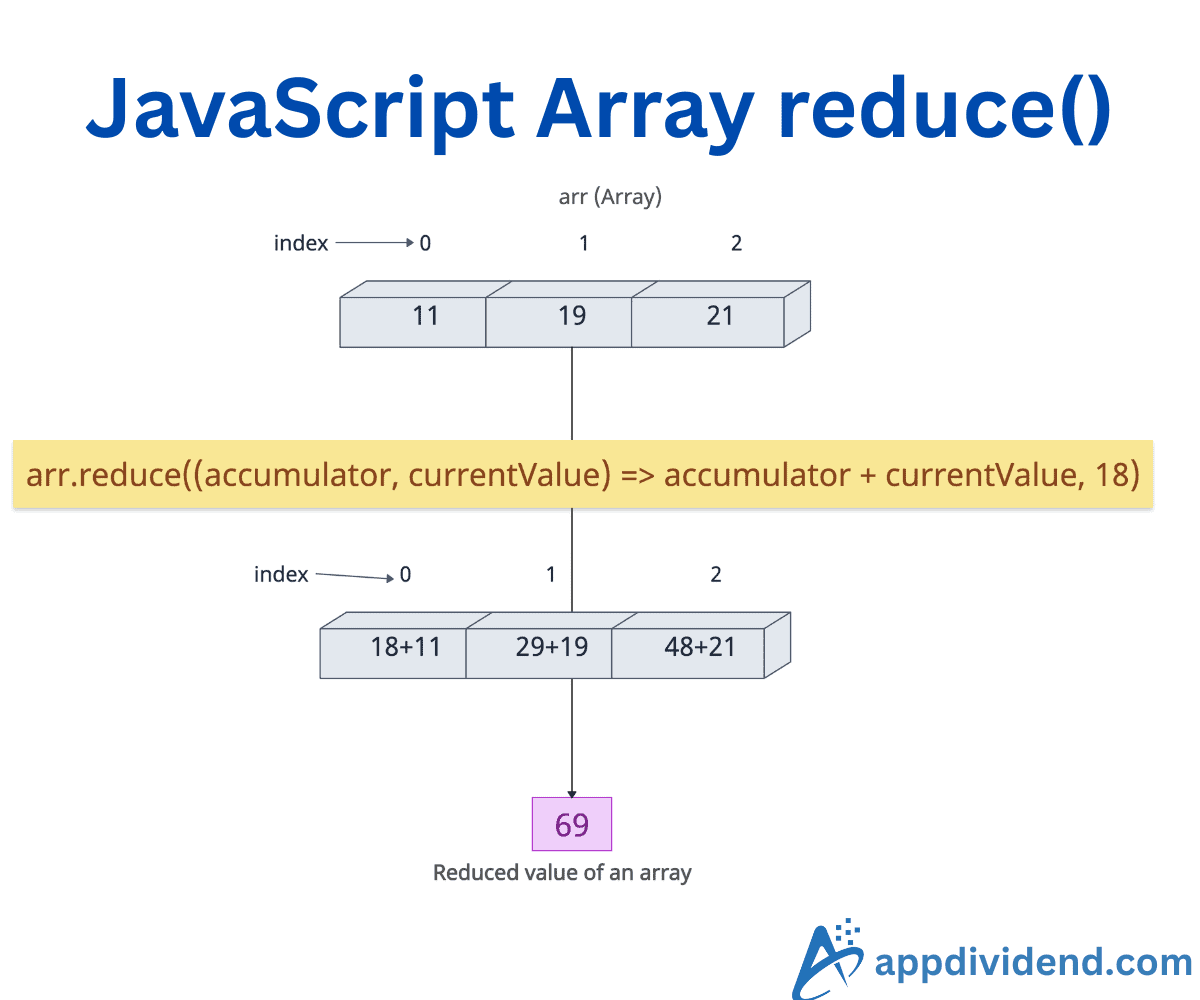
JavaScript array.reduce() method executes a provided reducer callback function on each element of the array, in ascending index order, to produce a single output value. It accumulates the callback’s return values sequentially, starting from an initial value (if provided) or the first element of the array.
