The JavaScript array push() method adds single or multiple elements at the end of the array. This method modifies the original array and returns the length of the modified array.
data = ['Python', 'Javascript', 'PHP']
element = 'Golang'
len = data.push(element)
console.log('The modified array is: ', data)
// Output: The modified array is: [ 'Python', 'Javascript', 'PHP', 'Golang' ]
console.log('The length of modified array is: ', len)
// Output: The length of modified array is: 4
The push() is not a pure function because it directly modifies the original array.
If you want to add elements without modifying the input array, use the array.concat(), which is also a pure function.
Syntax
array.push(element1, element2,...,elementN)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| element1, element2 | It represents one or more elements that need to be appended at the end of the array.
It can be of any data type, including numbers, strings, objects, arrays, or undefined. |
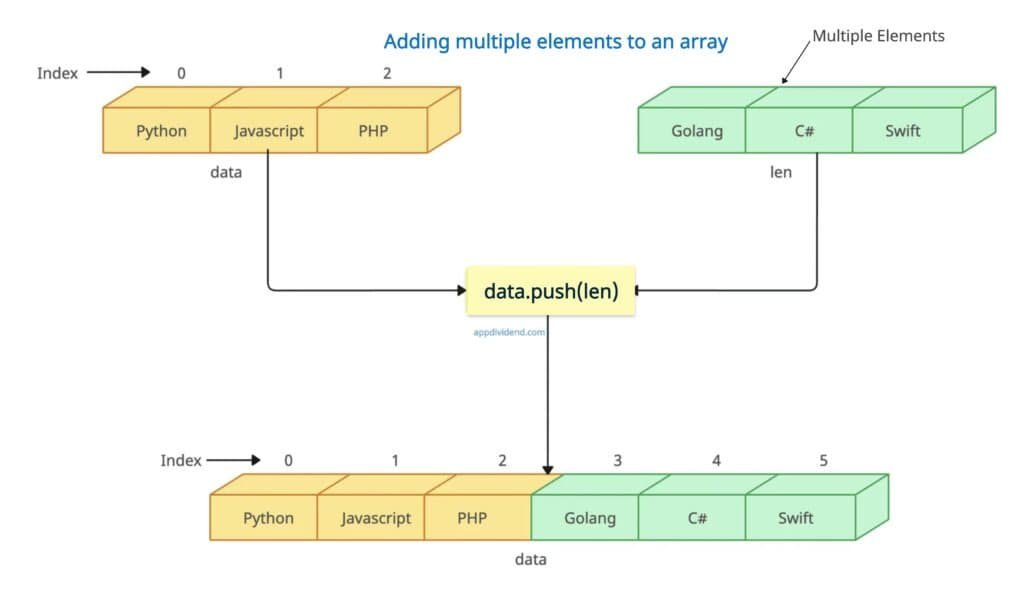
Adding multiple elements
Pass the multiple elements to the push() function you want to append to the end of the array without using any loop. It will append in the order they are pushed.
