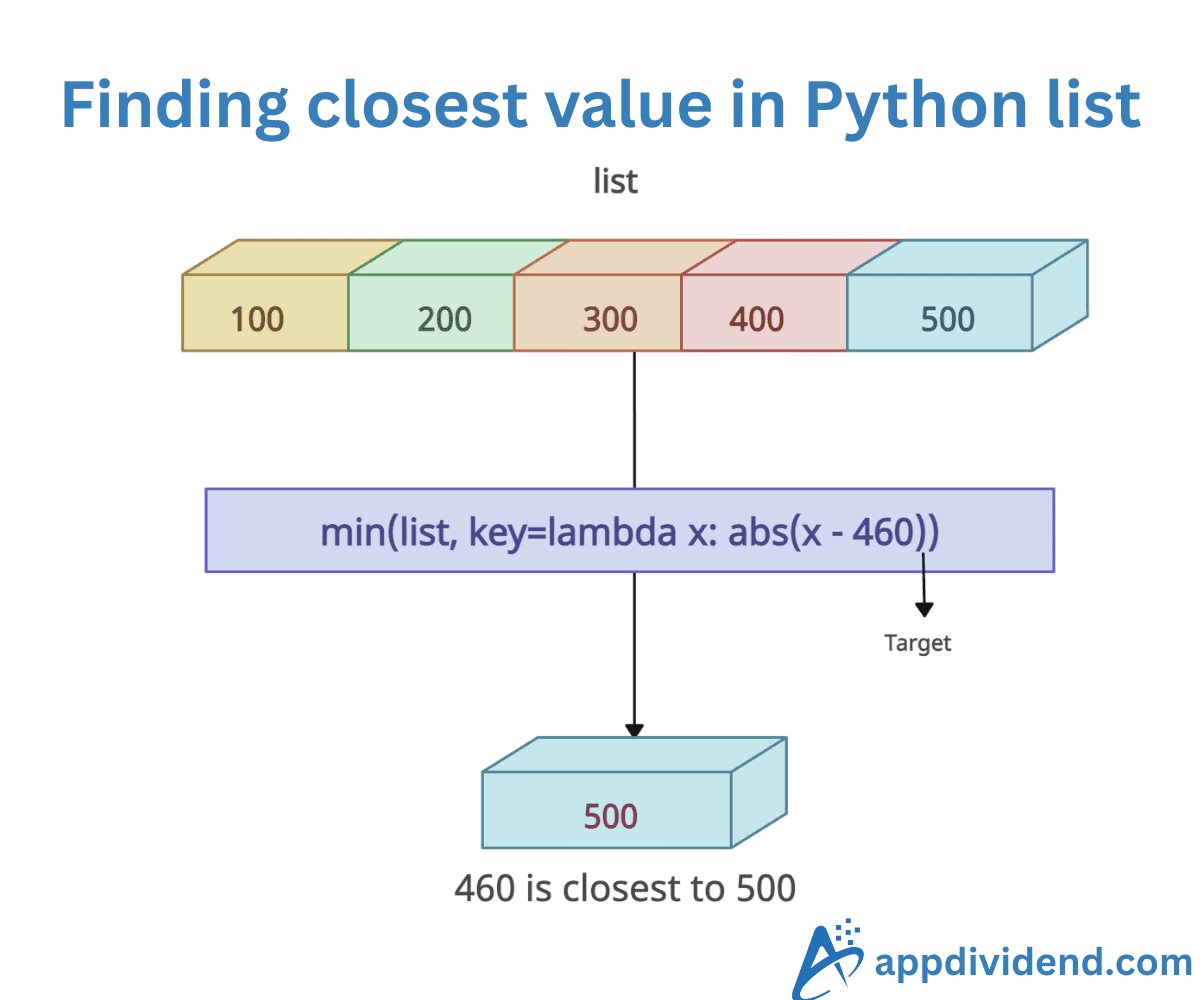
The best and efficient way to find the closest value in a Python list is to use the combination of min() and a lambda function. You can calculate the absolute difference using a lambda function to determine how close each number is to the target in the list.
