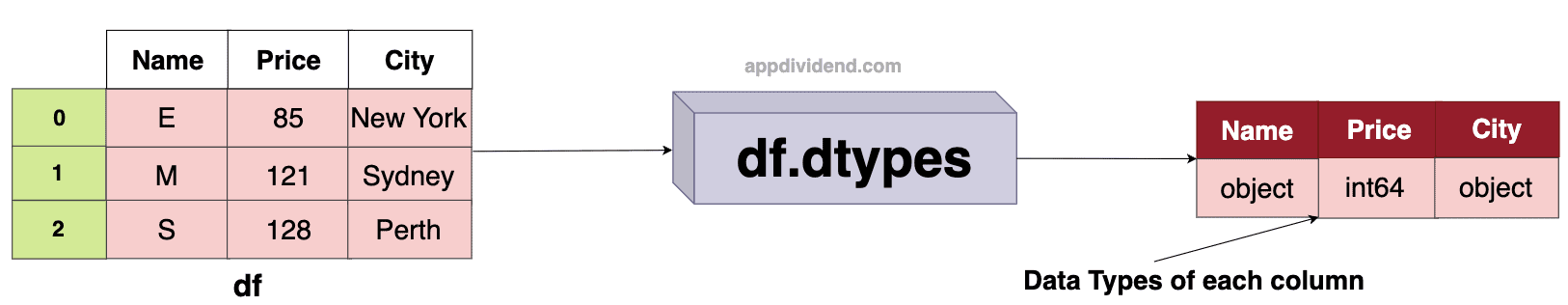
The easiest way to get the column type of a Pandas DataFrame is by using the “.dtypes” attribute. The “dtypes” attribute returns a Series with the data type of each column.
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ["E", "M", "S"],
'Price': [85, 121, 128],
'City': ['New York', 'Sydney', 'Perth']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.dtypes)
Output
As shown in the above figure, the Name and City columns are of type string, which is denoted in Pandas as “object”. The price is a numeric column, so it has a type “int64”.
Get the data type of a specific column
If you want to get the data type of a specific column of a DataFrame, use this syntax: df[‘column_name’].dtype.
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ["E", "M", "S"],
'Price': [85, 121, 128],
'City': ['New York', 'Sydney', 'Perth']}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df['Price'].dtype) # int64
Output
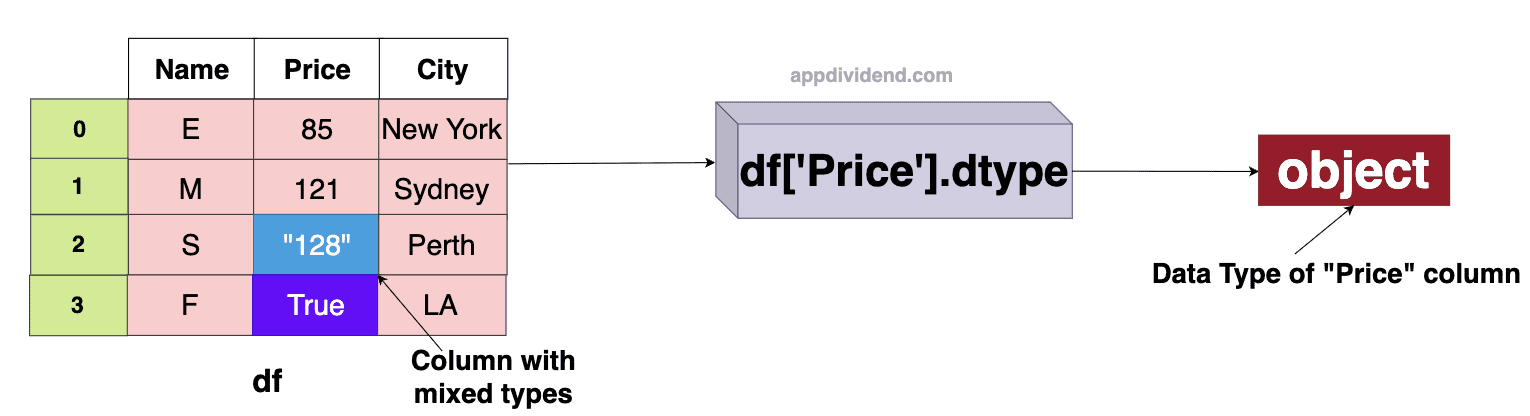
Getting the type of mixed values
If a column of a DataFrame contains mixed values (mixed data type values), the “.dtype” attribute will return “object” as an output.
