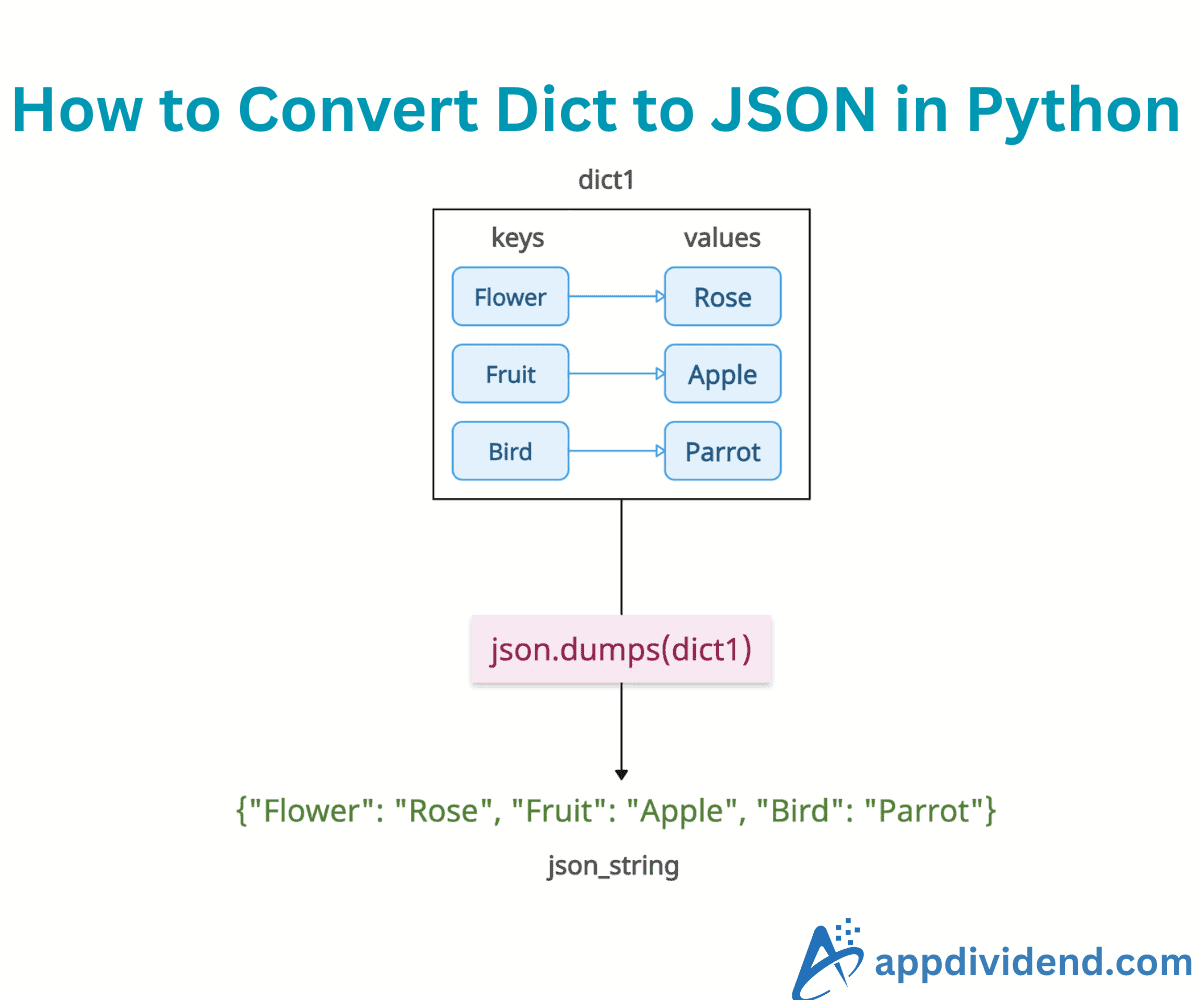
To convert a dictionary to a JSON string in Python, use the built-in json.dumps() method. If you want to write a json file, use the json.dump() method.
