Skipping a value in the list means ignoring specific value(s) while iterating. You can skip a value based on the indices, conditions, or particular values like None. It depends on your requirement.
When iterating a list, the best way to skip elements is to use the “continue” statement. It will not create a new list, but ignore the values in the existing list, so that you don’t need to process the skipped element(s).
Looping statements like the for loop and the while loop can accommodate the continue statement.
Let’s skip a specific value from a list and print the other values.
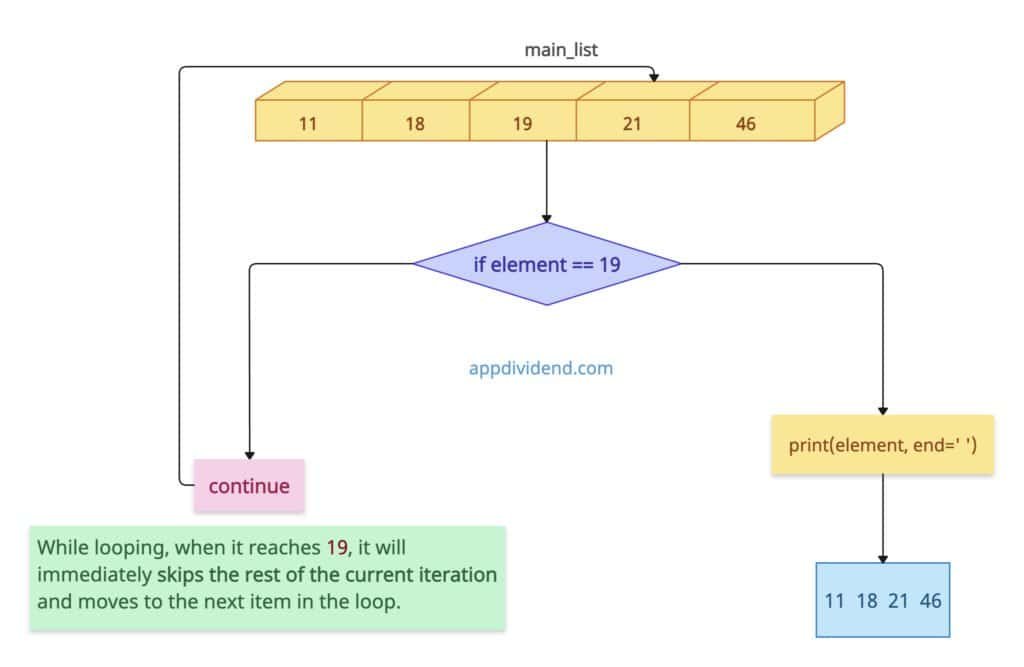
main_list = [11, 18, 19, 21, 46]
for element in main_list:
if element == 19: # Skip 19
continue
print(element, end=' ')
# Output: 11 18 21 46
In this code, while iterating, we want to skip the element 19. So, when the loop reaches 19, we don’t print it; instead, we use the continue statement to continue looping without taking any action. That way, we ignore the provided element.