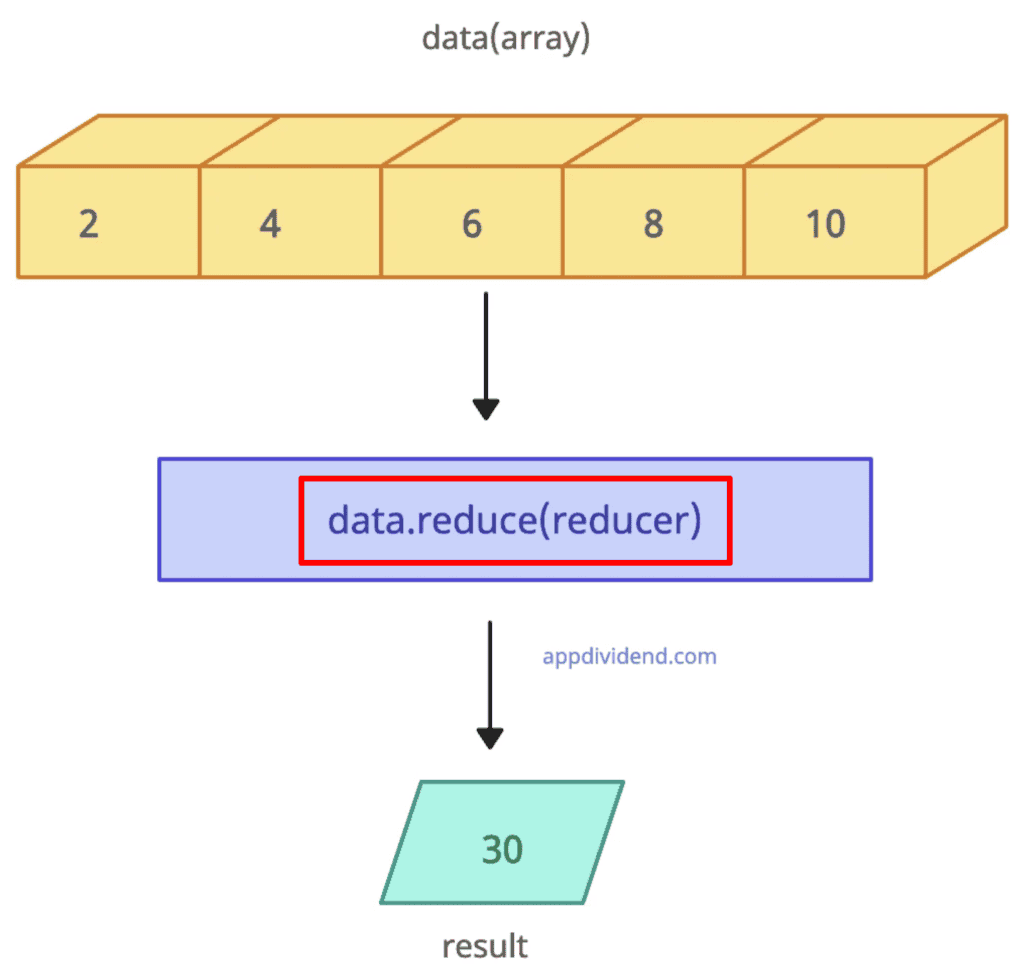
data = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue result = data.reduce(reducer) console.log(result) // Output: 30
Let’s see a descriptive table showing what happens on each iteration.
| callback iteration | accumulator | currentValue | currentIndex | array | return value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| first call | 2 | 4 | 1 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 6 |
| second call | 6 | 6 | 2 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 12 |
| third call | 12 | 8 | 3 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 20 |
| fourth call | 20 | 10 | 4 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 30 (output) |
The output value is 30, which is the reduced value of the input array.
Syntax
array.reduce(function(accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, arr), initialValue)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| function (required) |
It represents a reducer function that executes on each element of the array. It has four arguments.
|
| initialValue (optional) | It represents the value to use as the first accumulator value.
