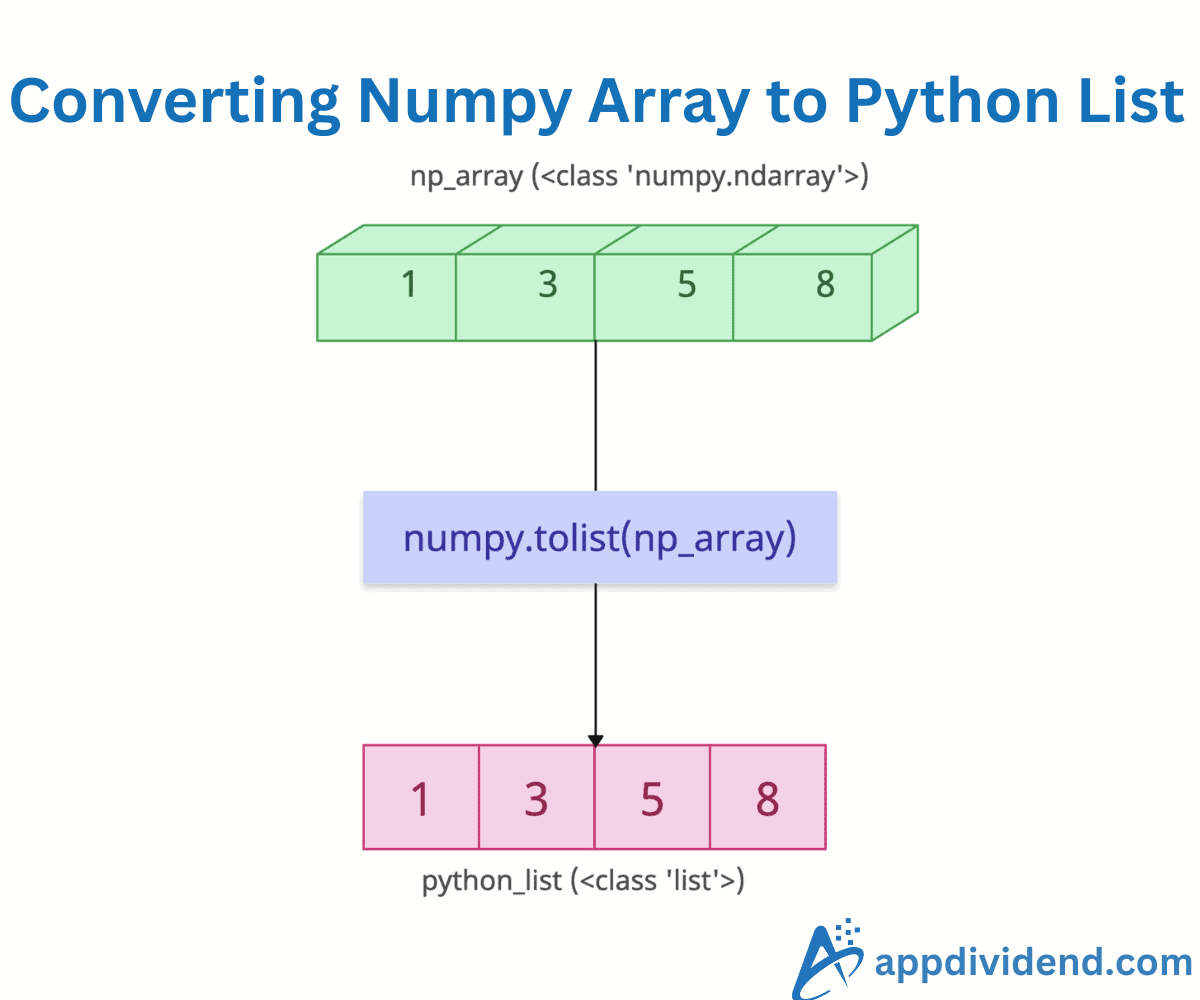
The best way to convert a Numpy array to a Python list is to use numpy.tolist() method. It converts a 1D array to a 1D list, a 2D array to a 2D list, a 3D array to a 3D list, or a multi-dimensional array to a multi-dimensional list.
