The most efficient and straightforward approach is to convert a tuple into a list using the list() Constructor. It is a built-in Constructor that accepts an iterable, such as a tuple, as an argument and returns a list.
# Creating a tuple with integers
numeric_tuple = (5, 10, 15, 20, 25)
print("Original Tuple:", numeric_tuple)
# Output: Original Tuple: (5, 10, 15, 20, 25)
print(type(numeric_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
# Converting the tuple into a list
numeric_list = list(numeric_tuple)
print("Converted List:", numeric_list)
# Output: Converted List: [5, 10, 15, 20, 25]
print(type(numeric_list))
# Output: <class 'list'>
Tuples are immutable objects, but lists are mutable objects. Converting a tuple to a list would be helpful to when modifying the sequence’s elements. Use the tuple() constructor for converting lists to tuples.
This method has an O(n) time complexity and applies to tuples of any size.
The list() Constructor creates a shallow copy.
Empty tuple to list
If you want to convert an empty tuple to a list, you will get an empty list.
# Creating an empty tuple
empty_tuple = ()
print("Original Tuple:", empty_tuple)
# Output: Original Tuple: ()
print(type(empty_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
# Converting the tuple into a list
empty_list = list(empty_tuple)
print("Converted List:", empty_list)
# Output: Converted List: []
print(type(empty_list))
# Output: <class 'list'>
Single-Element Tuples
Let’s create a single-element tuple and convert it into a list.
# Creating a single element tuple
single_tuple = (19, )
print("Original Tuple:", single_tuple)
# Output: Original Tuple: (19,)
print(type(single_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
# Converting the tuple into a list
single_list = list(single_tuple)
print("Converted List:", single_list)
# Output: Converted List: [19]
print(type(single_list))
# Output: <class 'list'>
Named Tuples to Lists
You can import a namedtuple from the “collections” module. To create a namedtuple, use the namedtuple() Constructor.
You can convert a namedtuple to a list using the list() Constructor.
from collections import namedtuple
Person = namedtuple('Person', ['name', 'age'])
p = Person('Krunal', 31)
# Converting to list (loses field names)
lst = list(p)
# Output: ['Krunal', 31]
# Preserve order via dictionary (if needed)
dict_p = p._asdict()
ordered_values = list(dict_p.values())
# Same as list(p)
Shallow Copy Issue
Since the list constructor creates a shallow copy, adding an element to a list after converting from a tuple will show that the tuple also reflects this addition.
tup = ([1, 2], 3) lst = list(tup) lst[0].append(3) # Modifies the original tuple's list! print(lst) # Output: ([1, 2, 3], 3) print(tup) # Output: ([1, 2, 3], 3)
To fix this issue, use the copy.deepcopy() to avoid unintended side effects.
import copy tup = ([1, 2], 3) print(tup) # Output: ([1, 2], 3) lst = copy.deepcopy(tup) # Perform deep copy lst[0].append(3) # This modification will NOT affect 'tup' print(lst) # Output: ([1, 2, 3], 3) print(tup) # Output: ([1, 2], 3) # Original remains unchanged
The output tuple is unaffected even after modifying the list.
Here are the four alternate ways to convert a tuple to a list:
- Using the list comprehension
- Using an asterisk(*) operator
- Using the map() Function
- Using a for loop
Approach 1: Using list comprehension
If you are dealing with a tuple of tuples and you want to convert it into a list of lists, you should definitely use “list comprehension”.
tpl_of_tpls = ((1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6)) print(tpl_of_tpls) # Output: ((1, 2), (3, 4), (5, 6)) lst_of_lsts = [list(inner) for inner in tpl_of_tpls] print(lst_of_lsts) # Output: [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]]
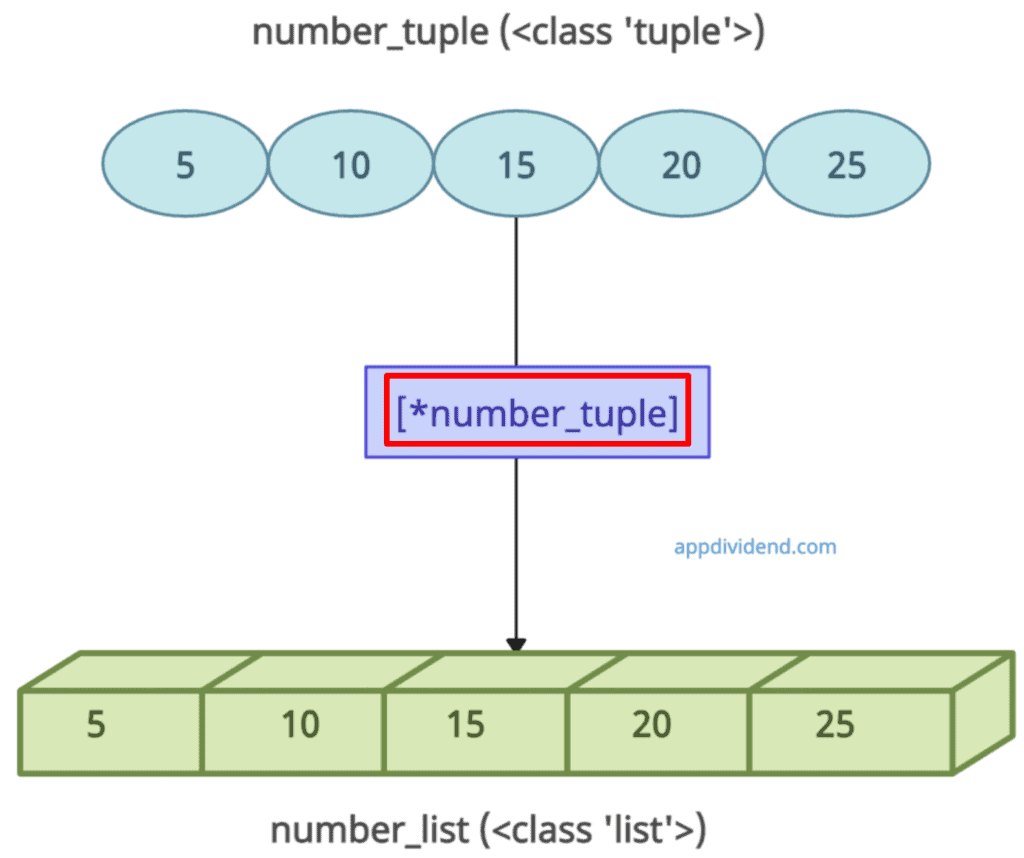
Approach 2: Using an asterisk(*) operator
The unpacking operator * allows you to unpack the elements of a tuple into a new list.