The min() function then compares these differences and returns the number from the list that has the smallest difference.
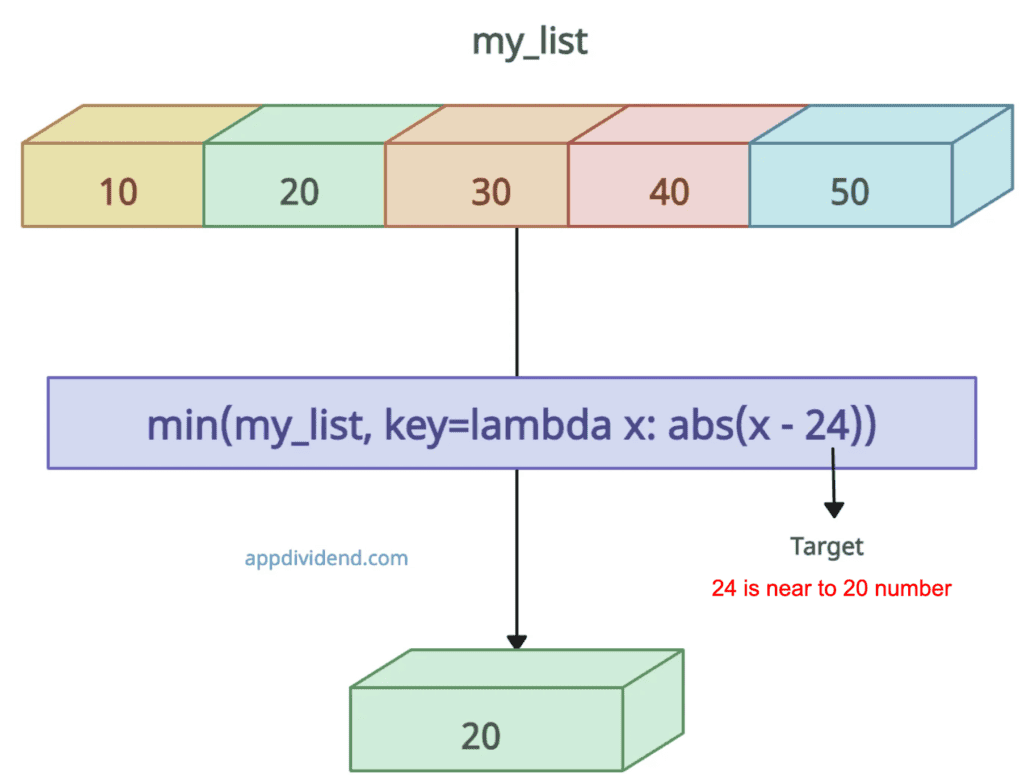
def closest_value(my_list, target):
return min(my_list, key=lambda x: abs(x - target))
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target_number = 24
print(closest_value(my_list, target_number))
# Output: 20
Using np.argmin()
Another approach is to convert the input list into a NumPy array and apply NumPy methods to find the closest value.
In this case, first, you need to use np.asarray() to convert the list into a NumPy array. Then, np.abs() computes the absolute value of the differences between each element in the array and the target number.
Finally, np.argmin() is used to find the index of the smallest value in the array of absolute differences.
import numpy as np
def closest_value(my_list, target):
arr = np.asarray(my_list)
index = (np.abs(arr - target)).argmin()
return arr[index]
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target_number = 24
print(closest_value(my_list, target_number))
# Output: 20
Using a for loop and abs()
You can use the for loop to iterate over each element in the list and use the abs() method to find the absolute value of the difference between the target number and the current number being evaluated in the list.
def closest_value(my_list, target):
closest = my_list[0]
for number in my_list:
if abs(number - target) < abs(closest - target):
closest = number
return closest
my_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
target_number = 24
print(closest_value(my_list, target_number))
# Output: 20
This is the least efficient way because it takes a long time to find the closest element.