data = ['Python', 'Javascript', 'PHP']
len = data.push('Golang', 'C#', 'Swift')
console.log('The modified array is: ', data)
// Output: The modified array is: [ 'Python', 'Javascript', 'PHP', 'Golang', 'C#', 'Swift' ]
console.log('The length of modified array is: ', len)
// Output: The length of modified array is: 6
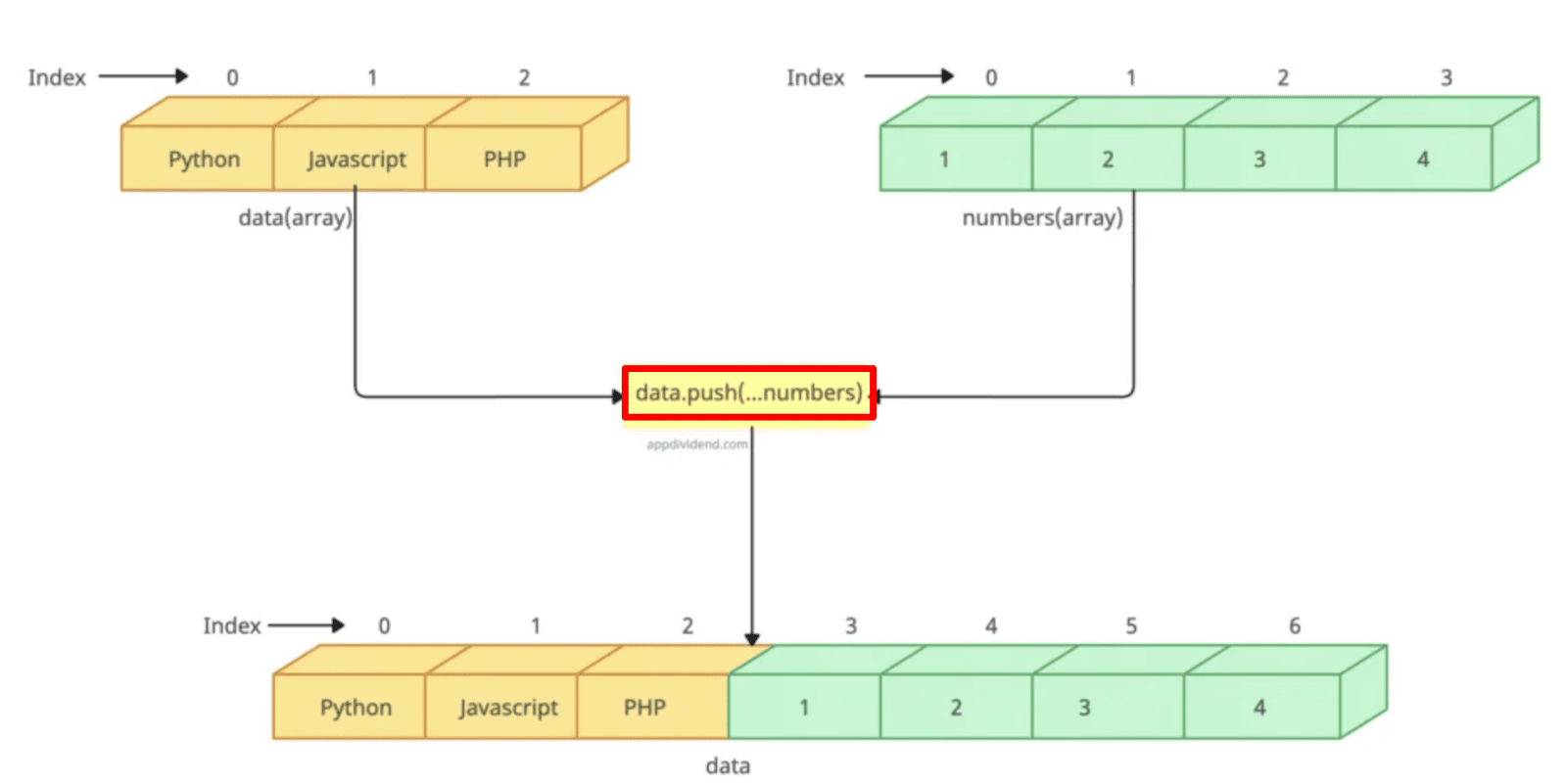
Appending elements of an array to another array
You can use the spread(…) operator with the push() to append elements of an array to another array.
let data = ["Python", "Javascript", "PHP"]; let numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4]; data.push(...numbers) console.log(data) // Output: ["Python", "Javascript", "PHP", 1, 2, 3, 4]
You can see the elements of the numbers array are appended to the end of the data array.
Adding different data types
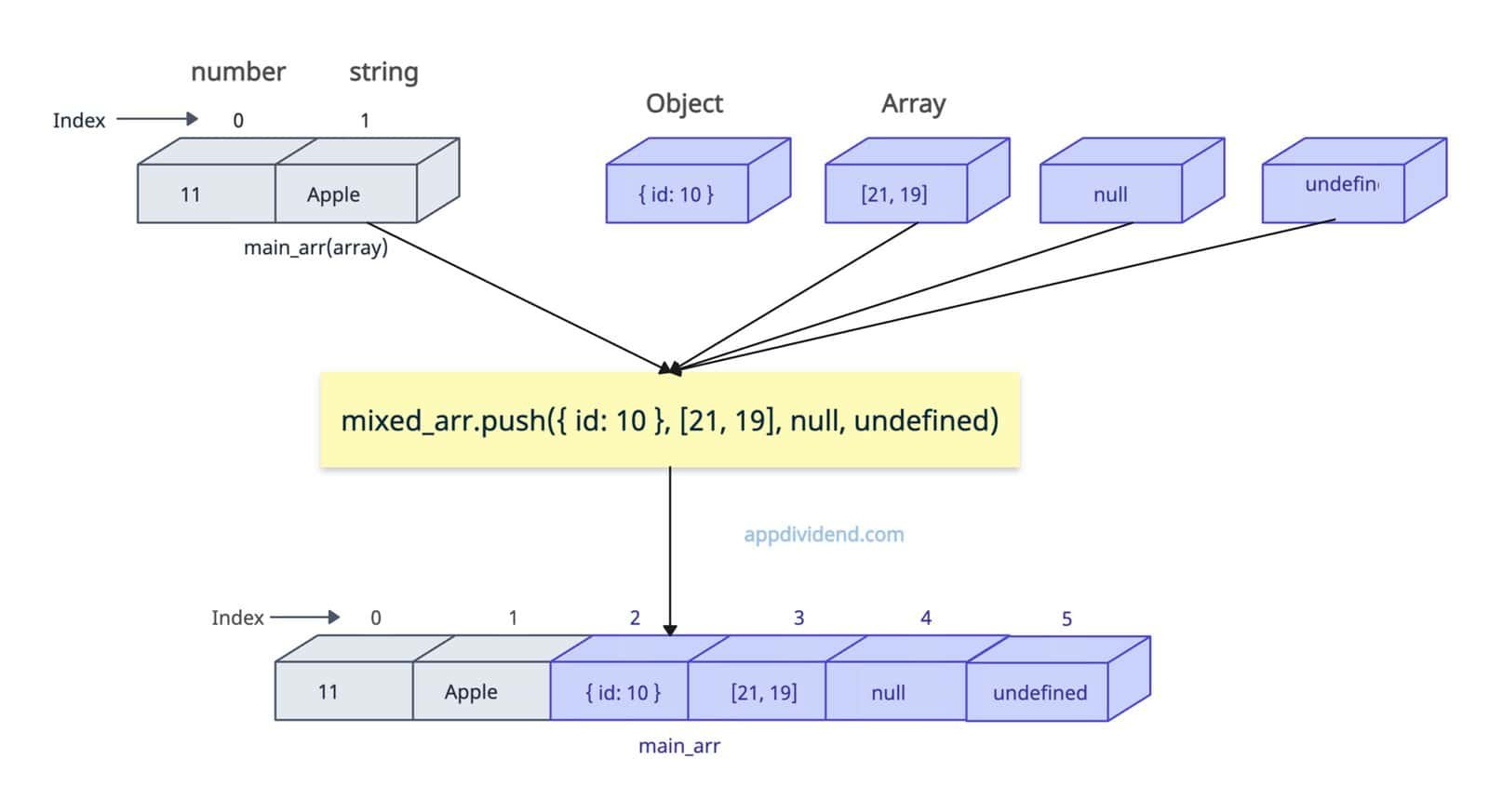
let mixed_arr = [11, 'Apple'];
mixed_arr.push({ id: 10 }, [21, 19], null, undefined);
console.log(mixed_arr);
// Output: [ 11, 'Apple', { id: 10 }, [ 21, 19 ], null, undefined ]
You can see that the input array has integer and string types, and we are trying to add an object, an array, an integer, null, and undefined.
