To sort a list alphabetically in Python, use either the list.sort() or sorted() method. It allows us to arrange string elements in lexicographic order (dictionary order), either ascending (A–Z) or descending (Z–A).
Method 1: Using a list.sort()
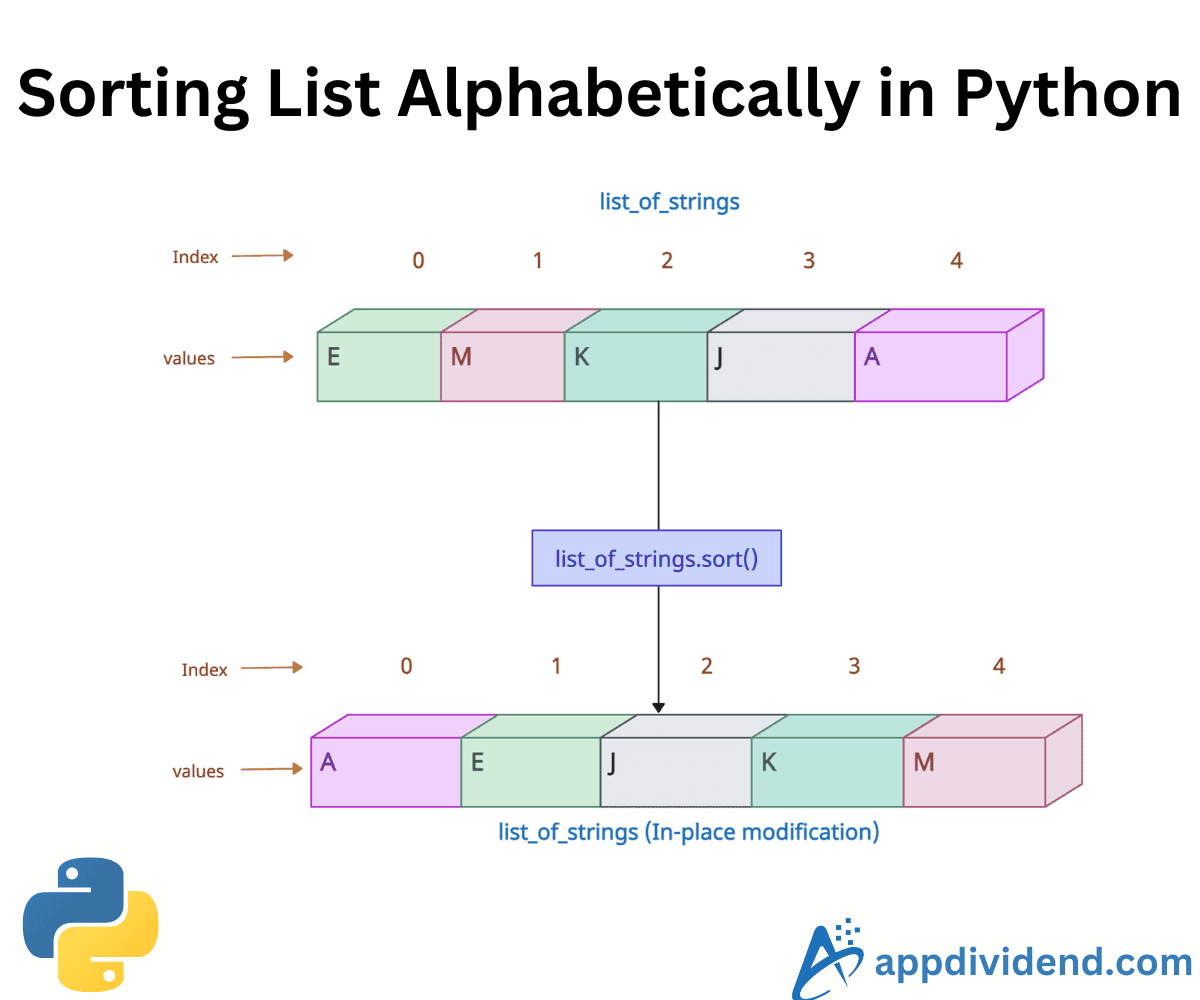
The list.sort() method sorts the list ascending by default and modifies the list in-place. It does not return any value because it is None.
