Python list pop() method removes an element at the specified index and returns the removed element. It is an in-place operation that does not create a new list.

main_list = [10, 20, 30, 40] popped_element = main_list.pop() # Removes and returns 40 print(popped_element) # Output: 40 print(main_list) # Output: [10, 20, 30]
In this code, the pop() method returns the removed element 40. The original list has been modified to contain only three elements.
If the index passed to the pop() method is not in the range or does not exist in the list, it throws the IndexError: pop index out of range exception.
Syntax
list.pop(index)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| index (optional, index) | It is the position where we need to remove the element from the list. If you don’t pass the index, then by default, the pop() function will remove the last element, whose index would be -1. |
Removing at a specific positive index
Let’s remove a specific element with the help of the index argument.
main_list = [10, 20, 30, 40] popped_at_1 = main_list.pop(1) # Removes and returns 20 print(popped_at_1) # Output: 20 print(main_list) # Output: [10, 30, 40]
In this code, we remove element 20 at index 1 and return it. It shifted subsequent elements left.
Removing an element from the beginning
To remove the first element, pass the index 0.
main_list = [10, 20, 30, 40] first_element = main_list.pop(0) # Removes and returns 10 print(first_element) # Output: 10 print(main_list) # Output: [20, 30, 40]
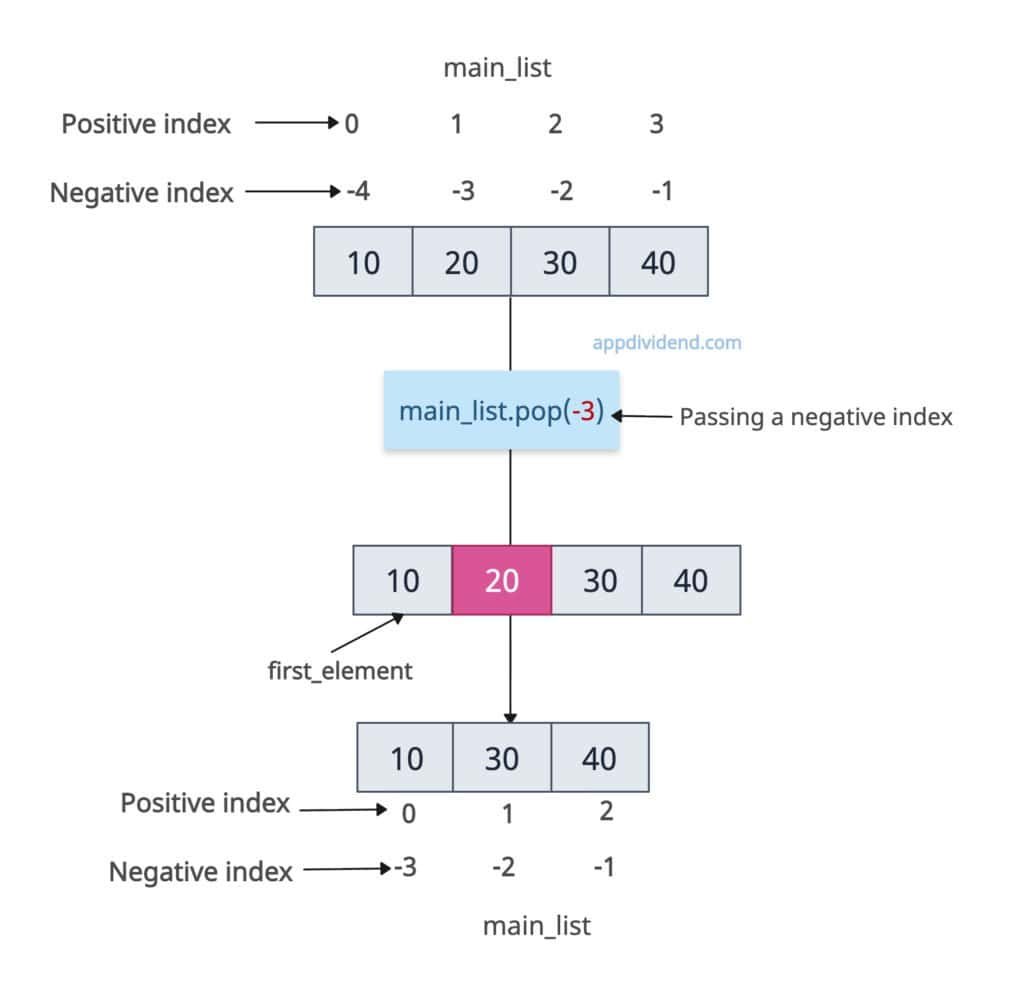
Pop with negative Index
Negative indices count from the end (-1 is last, -2 is second-to-last).
main_list = [10, 20, 30, 40] backward_element = main_list.pop(-3) print(backward_element) # Output: 20 print(main_list) # Output: [10, 30, 40]
Pop from an empty list
If the list is empty and you try to remove an element from it, it will raise an IndexError: pop from empty list exception.
empty_list = []
try:
empty_list.pop()
except IndexError as e:
print(e)
# Output: pop from empty list
Always check if the list is non-empty before popping to avoid IndexError.
IndexError: Index Out of Range
If the index is outside of 0 <= index < len(list), it will throw IndexError: Index Out of Range exception.
small_list = [5]
try:
small_list.pop(1)
except IndexError as e:
print(e)
# Output: pop index out of range
To prevent this type of error, validate indices beforehand.
Comparison with remove() and del
The main difference between remove(), del, and pop() is that the remove() function targets values, the del keyword targets indices without returning, contrasting with pop()’s index-based removal and return.
main_list = [1, 2, 3, 2] removed = main_list.remove(2) # Removes first 2, returns None print(removed) # Output: None print(main_list) # Output: [1, 3, 2] del main_list[0] # Removes 1, no return print(main_list) # Output: [3, 2] popped = main_list.pop(1) print(main_list) # Output: [3] print(popped) # Output: 2
That’s all!