Let’s use the while-loop with the continue statement to skip the None value from a list:
lst = [1, 2, None, 4, 5, 6]
i = 0
while i < len(lst):
if lst[i] == None: # Skip None
i += 1
continue
print(lst[i], end=' ')
i += 1
# Output: 1 2 4 5 6
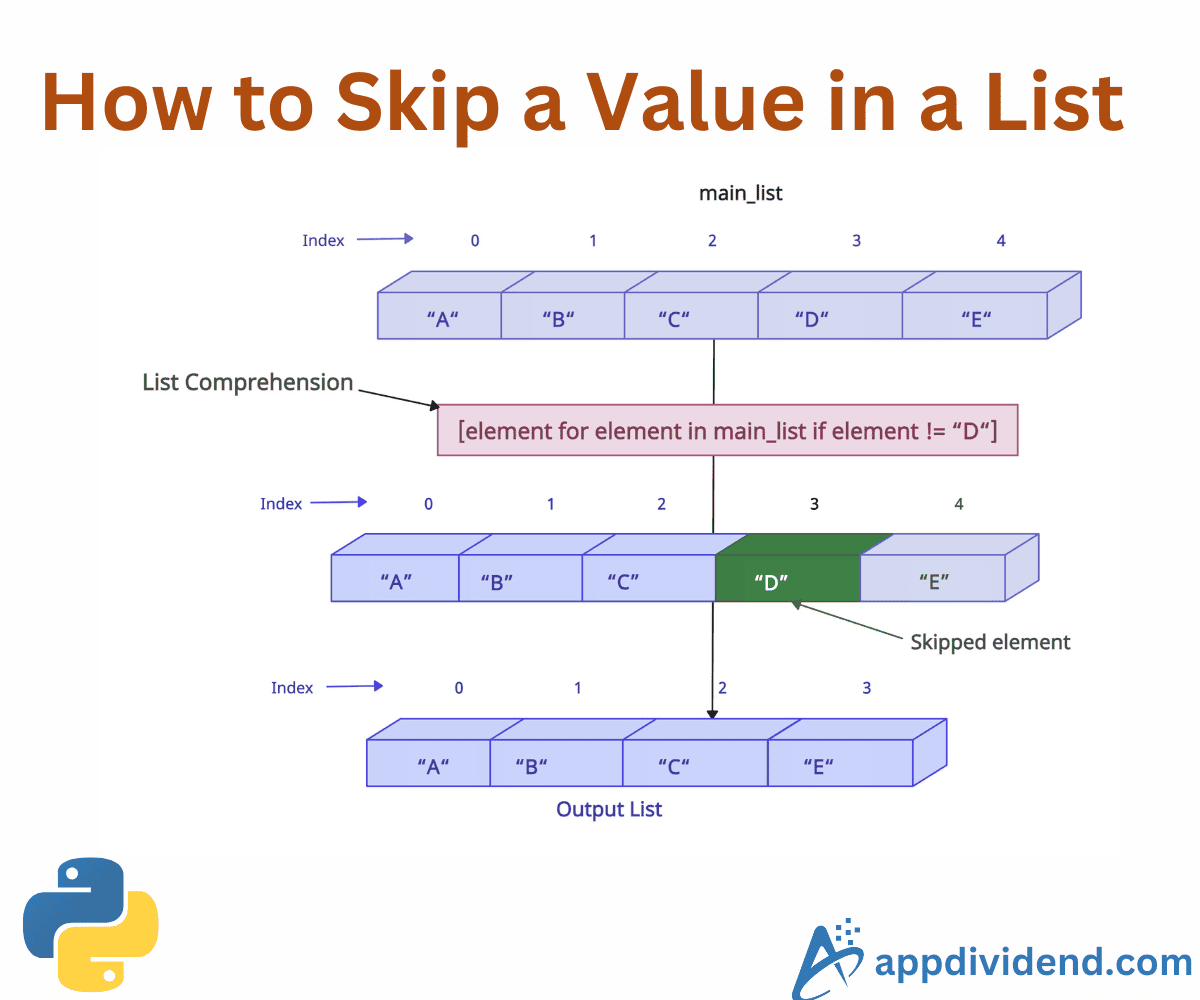
Skip a specific value with a new list
When you want to skip a specific value and create a new list, you should use a list comprehension.
List comprehensions are efficient for filtering and creating a new list without the skipped elements.
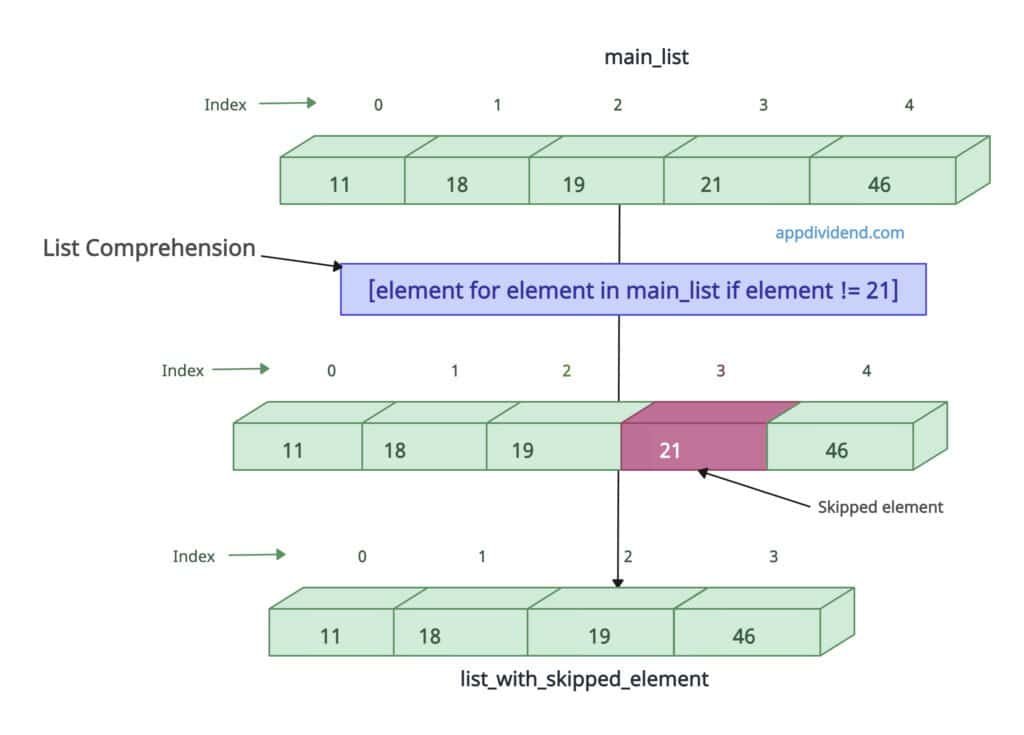
main_list = [11, 18, 19, 21, 46] list_with_skipped_element = [element for element in main_list if element != 21] print(list_with_skipped_element) # Output: [11, 18, 19, 46]
In this code, we explicitly specify that element 21 should be skipped and not included in the new list.