As you can see from the above picture, the json.dumps() method accepts a dictionary as input and converts it into a JSON-formatted string.
import json
app_dict = {
'name': 'messenger',
'playstore': True,
'company': 'Meta',
'price': 100
}
print(app_dict)
# Output: {'name': 'messenger', 'playstore': True, 'company': 'Meta', 'price': 100}
print(type(app_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
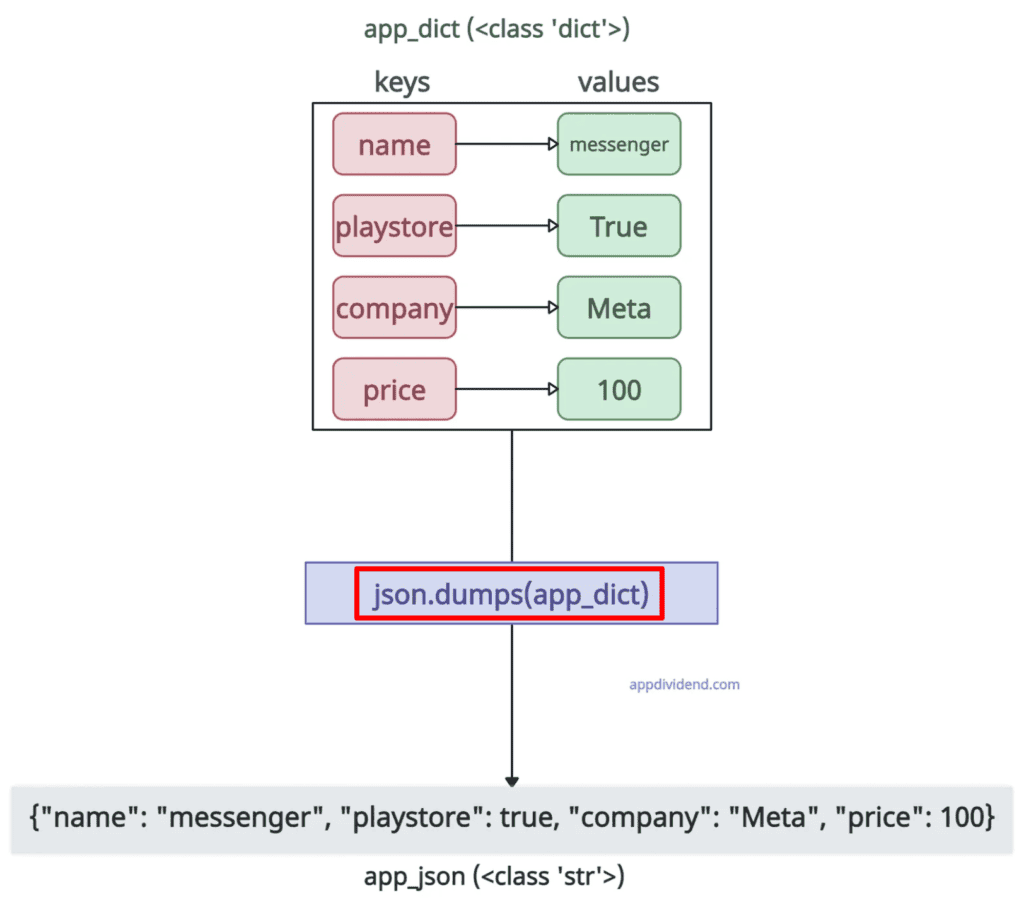
app_json = json.dumps(app_dict)
print(app_json)
# Output: {"name": "messenger", "playstore": true, "company": "Meta", "price": 100}
print(type(app_json))
# Output: <class 'str'>
If you analyze the output carefully, you can see that the Keys and string values are quoted; numbers and booleans are not.
Using a Nested Dictionary
If the input is a nested dictionary, it will create a json string with the same level of nesting.
import json
nested_app_dict = {
'app_info': {
'name': 'messenger',
'playstore': True
},
'company_info': {
'company_name': 'Meta',
'price': 100
}
}
print(nested_app_dict)
# Output:
# {'app_info': {'name': 'messenger', 'playstore': True},
# 'company_info': {'company_name': 'Meta', 'price': 100}}
print(type(nested_app_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
app_json = json.dumps(nested_app_dict, indent=3)
print(app_json)
# Output:
# {
# "app_info": {
# "name": "messenger",
# "playstore": true
# },
# "company_info": {
# "company_name": "Meta",
# "price": 100
# }
# }
print(type(app_json))
# Output: <class 'str'>
While using json.dumps(), we passed indent = 3 argument for pretty-print json, which improves the readability of the JSON output, especially for nested structures.