If you omit the initialValue, the accumulator starts as an array[0]. |
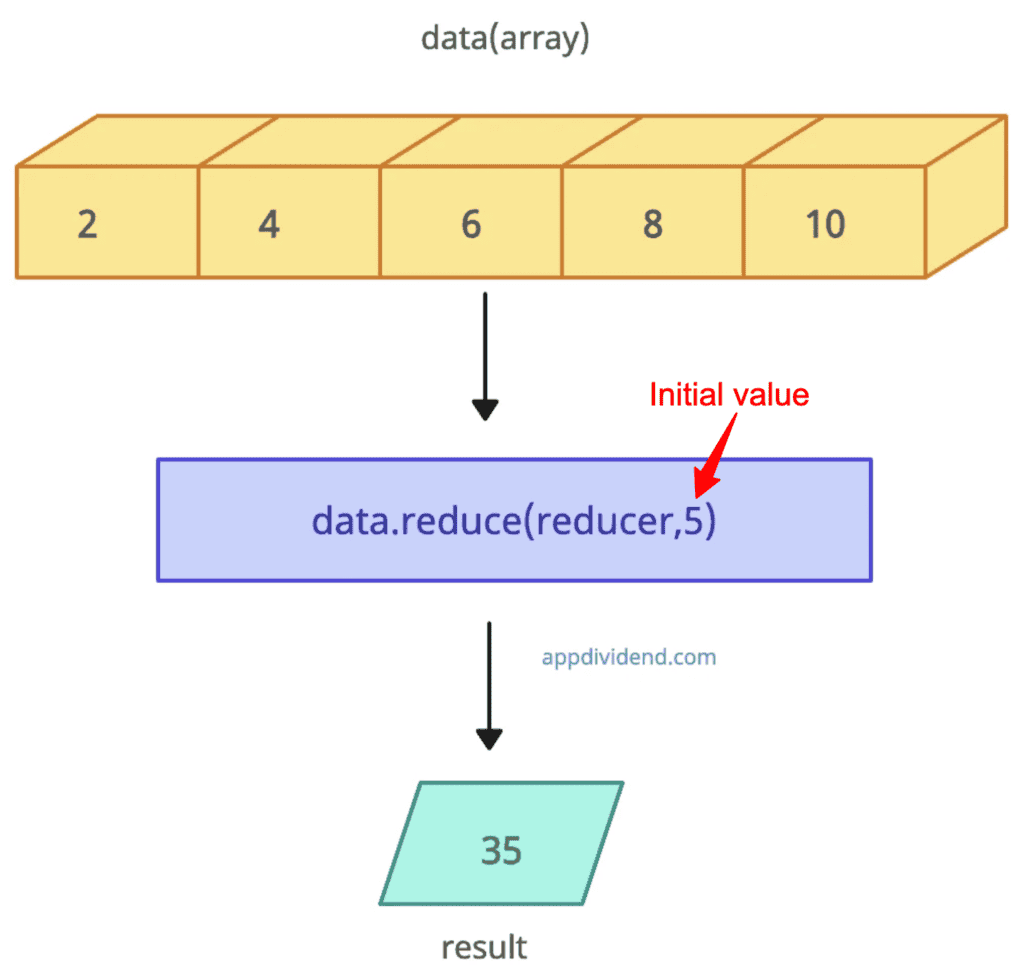
Providing an initial value
When you provide an initialValue via an argument, it serves as the first element, followed by a reduction process.
data = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue result = data.reduce(reducer, 5) console.log(result) // Output: 35
Here is the table that defines the iterative process:
| callback iteration | accumulator | currentValue | currentIndex | array | return value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| first call | 5 | 2 | 0 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 7 |
| second call | 7 | 4 | 1 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 11 |
| third call | 11 | 6 | 2 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 17 |
| fourth call | 17 | 8 | 3 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 25 |
| fifth call | 25 | 10 | 4 | [2, 4, 6, 8, 10] | 35 |
Flattening arrays
Array.reduce() function provides a way to collapse a multidimensional array into a single dimension (1D).