You can see that 21 is not there and has been successfully ignored.
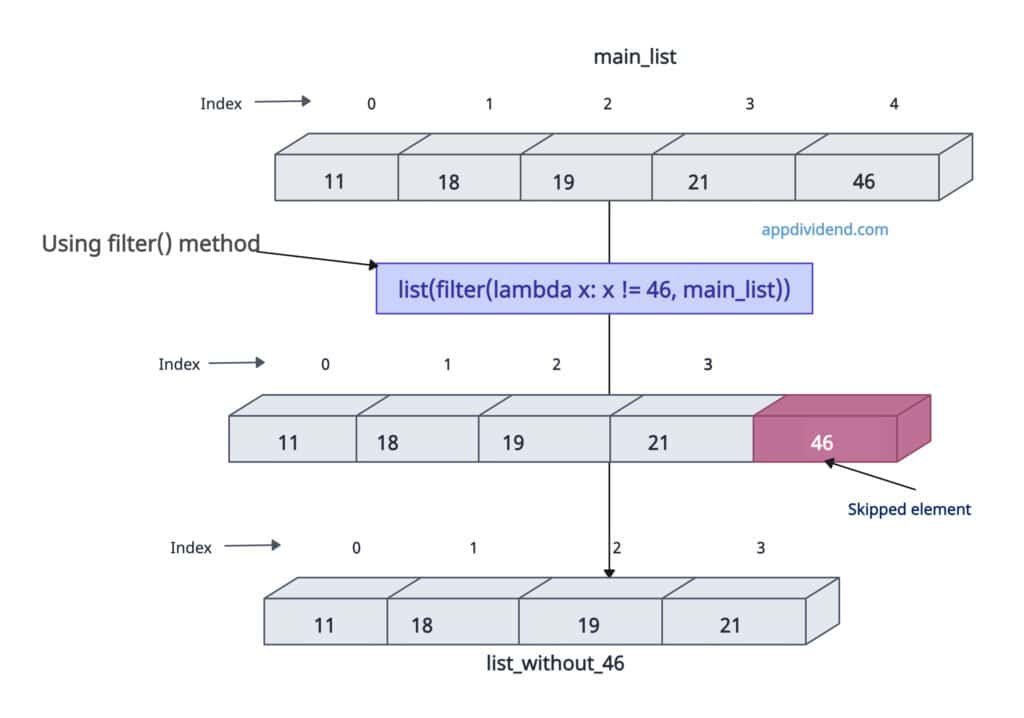
Using filter() method
Let’s skip a specific value from the list by using filter() and a lambda function. The lambda function defines the custom logic to identify the specific value, and filter() will filter it out and create a new list.
main_list = [11, 18, 19, 21, 46] list_without_46 = list(filter(lambda x: x != 46, main_list)) print(list_without_46) # Output: [11, 18, 19, 21]
In this code, we are ignoring the 46th element and creating a new list without it.
Skipping multiple values
If you want to skip multiple values, you can also use a list comprehension.
