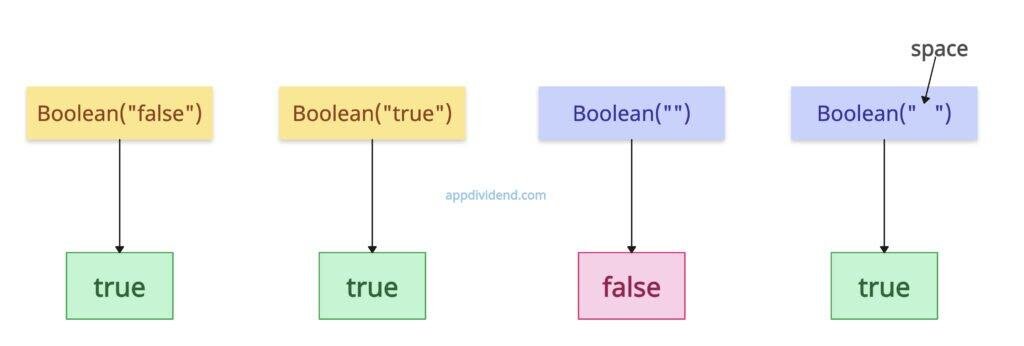
The most reliable and efficient way to convert a String to a Boolean type is to use the Boolean() constructor and pass the string value to it. The empty string (“”) becomes false, and a non-empty string becomes true.
console.log(Boolean("true"));
// Output: true (non-empty)
console.log(Boolean("false"));
// Output: true (non-empty, unexpected!)
console.log(Boolean(""));
// Output: false
console.log(Boolean("0"));
// Output: true
console.log(Boolean("yes"));
// Output: true
console.log(Boolean(" "));
// Output: true
In this code, “true” and “false” refer to a string and not a Boolean value, so Boolean() returns true in both cases. An empty string is considered false because there is no value.
When it comes to 0, it should return false, but “0” here is a string, so it returns true.
If you pass the space to the Boolean() constructor, it returns true because the space is counted as a character. An empty string and a space are two different things.
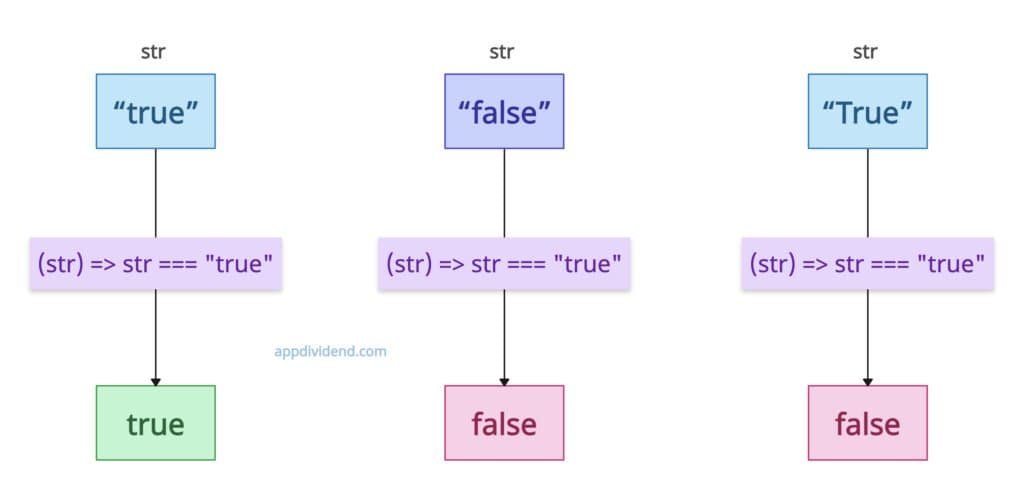
Using strict equality comparison (===)
The strict equality operator (===) compares the string directly to “true”. If it matches, it returns true; otherwise, it returns false. It is a case-sensitive approach, which is why, in the last part of the above figure, ‘True’ and ‘true’ are not the same and return false.
// Creating a custom arrow function
const strToBool = (str) => str === "true";
console.log(strToBool("true"));
// Output: true
console.log(strToBool("false"));
// Output: false
console.log(strToBool("True"));
// Output: false (case-sensitive)
console.log(strToBoolInsensitive("yes"));
// Output: false
As you can see, it handles only “true” and “false” values correctly, but what about the synonyms like “yes”? Well, it can’t handle those other synonyms. That is the limitation.