Sorting Keys
import json
app_dict = {
'name': 'messenger',
'playstore': True,
'company': 'Meta',
'price': 100
}
print(app_dict)
# Output: {'name': 'messenger', 'playstore': True, 'company': 'Meta', 'price': 100}
print(type(app_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
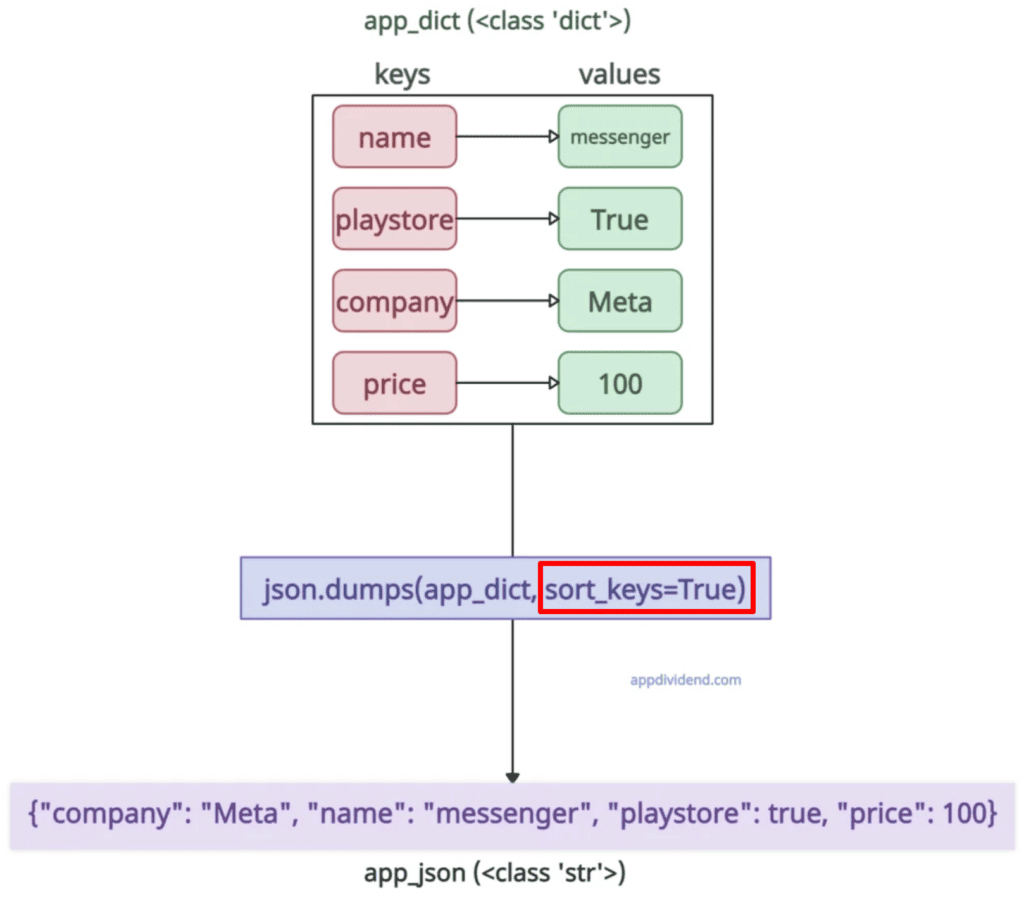
app_json = json.dumps(app_dict, sort_keys=True)
print(app_json)
# Output: {"company": "Meta", "name": "messenger", "playstore": true, "price": 100}
print(type(app_json))
# Output: <class 'str'>
Dict to JSON Array
If you want to convert a dictionary to a JSON array, you first need to create a list using list comprehension, where each element is a dictionary containing one key-value pair from the original dictionary, and then use the json.dumps() method to convert it.
import json
app_dict = {
'name': 'messenger',
'playstore': True,
'company': 'Meta',
'price': 100
}
print(app_dict)
# Output: {'name': 'messenger', 'playstore': True, 'company': 'Meta', 'price': 100}
print(type(app_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
arr = [{x: app_dict[x]} for x in app_dict]
app_json_arr = json.dumps(arr, indent=3)
print(app_json_arr)
# Output:
# [
# {
# "name": "messenger"
# },
# {
# "playstore": true
# },
# {
# "company": "Meta"
# },
# {
# "price": 100
# }
# ]
print(type(app_json_arr))
# Output: <class 'str'>
Writing a dictionary into a file in JSON string
You use the json.dump() method to write the dictionary to the file in JSON format.
The “with statement” context manager ensures the file is properly handled and closed after writing.
import json
app_dict = {
'name': 'messenger',
'playstore': True,
'company': 'Meta',
'price': 100
}
print(app_dict)
# Output: {'name': 'messenger', 'playstore': True, 'company': 'Meta', 'price': 100}
print(type(app_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
with open('app.json', 'w') as json_file:
json.dump(app_dict, json_file)
print("Dictionary has been successfully written to JSON File")
# Output: Dictionary has been successfully written to JSON File
Here is the written app.json file:
That’s all!



Hannah Dean
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
In [34]:
Line 116: jsonData = json.loads(ms_json)
AttributeError: ‘bytes’ object has no attribute ‘loads’
is this a common issue
Forhave
This is a great tutorial on how to convert a dictionary to JSON. I have used this technique before to convert a dictionary of user data into a JSON object.