import numpy as np
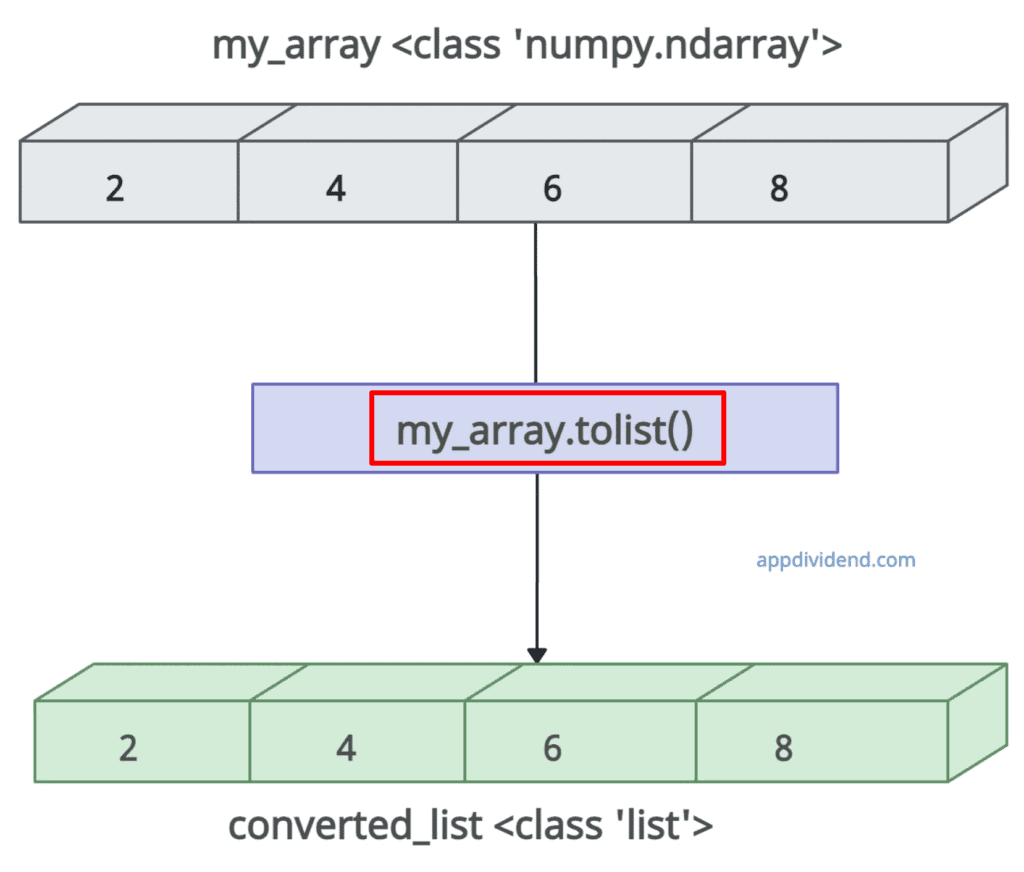
my_array = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8])
print("Before converting to list:", my_array)
# Output: Before converting to list: [2 4 6 8]
print("Type before conversion:", type(my_array))
# Output: Type before conversion: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
converted_list = my_array.tolist()
print("After converting to list:", converted_list)
# Output: After converting to list: [2, 4, 6, 8]
print("Type after conversion:", type(converted_list))
# Output: Type after conversion: <class 'list'>
Multi-Dimensional Arrays (2D, 3D, etc.)
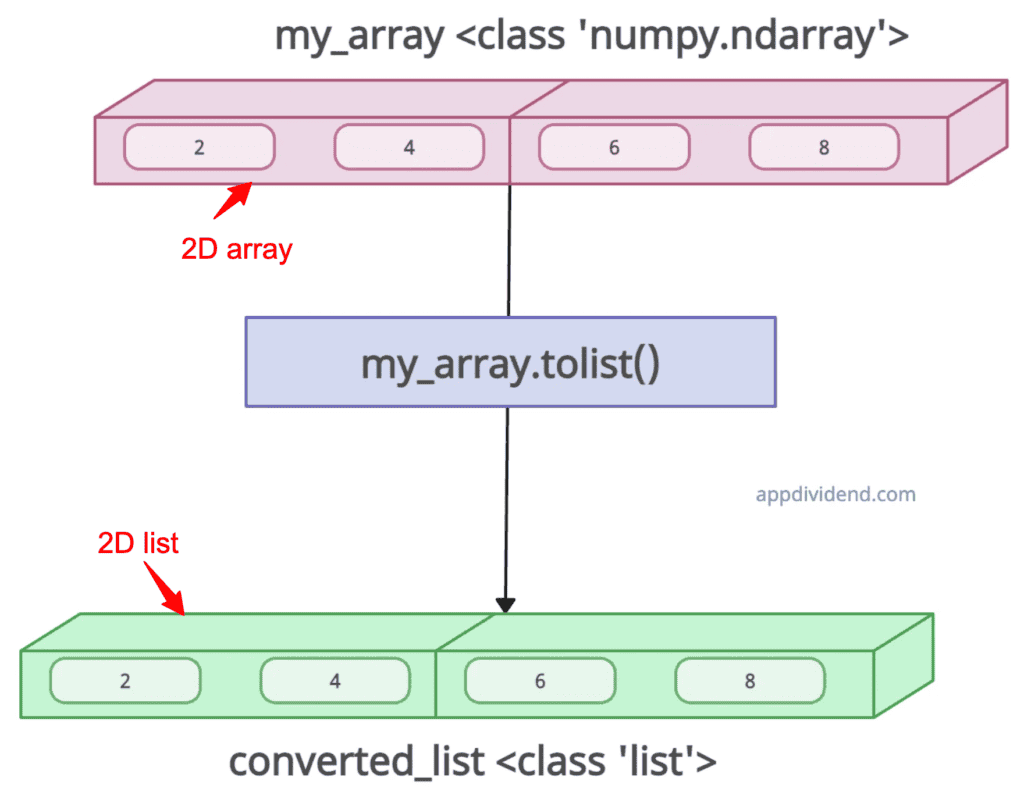
If the input array is a multi-dimensional array, the np.tolist() method creates nested lists to match the array’s shape. So, the output list has the exact dimensions as the input array.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([[2, 4], [6, 8]])