For case-insensitiveness, we can create another custom arrow function that converts the input string to lowercase and then compares it with the “true” value.
const strToBoolInsensitive = (str) => (str || "").toLowerCase() === "true";
console.log(strToBoolInsensitive("True"));
// Output: true
console.log(strToBoolInsensitive("FALSE"));
// Output: false
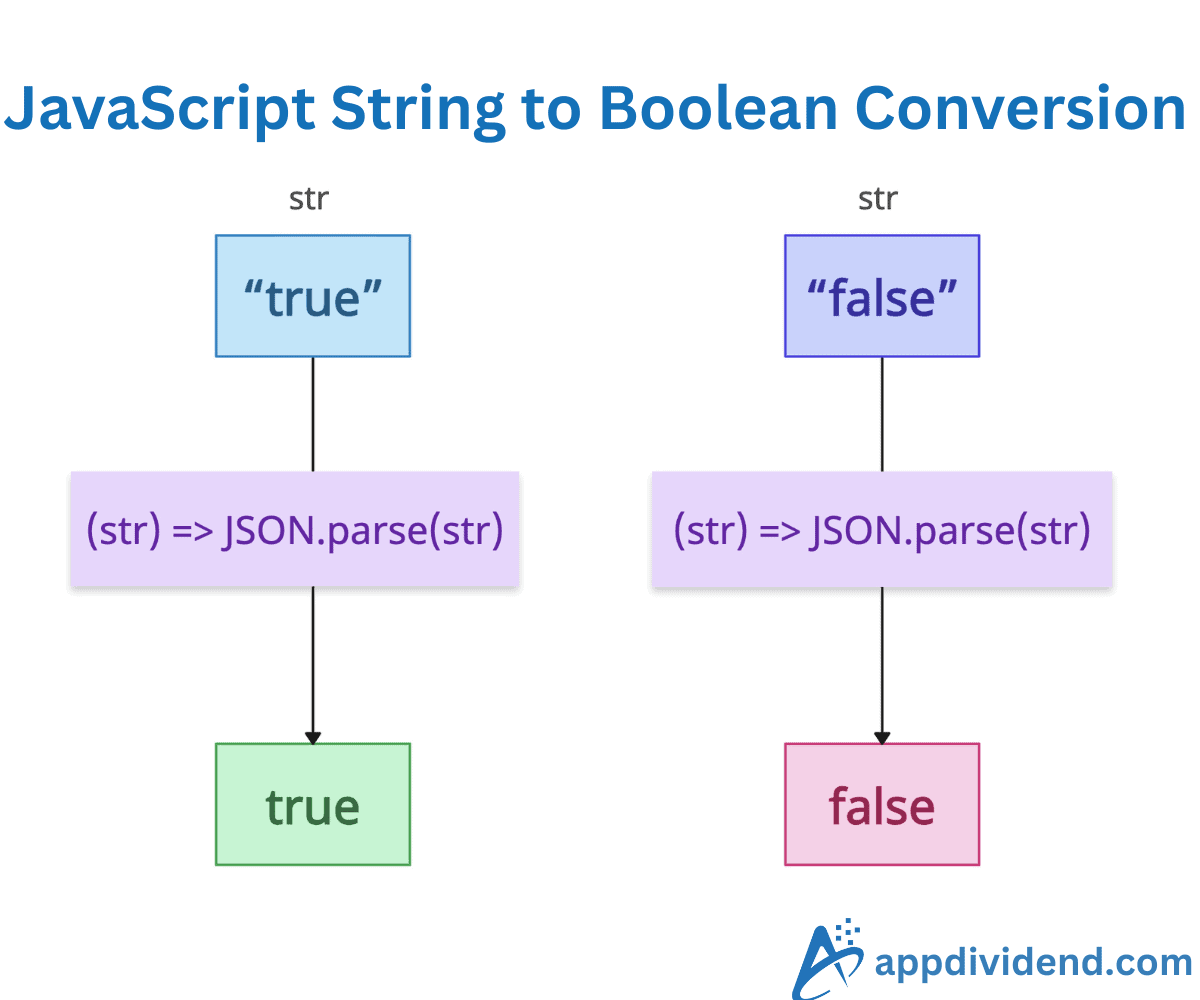
Using JSON.parse()
The JSON.parse() method parses the string as JSON, where “true” becomes true and “false” becomes false. For requiring an exact lowercase match, use .toLowerCase() for case-insensitivity. Wrap in try-catch for safety.
// Creating a custom arrow function
const strToBool = (str) => JSON.parse(str);
console.log(strToBool("true"));
// Output: true
console.log(strToBool("false"));
// Output: false
The above code shows that the JSON.parse() method correctly handles the “true” and “false” values.
For potential errors, we can handle different scenarios using a try-catch block.
// Case-insensitive with error handling
const safeStrToBool = (str) => {
try {
return JSON.parse((str || "").toLowerCase());
} catch {
return false; // or throw error
}
};
console.log(safeStrToBool("True"));
// Output: true
console.log(safeStrToBool("FALSE"));
// Output: false
console.log(safeStrToBool("yes"));
// Output: false (error caught)
In the above code, we handle other truthy or falsy values such as “Yes” or “No”. So, this is also a limitation of this approach.
That’s all!