There is a straightforward formula that you can use to calculate a percentage in Python: (part / whole) * 100. That means the part is % of a whole number.
Use the division operator to divide one number by another, and then multiply the result by 100.
part = 3 whole = 5 percentage = (part / whole) * 100 print(percentage) # Output: 60.0
That means 30 is 60% of 50.
Handling a ZeroDivisionError exception
What if the whole is 0? It will throw a ZeroDivisionError exception. To handle this exception, we can use a try-except block and manually return 0.
def calculate_percentage(part, whole):
try:
return (part / whole) * 100
except ZeroDivisionError:
return 0
percentage = calculate_percentage(3, 0)
print(percentage)
# Output: 0
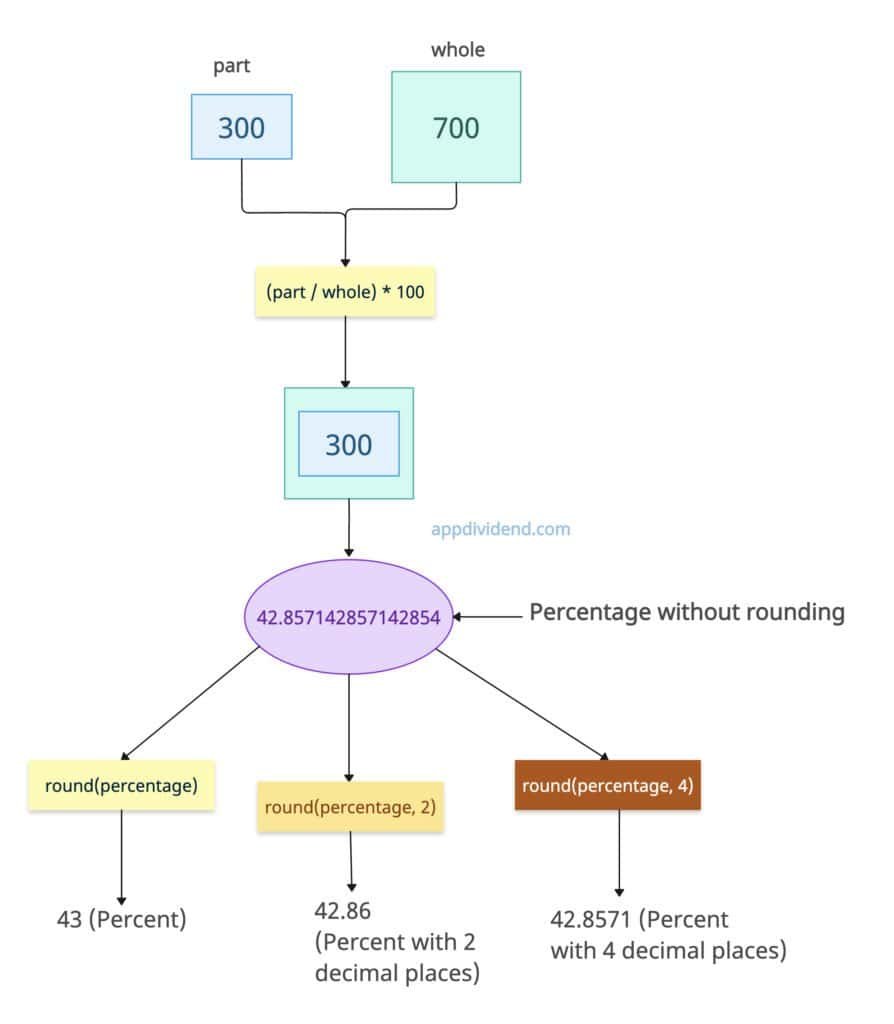
Rounding percentages
If you want percentages as integers or with limited decimals, use the round() method.
For rounding up to two decimal points, pass 2 as a second argument to the round() method. For rounding up to four decimal points, pass 4.
part, whole = 300, 700 percentage = (part / whole) * 100 print(round(percentage)) # Output: 43 print(round(percentage, 2)) # Output: 42.86 (2 decimal places) print(round(percentage, 4)) # Output: 42.8571 (4 decimal places)
Calculating percentage change
To calculate the percentage change between an old_value and a new_value, you can use the formula:
((new_value - old_value) / old_value) * 100
Increase percentage
Let’s take an old value of 75 and a new value of 100 and find the percentage increase from 75 to 100.
old_value = 75
new_value = 100
change = ((new_value - old_value) / old_value) * 100
print(f"Increase: {change}%")
# Output: Increase: 33.33333333333333%
That means it is a change of 33.33% increase.
Decrease percentage
Let’s take the old value of 100 and the new value of 75, and calculate the decreasing percentage.
old_value = 100
new_value = 75
change = ((new_value - old_value) / old_value) * 100
print(f"Decrease: {change}%")
# Output: Decrease: -25.0%
That means, it is a 25% reduction from 100 to 75.
You can see that when it comes to increase, it is up by 33.33% but when you decrease, it is 25%.
So, increase and decrease depend on which value you are calculating. It will make a base of that value and start calculating.
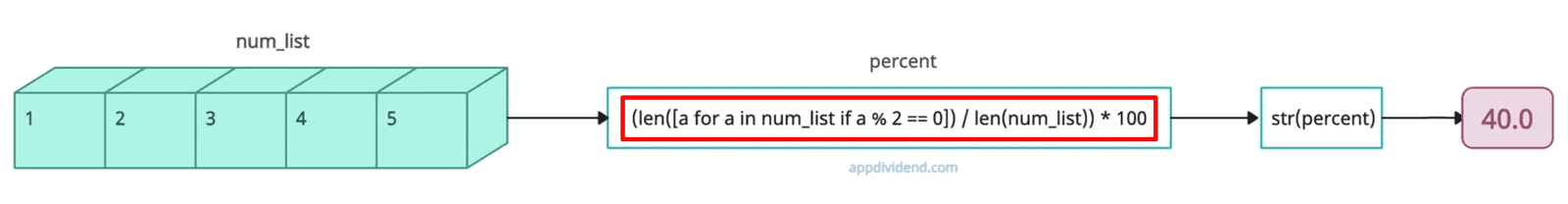
Percentage of a list
Let’s calculate the percentage of even numbers from the total number of elements in a list. For that, we need a list comprehension and the len() function.
We can calculate the number of even elements with list comprehension and len(), then divide by the total number of elements and multiply by 100.
num_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] percent = (len([a for a in num_list if a % 2 == 0]) / len(num_list)) * 100 print(str(percent)) # Output: 40.0
That means 40% of the elements in the input num_list are even numbers.
Alternate ways
Using a custom function
We can write a custom function that accepts two arguments: part and whole, and returns the percentage.
def calculate_percentage(part, whole):
return str((part / whole) * 100) + "%"
percentage = calculate_percentage(3, 5)
print(percentage)
# Output: 60.0%
Using fractions.Fraction for exact percentages
The fractions.Fraction is a built-in class that represents numbers as exact rational values (numerator/denominator), avoiding floating-point rounding errors. This makes it great for precise percentage calculations.
from fractions import Fraction part = 2 whole = 7 percentage = Fraction(part, whole) * 100 print(percentage) # Output: 200/7 print(float(percentage)) # Output: 28.571428571428573
That means number 2 is 28.57142% of number 7.




Yathartha
really helpful
duffer
i dont’ know