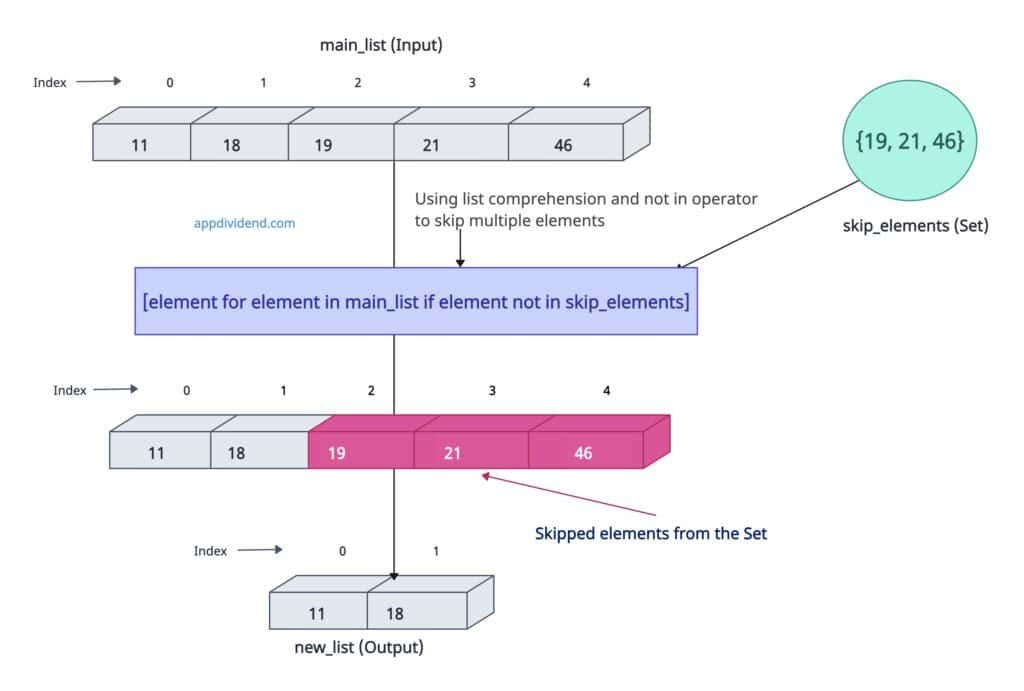
Create a set of unwanted values and use the “not in” operator inside the list comprehension to exclude them from the output list.
main_list = [11, 18, 19, 21, 46]
skip_elements = {19, 21, 46}
new_list = [element for element in main_list if element not in skip_elements]
print(new_list)
# Output: [11, 18]
Skipping values based on a condition
Let’s define a list with integers and apply a condition to skip all even values.
main_list = [11, 18, 19, 21, 46] odd_list = [item for item in main_list if item % 2 != 0] print(odd_list) # Output: [11, 19, 21]
The output odd_list contains only odd values.
Duplicate values
What if there are duplicate even and odd values in a list? Well, it will skip all the even values, including duplicates, whereas we will include all the odd values, including duplicates, in the output list.
duplicate_list = [46, 19, 12, 46, 11, 12, 19] odd_list = [item for item in duplicate_list if item % 2 != 0] print(odd_list) # Output: [19, 11, 19]