list_of_strings = ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] print(list_of_strings) # Output: ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] list_of_strings.sort() print(list_of_strings) # Output: ['Atreus', 'Elle', 'Joel', 'Kratos', 'Miles']
Reverse alphabetical order
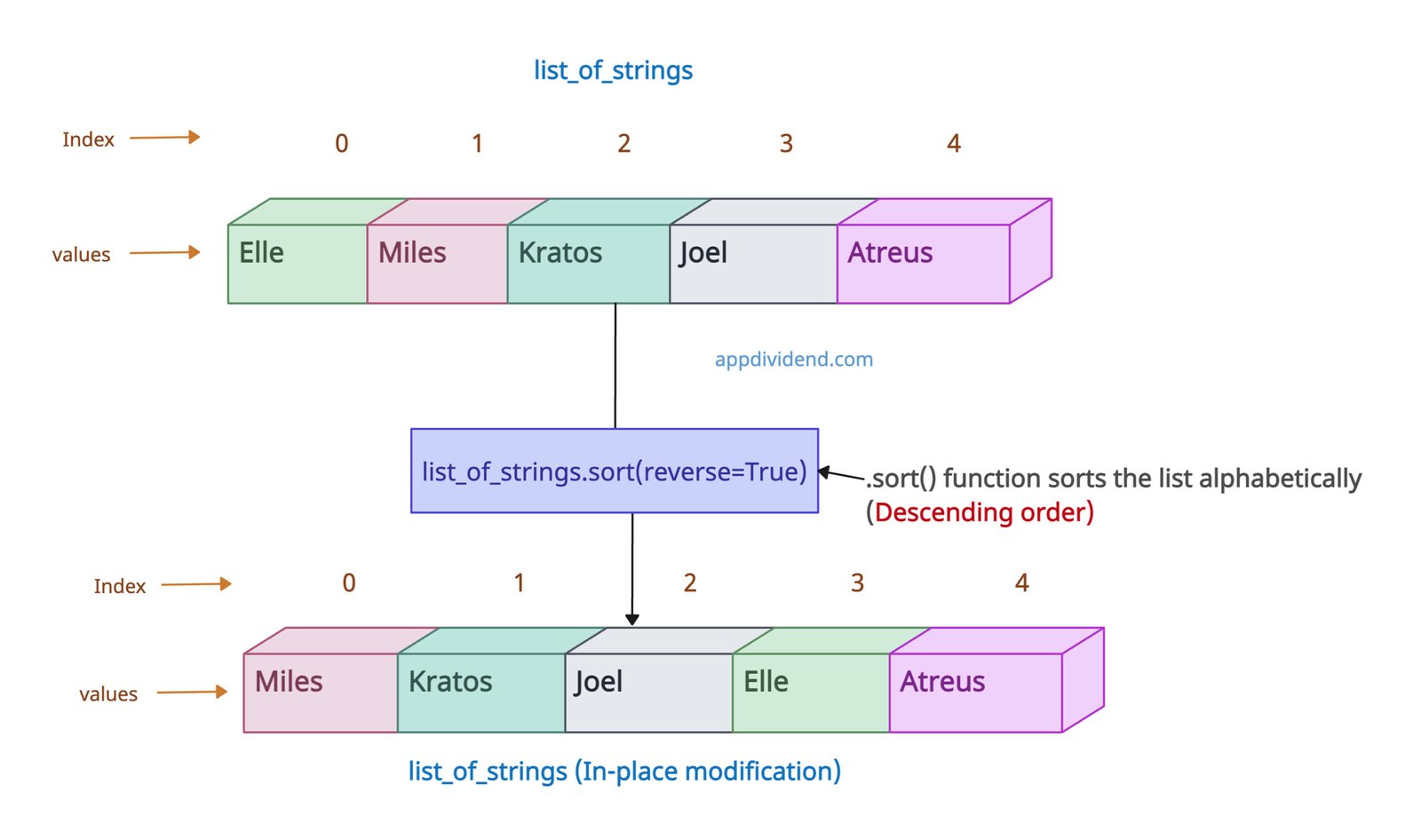
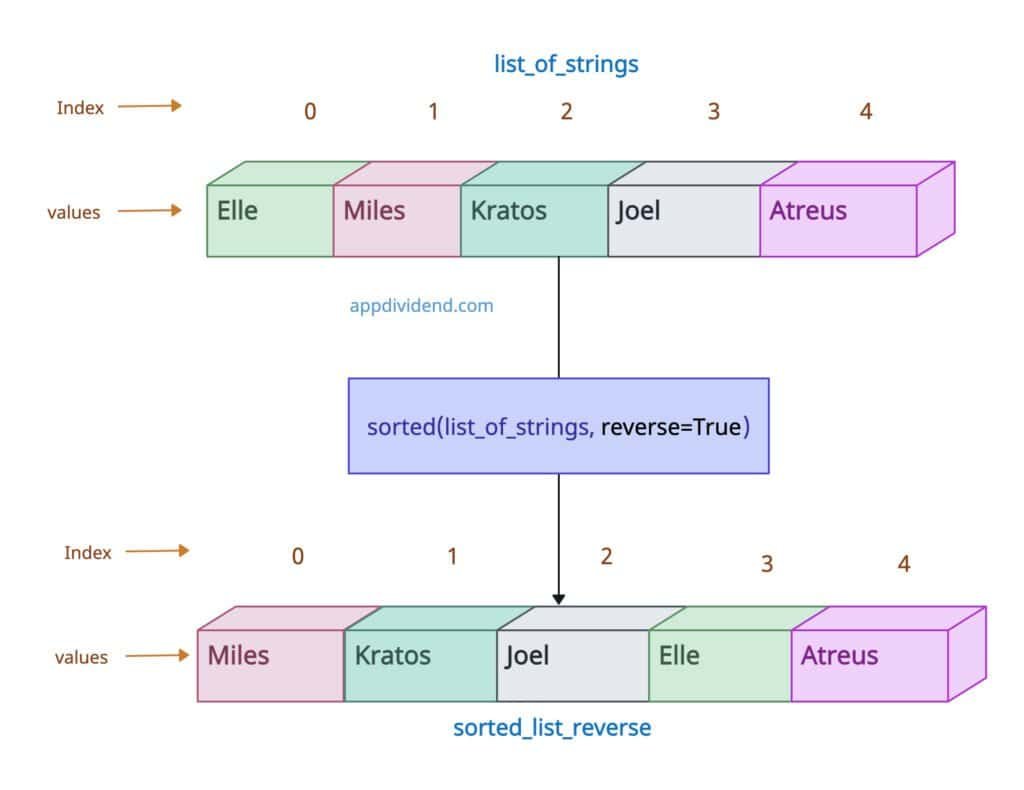
To sort our list in reverse alphabetical (descending) order, pass the “reverse = True” argument.
list_of_strings = ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] print(list_of_strings) # Output: ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] list_of_strings.sort(reverse=True) print(list_of_strings) # Output: ['Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Elle', 'Atreus']
The above output shows that we are reversing the order of the Ascending sorting, which is descending.
Empty list
If the list is empty, there is nothing to sort, so it returns an empty list too.
empty_list = [] empty_list.sort() print(empty_list) # Output: []
Method 2: Using sorted()
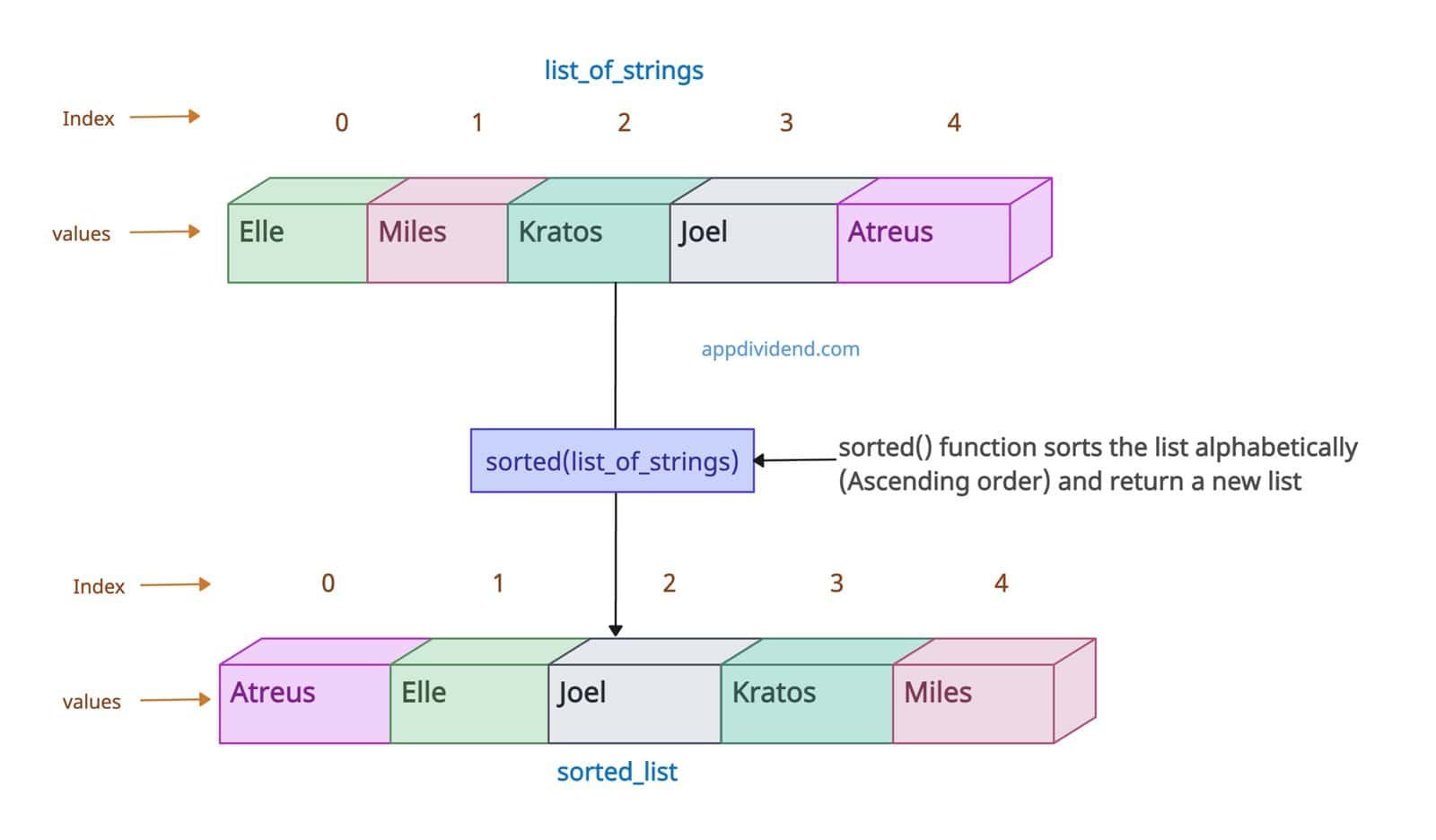
The sorted() function returns a new sorted list in ascending order by default. It does not modify an original list.
