PIL Image.save(): Saving JPEG File in Python
To save an image in JPEG format in Python, use the PIL library’s Image.save() method. The Image.save() method serializes an…
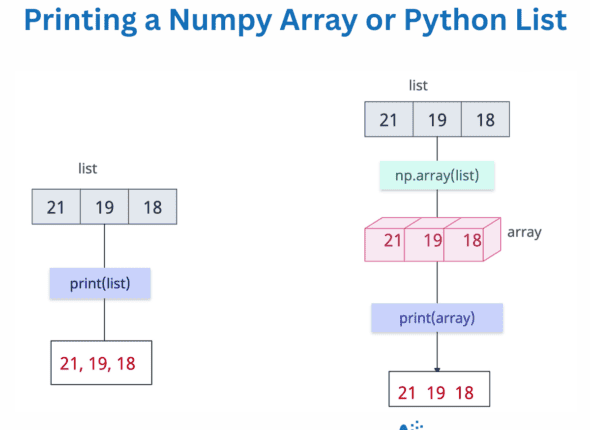
How to Print a Numpy Array in Python
For debugging, inspecting intermediate outputs, or displaying structured results, you need to print the numpy array or list. Method 1:…
How to Assign Variable Inside an Expression in Python
If you are using a Python 3.8+ version, you can use the Walrus Operator (:=) also known as the assignment operator,…
How to Check If Numpy Array Contains an Element
The most efficient way to check whether a numpy array contains a specific element in Python is to use either…
Python Multi-line Statements: Writing Continue On Next Line
Python statements usually end with a newline. However, if you are writing a lengthy statement or code that requires multiple…
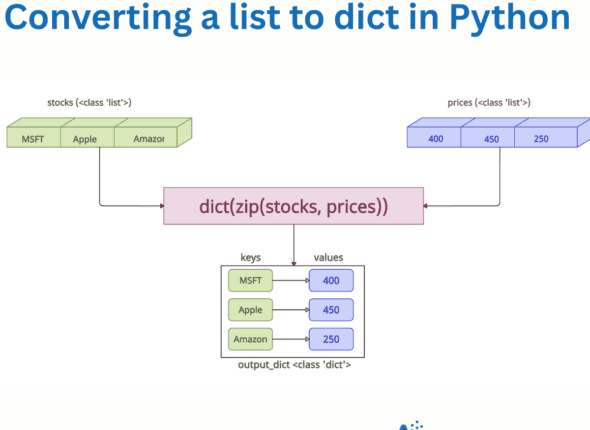
How to Convert List to Dictionary in Python
Converting a list to a dictionary in Python demands the type of input data you have and what your dictionary…
How to Split String (Tokens) on Multiple Delimiters in Python
To split a string into substrings (tokens), you need to define separators. The separators can be the same (repetitive) and…
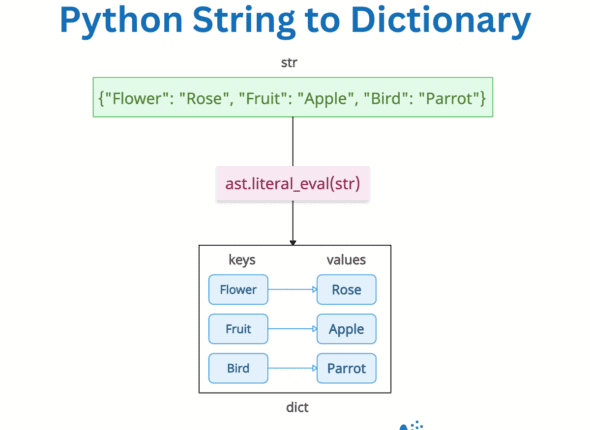
How to Convert a String to a Dictionary in Python
What does it mean when you say you want to convert a string that represents a dictionary to a valid…
How to Find the Cube Root of a Number in Python
The most straightforward and Pythonic method is to use the exponentiation operator (**), which raises the number to the power…
How to Search a File using “grep” in Python
To search a file using grep-like functionality in Python, you can read the file and then use regular expressions provided…