To convert a tuple to JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) in Python, use the json.dumps() method. The json.dumps() method serializes objects (like tuples, lists, dict, etc.) into a JSON-formatted string and returns it.
import json
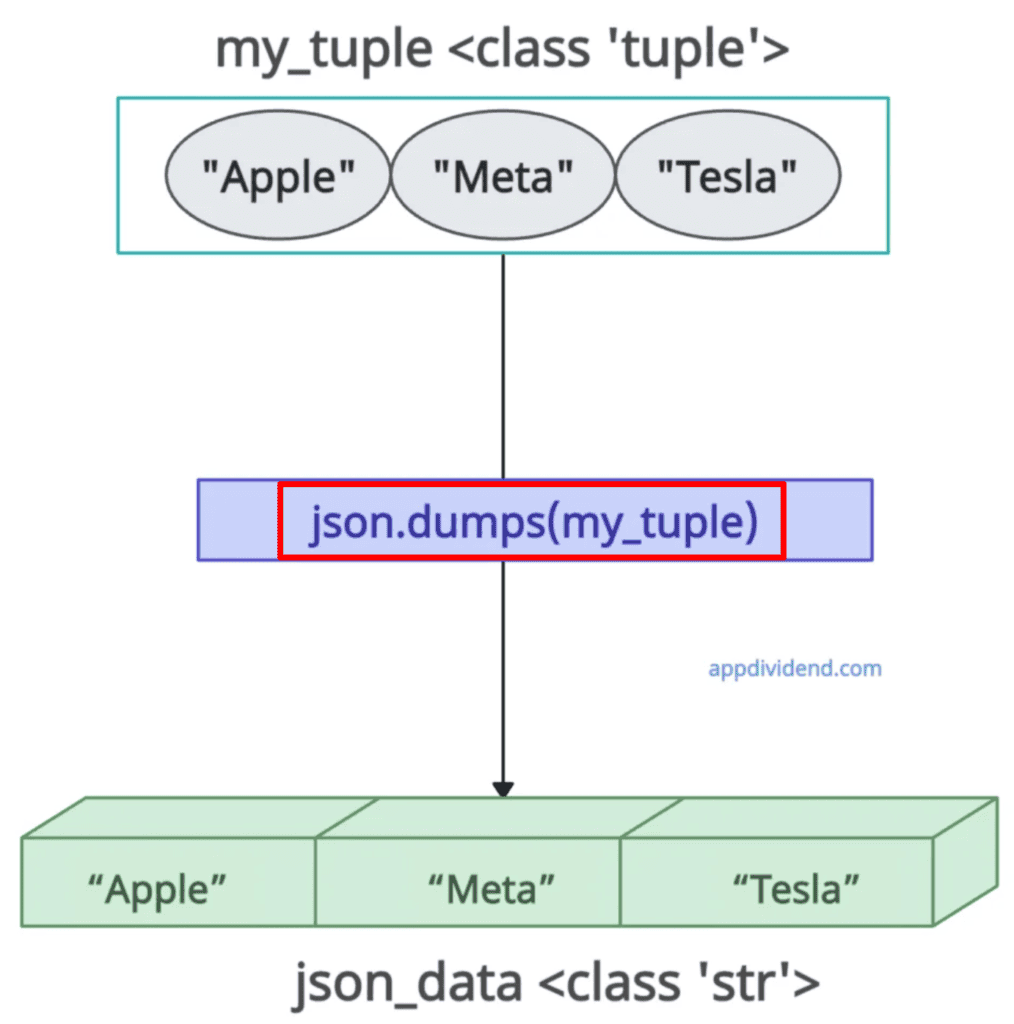
my_tuple = ("Apple", "Meta", "Tesla")
print(my_tuple)
# Output: ('Apple', 'Meta', 'Tesla')
print(type(my_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
# Conversion to JSON
json_data = json.dumps(my_tuple)
print(json_data)
# Output: '["Apple", "Meta", "Tesla"]'
print(type(json_data))
# Output: <class 'str'>
In the above code, we first define a tuple with three elements and then print its type.