Skipping first and last elements from the list
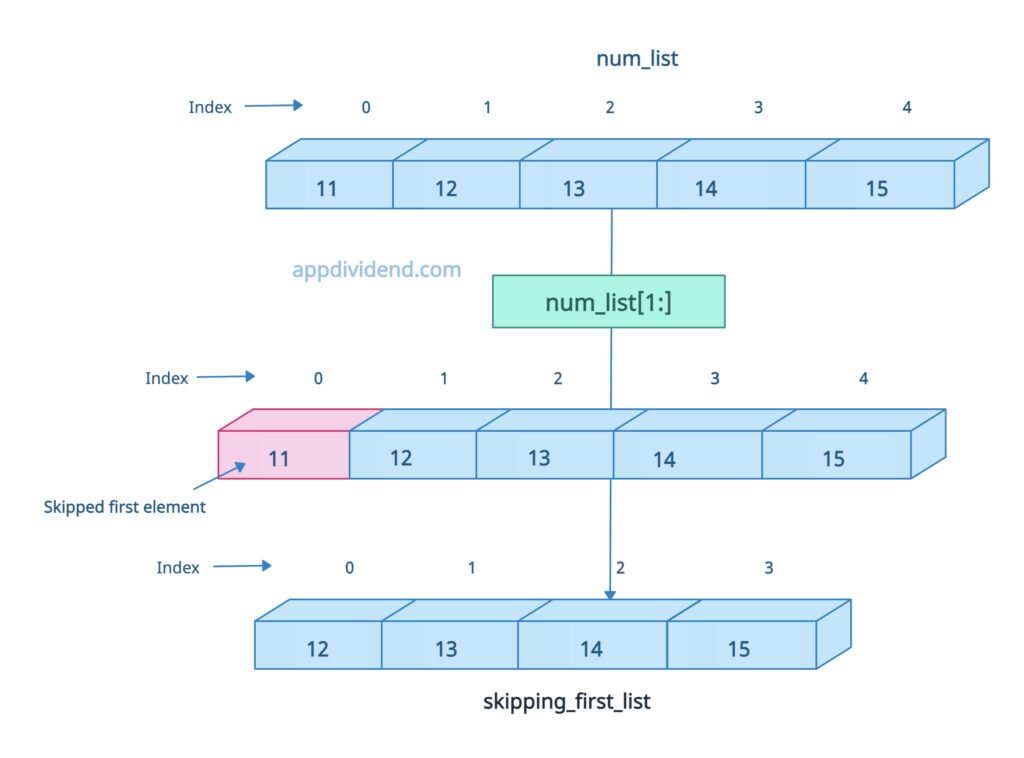
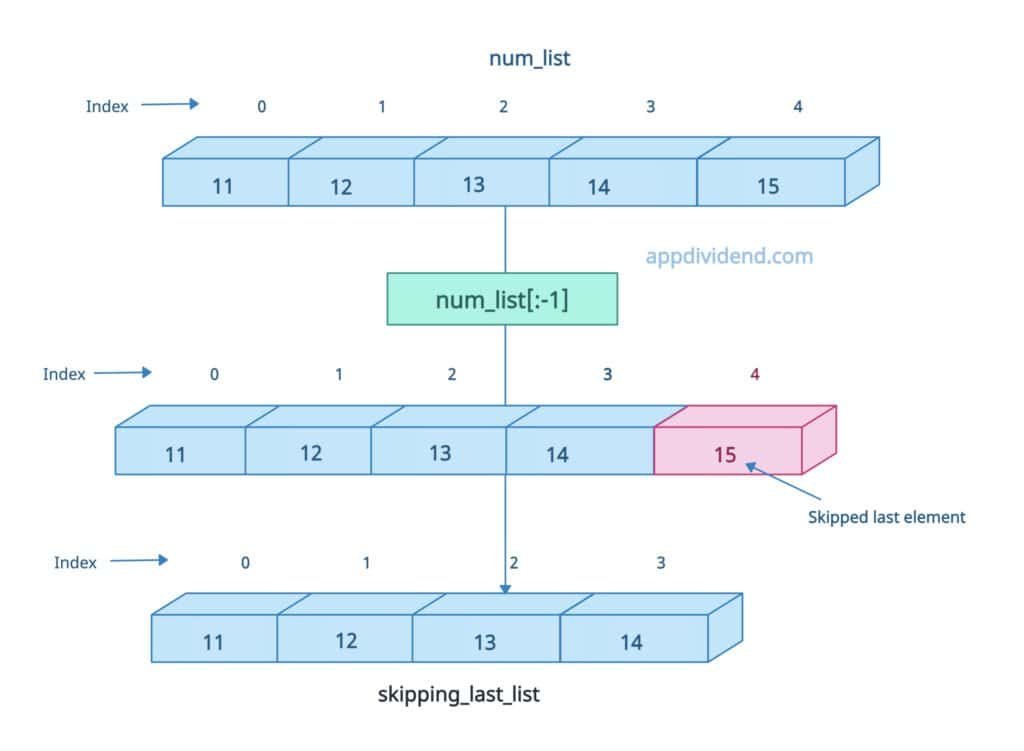
Using slicing, we can skip the first and last elements.
For skipping the first element, use list[1:].
For skipping the last element, use list[:-1].
num_list = [11, 12, 13, 14, 15] print(num_list) # Output: [11, 12, 13, 14, 15] skipping_first_list = num_list[1:] print(skipping_first_list) # Output: [12, 13, 14, 15] skipping_last_list = num_list[:-1] print(skipping_last_list) # Output: [11, 12, 13, 14]
Empty list
When your input list is empty, no matter which of the methods mentioned above you use, it returns an empty list without any error.
empty_list = [] print([x for x in empty_list if x != 5]) # Output: [] print(list(filter(lambda x: x != 5, empty_list))) # Output: [] print(empty_list[::2]) # Output: []
Even if your input list contains only a single element and you skip it, the output will still be an empty list.
That’s all!