print("Before converting to list:", my_array)
# Output: Before converting to list: [[2 4]
# [6 8]]
print("Type before conversion:", type(my_array))
# Output: Type before conversion: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
converted_list = my_array.tolist()
print("After converting to list:", converted_list)
# Output: After converting to list: [[2, 4], [6, 8]]
print("Type after conversion:", type(converted_list))
# Output: Type after conversion: <class 'list'>
3D array to 3D list
Let’s take a 3D input array.
import numpy as np arr_3d = np.array([[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]]) print(arr_3d) # Output: # [[[1 2] # [3 4]] # [[5 6] # [7 8]]] lst_3d = arr_3d.tolist() print(lst_3d) # Output: [[[1, 2], [3, 4]], [[5, 6], [7, 8]]]
Structured arrays
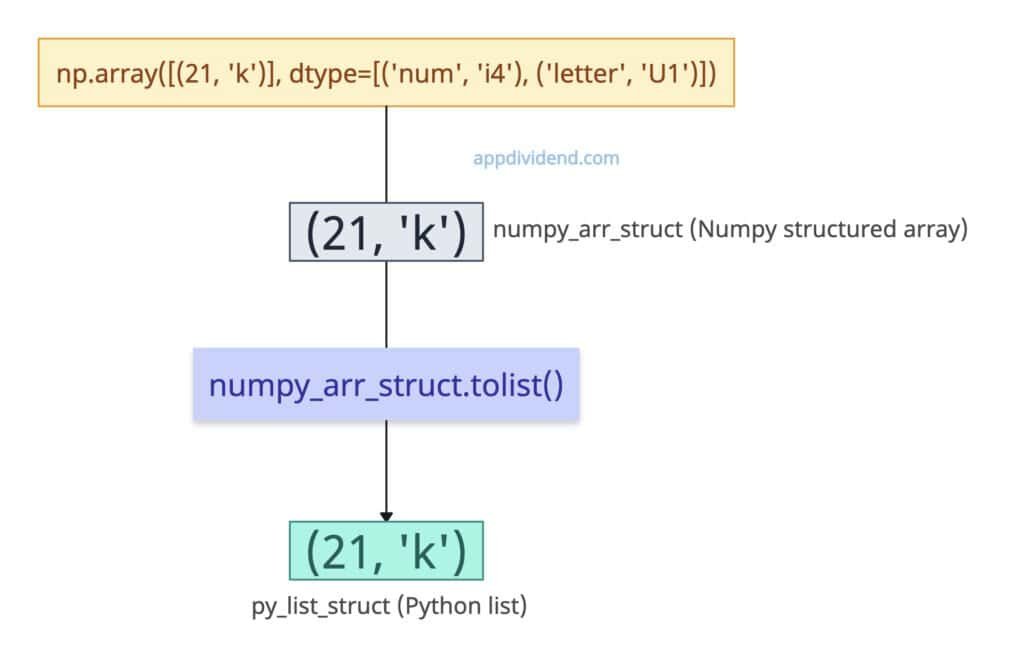
In numpy, structured arrays allow us to create an array where each element can contain multiple fields, each with potentially different data types.
