a given range, use the range() function with the start, endpoint, and step arguments. It will return a range object and then convert it to a list using the list() function.
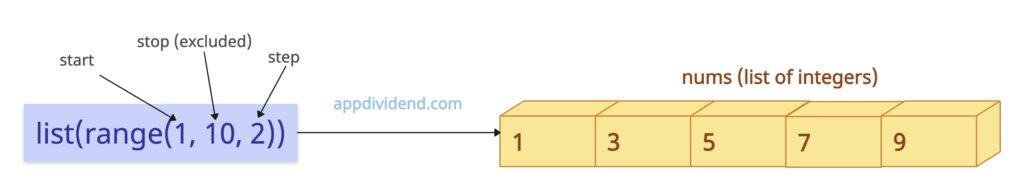
nums = list(range(1, 10, 2)) print(nums) # Output: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
In this code, range(1, 10, 2) means 1 is the starting point of the sequence, 10 is the ending point, and 2 is the step. The output list sequence would be 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and the endpoint will be excluded.
It is the most common way to create a list of sequences.
Method 2: Using List Comprehension
If you want to create a list with a custom sequence, like a sequence that requires custom logic, you can always go for a list comprehension. It can generate a sequence with conditions or formulas.
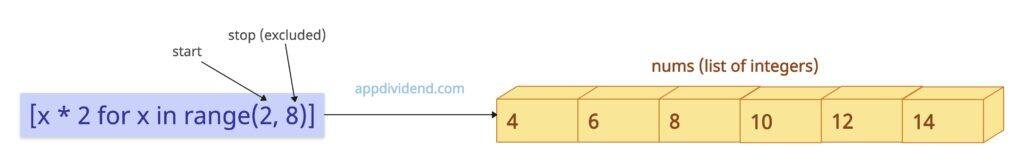
nums = [x * 2 for x in range(2, 8)] print(nums) # Output: [4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14]
In this code, range(2, 8) means the starting point of our sequence is 2, and the ending point is 8. Now, the ending point will be excluded from the final sequence since the range() function by default does not include it.
In list comprehension, each value from the range will be multiplied by 2(2*2 =4, 3*2=6,…,7*2=14). So, the final list of values will be [4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14]. It is a new list with a specified range.
Method 3: Using numpy.arange()
What if you are working with numpy arrays and you want to create a sequence for an AI or ML modeling? That’s where the np.arange() function comes into play.
It generates an array of evenly spaced values over a specified range.
import numpy as np nums = np.arange(1, 5, 0.5) print(nums.tolist()) # Output: [1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5]
That’s all!