The output modified array has each type of element without any error.
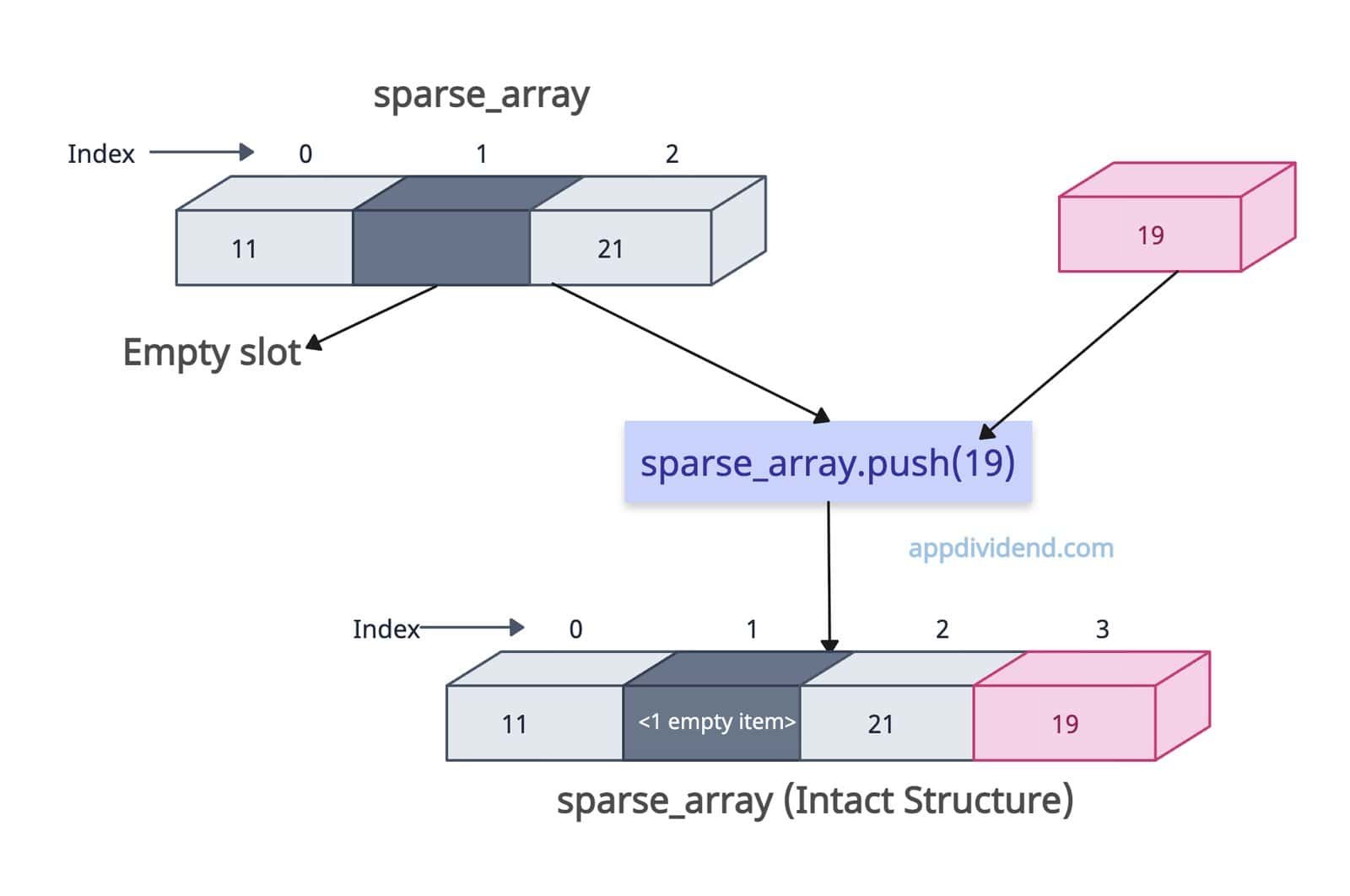
Sparse arrays
In JavaScript, a sparse array is an array where elements do not occupy contiguous indices starting from zero, resulting in “holes” or “empty slots” within the array.
let sparse_array = [11, , 21]; sparse_array.push(19); console.log(sparse_array); // Output: [ 11, <1 empty item>, 21, 19 ] console.log(sparse_array.length); // 4
The above output shows that the push() method preserves the sparse structure and adds an element at the end of the array. In the output, <1 empty item> is that empty slot.
Empty array
If the input array is empty and you add a single element, it will be appended at index 0 since there were no elements.
let empty_array = [];
let length = empty_array.push('Amazon');
console.log(empty_array);
// Output: [ 'Amazon' ]
console.log(length);
// Output: 1
Since there is only one element in the array, it returns a length of 1.
No arguments
If you have an array of length 4 and you are using the .push() method without any arguments, it will return the same length and does not modify the array.
let main_array = [true, false]; let length = main_array.push(); console.log(main_array); // Output: [ true, false ] console.log(length); // Output: 2
Array-like Objects
You can apply the push() method to array-like objects using call() or apply(), updating their length and adding indexed properties.
let arrayLikeObject = {
0: 'Python',
1: 'Javascript',
2: 'PHP',
length: 3
};
Array.prototype.push.call(arrayLikeObject, 'Golang', 'C#');
console.log(arrayLikeObject);
// Output:
// {
// '0': 'Python',
// '1': 'Javascript',
// '2': 'PHP',
// '3': 'Golang',
// '4': 'C#',
// length: 5
// }
We have successfully added ‘Golang‘ and ‘C#‘ to your array-like object, and the length property has also been updated to 5.
TypeError: data.push is not a function
The push() method is specifically designed for the Array and not Object or other types. If you attempt to use the .push() function on an Object, it will throw an error like this: TypeError: data.push is not a function
let obj = {};
try {
obj.push('test');
} catch (e) {
console.log(e.message);
}
// Output: obj.push is not a function
To prevent this type of error, you should use non-array objects with call() or apply() methods.




muavia haidry
Usefull post
thank you soo much