const data = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]];
const flatValues = data.reduce((total, value) => {
return total.concat(value);
}, []);
console.log(flatValues);
// Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
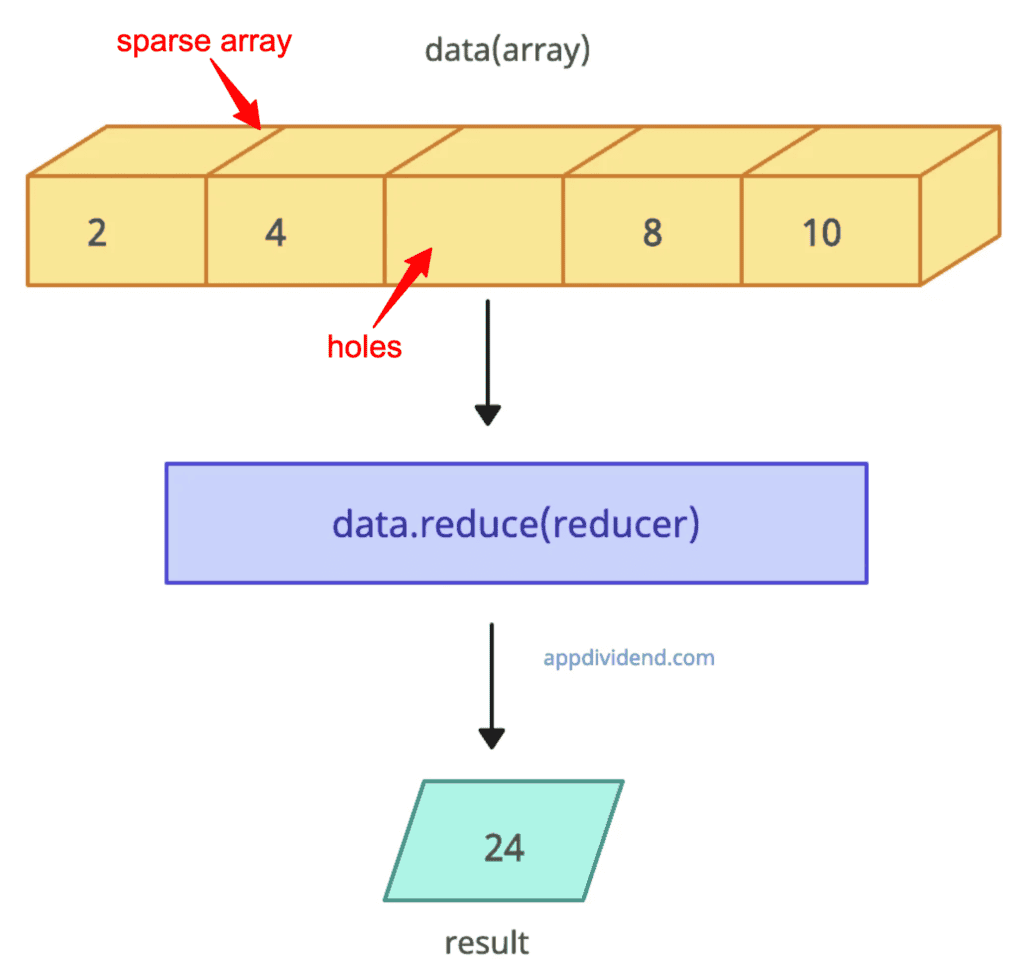
Using a sparse array
If the array is sparse (containing holes), the reduce() overlooks them and runs the reducer function on the remaining available values.
data = [2, 4, , 8, 10] const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue result = data.reduce(reducer) console.log(result) // Output: 24
Array contains an “undefined” value
An “undefined” value in the array causes the reduction to yield NaN, as we lack understanding of what undefined represents, resulting in NaN.
data = [2, 4, undefined, 8, 10] const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue result = data.reduce(reducer) console.log(result) // Output: NaN
Empty array without an initial value
Attempting to reduce an empty array without specifying an initial value results in a TypeError: Reduce of empty array with no initial value.
empty_arr = [] const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue result = empty_arr.reduce(reducer) console.log(result) // TypeError: Reduce of empty array with no initial value
To prevent this type of error, always provide an initialValue if the array might be empty.
Single element without an initial value
When you attempt to reduce an array of one element without an initial value, it simply returns the element, as no other reduction is applicable.
single = [21] const reducer = (accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue result = single.reduce(reducer) console.log(result) // Output: 21
That’s all!