The most efficient and easiest way to convert an input set to an output dictionary is to use the dictionary.keys() method.
When you use dict.fromkeys() method, each key in the dictionary will have the same default value. If no default value is provided, it defaults to None.
sample_set = {1, 3, 5, 7}
print(sample_set)
# Output: {1, 3, 5, 7}
print(type(sample_set))
# Output: <class 'set'>
sample_dict = dict.fromkeys(sample_set, 'Ronaldo')
print(sample_dict)
# Output: {1: 'Ronaldo', 3: 'Ronaldo', 5: 'Ronaldo', 7: 'Ronaldo'}
print(type(sample_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
Remember, sets are unordered collections, so the order of keys in the resulting dictionary can be different from the order of elements in the set.
Alternate approaches
Using zip() function
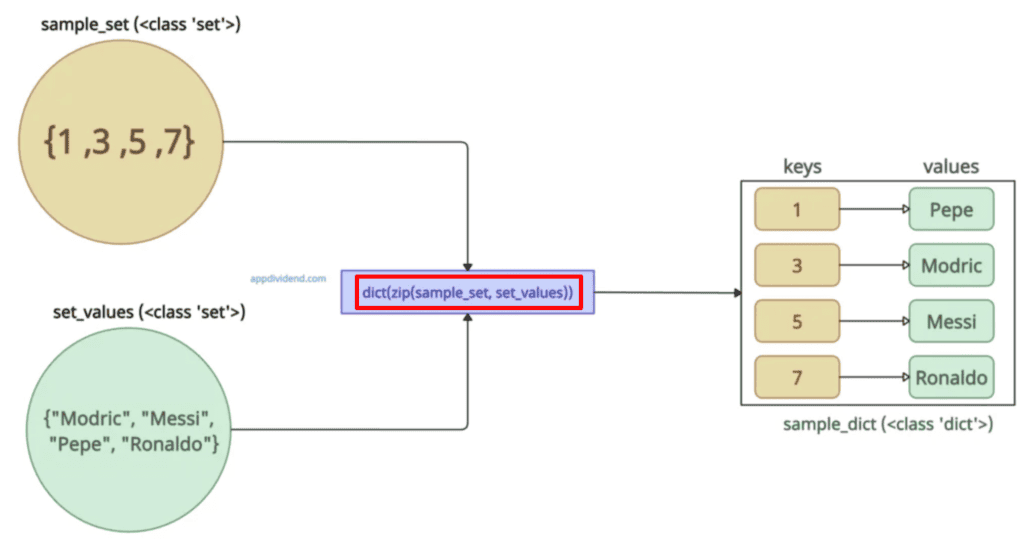
In this code, we took two sets: the First acts as a key and the second set acts as values for the dictionary. Then, we use the zip() function to pair elements from the two sets, which returns an iterable.
Then, convert this iterable to a dictionary using the dict() method and we have a final dictionary.
sample_set = {1, 3, 5, 7}
set_values = {"Modric", "Messi", "Pepe", "Ronaldo"}
print(sample_set)
# Output: {1, 3, 5, 7}
print(type(sample_set))
# Output: <class 'set'>
print(set_values)
# Output: {'Modric', 'Pepe', 'Messi', 'Ronaldo'}
print(type(set_values))
# Output: <class 'set'>
# Conversion from set to dictionary
sample_dict = dict(zip(sample_set, set_values))
print(sample_dict)
# Output: {1: 'Modric', 3: 'Pepe', 5: 'Messi', 7: 'Ronaldo'}
print(type(sample_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
Using dictionary comprehension
Dictionary comprehension is similar to the fromkeys() method. It iterates over each element in the set and assigns a default value to each key in the dictionary.
sample_set = {1, 3, 5, 7}
print(sample_set)
# Output: {1, 3, 5, 7}
print(type(sample_set))
# Output: <class 'set'>
sample_dict = {element: 'Ronaldo' for element in sample_set}
print(sample_dict)
# Output: {1: 'Ronaldo', 3: 'Ronaldo', 5: 'Ronaldo', 7: 'Ronaldo'}
print(type(sample_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
That’s all!