In the next step, we used the json.dumps() method and pass the “my_tuple” as an argument that returns a JSON-formatted string. Note that even if the output is JSON-formatted, its type in Python is string.
Nested Tuple
If the tuple is nested, it is recursively converted into nested lists.
import json
nested_tuple = ("x", (11, 21, 31), ("b", "c"))
print(nested_tuple)
# Output: ('x', (11, 21, 31), ('b', 'c'))
print(type(nested_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
# Conversion to JSON
json_data = json.dumps(nested_tuple)
print(json_data)
# Output: '["x", [11, 21, 31], ["b", "c"]]'
print(type(json_data))
# Output: <class 'str'>
In this code, the nested tuple in the input is (11, 21, 31), and the output string contains [11, 21, 31] as a list.
Using different datatypes
Here’s a table that outlines the default conversions performed by the JSON module:
| Python | JSON |
| dict | Object |
| tuple | Array |
| list | Array |
| str | String |
| number – int, long | number – int |
| float | number – real |
| True | true |
| False | false |
| None | null |
import json
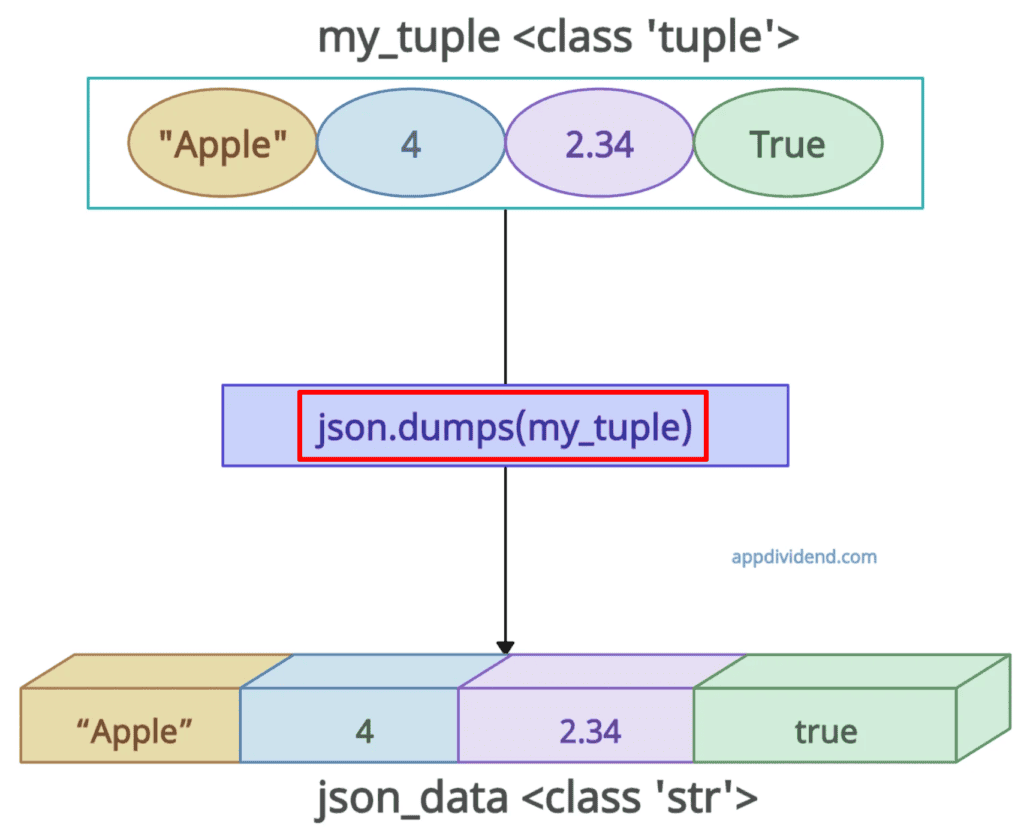
my_tuple = ("Apple", 4, 2.34, True)
print(my_tuple)
# Output: ('Apple', 4, 2.34, True)
print(type(my_tuple))
# Output: <class 'tuple'>
json_data = json.dumps(my_tuple)
print(json_data)
# Output: '["Apple", 4, 2.34, true]'
print(type(json_data))
# Output: <class 'str'>
That’s all!