The tolist() method handles the structured array effectively and returns a valid list without any errors.
import numpy as np
numpy_arr_struct = np.array([(21, 'k')],
dtype=[('num', 'i4'), ('letter', 'U1')])
print(numpy_arr_struct)
# Output: [(21, 'k')]
py_list_struct = numpy_arr_struct.tolist()
print(py_list_struct)
# Output: [(21, 'k')]
An array containing complex numbers
What if the input numpy array contains complex values? The output list also contains complex values, and this method handles this type of array perfectly.
import numpy as np arr_complex = np.array([1+2j, 3+4j]) print(arr_complex) # Output: [1.+2.j 3.+4.j] py_list_complex = arr_complex.tolist() print(py_list_complex) # Output: [(1+2j), (3+4j)]
Alternative Method: List Comprehension
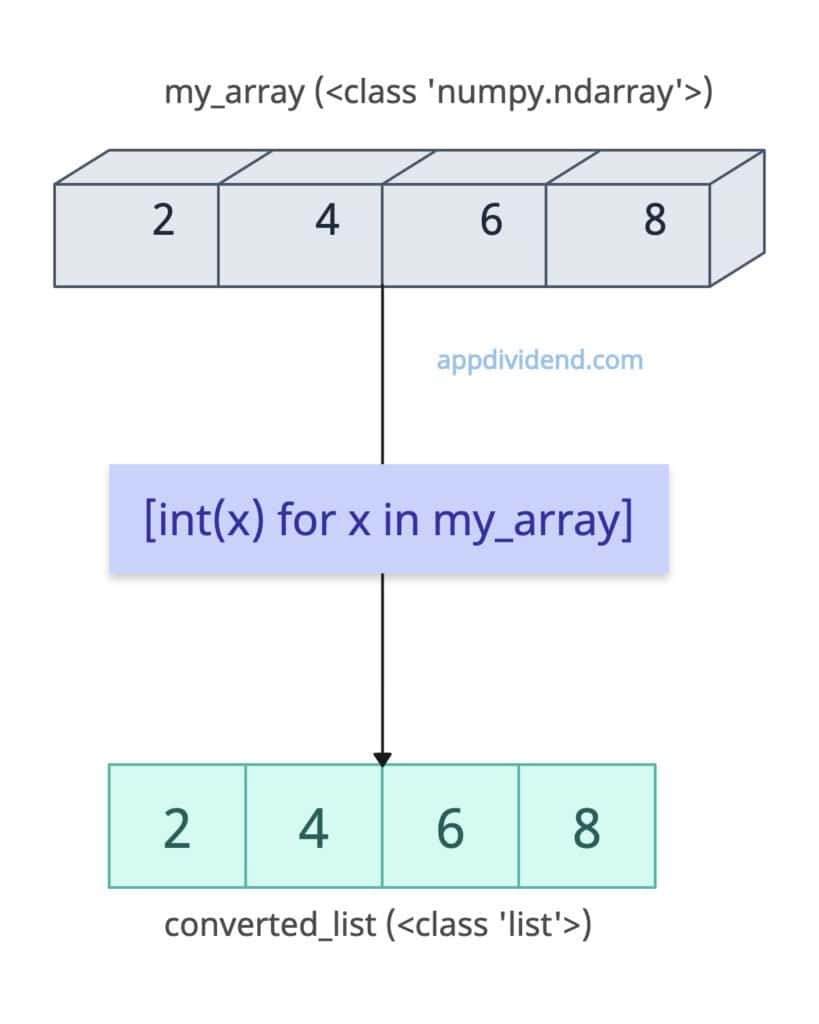
List comprehension iterates over each element in an array and creates a new list containing the same elements.
When you convert a NumPy array to a list, NumPy doesn’t magically cast its internal types to native Python types.
import numpy as np
my_array = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8])
print("Before converting to list:", my_array)
# Output: Before converting to list: [2 4 6 8]
print("Type before conversion:", type(my_array))
# Output: Type before conversion: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
converted_list = [int(x) for x in my_array]
print("After converting to list:", converted_list)
# Output: After converting to list: [2, 4, 6, 8]
print("Type after conversion:", type(converted_list))
# Output: Type after conversion: <class 'list'>
Internally, the elements in the list are still numpy.int64, not built-in int.
So, we need to apply the int() function to each element while converting them into a list.
That way, we will have a proper list with integers in the output.
You can also use the list() constructor, but it only works with a 1D array, and the elements in the output list are still np.int64 and not built-in integers. So, you have to convert each element to a built-in integer.