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ["E", "M", "S", "F"],
'Price': [85, 121, "128", True],
'City': ['New York', 'Sydney', 'Perth', "LA"]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df['Price'].dtype) # object
Output
Common data types in Pandas
| Data Types | Description |
| object | It is a text or a combination of numeric and non-numeric values. |
| int64 | It is a type of integer number. |
| float64 | It is a type of floating-point number. |
| bool | It is a type for Boolean (True or False) values. |
| datetime64 | It is a type for date and time values. |
| category | It is a data type for categorical values. |
Alternate approach
There is an alternative approach to get the data type of a column, using the “DataFrame.info()” method. This method basically returns a concise summary of the DataFrame‘s structure.
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name': ["E", "M", "S", "F"],
'Price': [85, 121, "128", True],
'City': ['New York', 'Sydney', 'Perth', "LA"]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.info())
Output
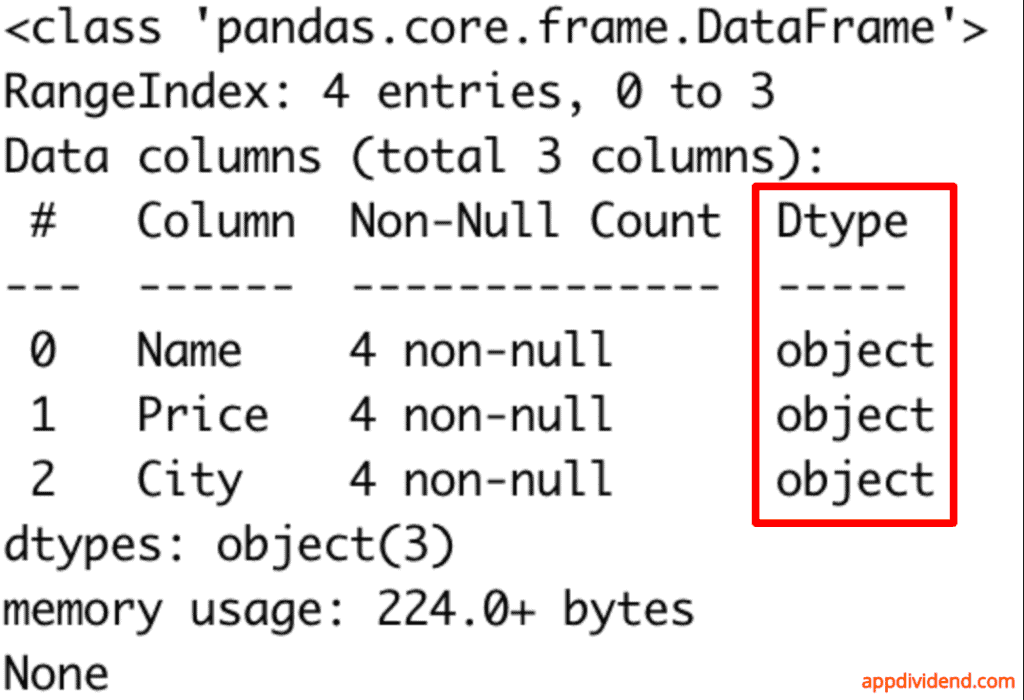
In the above screenshot, you can see that it returns the “Dtype” column, which contains the type of each column.
It provides a concise overview of the DataFrame’s structure and displays the data types for all columns simultaneously.
Apart from column types, it also returns “index”, “column name”, “non-null”, and “count”. Also, returns memory usage.