list_of_strings = ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] print(list_of_strings) # Output: ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] sorted_list = sorted(list_of_strings) print(sorted_list) # Output: ['Atreus', 'Elle', 'Joel', 'Kratos', 'Miles']
Sorting in descending order
To reverse the default order, we need to pass reverse=True to the sorted() function.
list_of_strings = ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] print(list_of_strings) # Output: ['Elle', 'Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Atreus'] sorted_list_reverse = sorted(list_of_strings, reverse=True) print(sorted_list_reverse) # Output: ['Miles', 'Kratos', 'Joel', 'Elle', 'Atreus']
Lexicographical order
The sorted() function is case-sensitive, but what if all strings begin with the uppercase ‘A’? How will it sort then? Well, that’s where lexicographic (dictionary) order comes into the picture.
The sorted() function sorts the list of strings by comparing strings character by character from left to right.
If all names start with ‘A’, the sorting will continue to the second character. If the second character is also the same, it will begin processing the third character and so on.
names = ["Anne", "Alok", "Alex", "Aimee"] print(sorted(names)) # Output: ['Aimee', 'Alex', 'Alok', 'Anne']
Here,
- “i” in Aimee → ASCII 105
- “l” in Alex, Alok → ASCII 108
- “n” in Anne → ASCII 110
So the actual alphabetical order is: “Aimee” < “Alex” < “Alok” < “Anne”.
Sorting with mixed cases
What if you have two strings with the same value in the list, but one is in lowercase and the other’s first character is uppercase? How will it sort then?
In this case, the priority will be to the string with the first uppercase letter. After sorting all the strings with uppercase, it will start searching for lowercase.
You can think of it as the priority will be from A-Z, and then a-z will be counted.
netflix = ["Wednesday", "ozark", "Ozark"] print(sorted(netflix)) # Output: ['Ozark', 'Wednesday', 'ozark']
In this code, since Ozark’s first character “O” is uppercase, it is the first element. Then, it encounters the word “W”, which appears after “o”, but since “o” is in lowercase, it is not included. Instead, it only includes words with uppercase letters first, followed by lowercase letters.
That’s it!