# Creating a tuple number_tuple = (5, 10, 15, 20, 25) print(number_tuple) # Output: (5, 10, 15, 20, 25) print(type(number_tuple)) # Output: <class 'tuple'> number_list = [*number_tuple] print(number_list) # Output: [5, 10, 15, 20, 25] print(type(number_list)) # Output: <class 'list'>
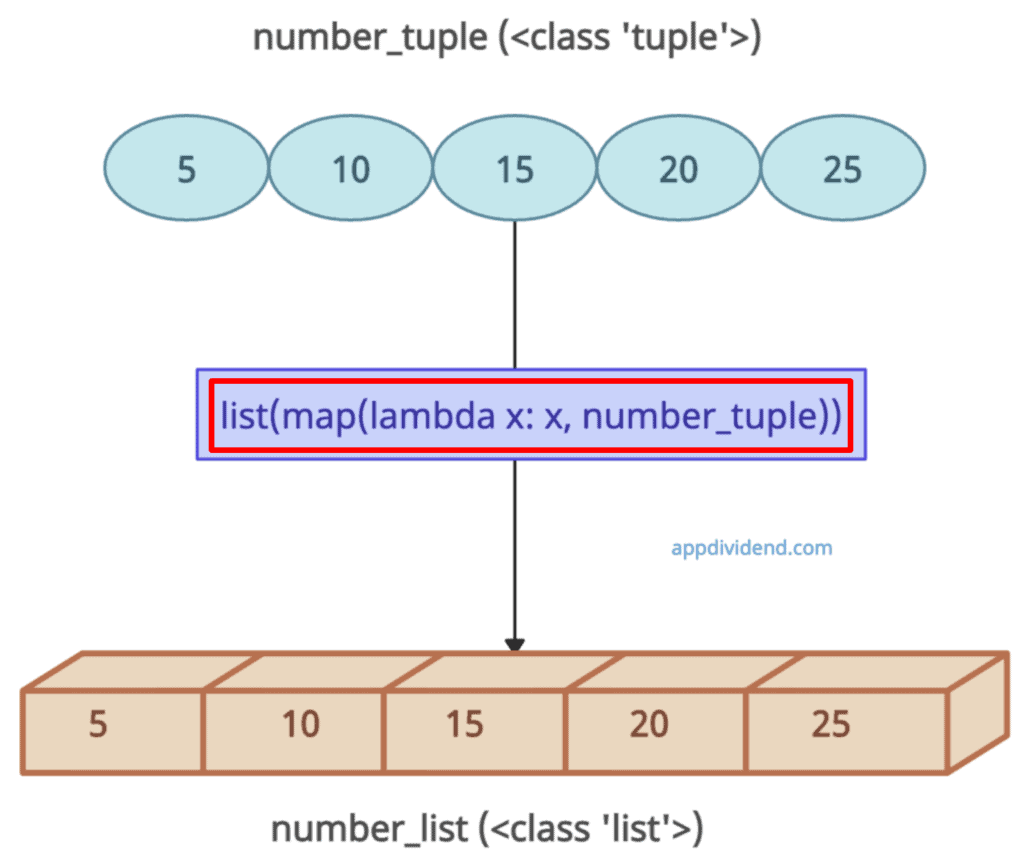
Approach 3: Using the map()
The map() function applies a specified function to each item of an iterable and converts the result into a list.
# Creating a tuple number_tuple = (5, 10, 15, 20, 25) print(number_tuple) # Output: (5, 10, 15, 20, 25) print(type(number_tuple)) # Output: <class 'tuple'> number_list = list(map(lambda x: x, number_tuple)) print(number_list) # Output: [5, 10, 15, 20, 25] print(type(number_list)) # Output: <class 'list'>
Approach 4: Using a for loop
Create an empty list and use the append() method within a for loop to add each element of the tuple, one at a time.
# Creating a tuple
number_tuple = (5, 10, 15, 20, 25)
print(number_tuple)
# Output: (5, 10, 15, 20, 25)
print(type(number_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
# Initialize an empty list
number_list = []
# Iterate over each element in the tuple
for item in number_tuple:
# Append each element to the list
number_list.append(item)
print(number_list)
# Output: [5, 10, 15, 20, 25]
print(type(number_list))
# Output: <class 'list'>
That’s all!