A Python dictionary contains keys and values, and when you want to convert it to a numpy array, you need to make sure what type of array you need. For example, you can create an array of either keys or values, or create a 2D array of key-value pairs.
Here are three main ways to convert a dictionary to a numpy array:
- Dictionary keys to a 1D numpy array
- Converting Dictionary values to a 1D numpy array
- Converting key-value pairs to a structured 2D array
Method 1: Dictionary keys to 1D numpy array
For extracting keys as a list from a dictionary, use the list(dict.keys()) method and pass this list to the numpy.array() method that returns an array of keys as an output.
import numpy as np
dict = {'k': 2.1, 'b': 1.9, 'l': 10.0}
print(dict)
# Output" {'k': 2.1, 'b': 1.9, 'l': 10.0}
print(type(dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
keys_array = np.array(list(dict.keys()))
print(keys_array)
# Output: ['k' 'b' 'l']
print(type(keys_array))
# Output: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
In this code, we went step by step. First, we extracted keys using a dict.keys() method and converted into the list using list() method. Finally, pass the list to the np.array() method to get an array.
The output 1D array shows only the dictionary’s keys. We verified the data type using the type() method.
Method 2: Dictionary values to 1D numpy array
You can use the list(dict.values()) function to convert a dictionary’s values to a list and then pass that list to the np.array() method to create an array out of it.
import numpy as np
dict = {'k': 2.1, 'b': 1.9, 'l': 10.0}
print(dict)
# Output" {'k': 2.1, 'b': 1.9, 'l': 10.0}
print(type(dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
values_array = np.array(list(dict.values()))
print(values_array)
# Output: [ 2.1 1.9 10. ]
print(type(values_array))
# Output: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
And in the output, we get a 1D numpy array of dictionary values. One thing to note here is that the keys have the same data type of floating-point values.
What if the values are of different types? Let’s find out.
Mixed-Type values
If the input dictionary contains values of different types, Numpy defaults to the <U32 dtype, losing numerical efficiency. Filter numerics first.
import numpy as np
mixed_dict = {'lr': 0.01, 'epochs': 100, 'mode': 'train'}
print(mixed_dict)
# Output: {'lr': 0.01, 'epochs': 100, 'mode': 'train'}
print(type(mixed_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
mixed_list = list(mixed_dict.values())
mixed_array = np.array(mixed_list)
print(mixed_array)
# Output: ['0.01' '100' 'train']
print(type(mixed_array))
# Output: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print(mixed_array.dtype)
# Output: <U32
The input dictionary contains integer, float, and string types. Numpy infers float64 types for ints/floats, but since our array also contains strings, it automatically infers to <U32.
NumPy forces a single uniform dtype for every element. So, int can upcast to float64, float can upcast to float64. But string cannot share numeric dtype, so everything upcasts to Unicode string <U…
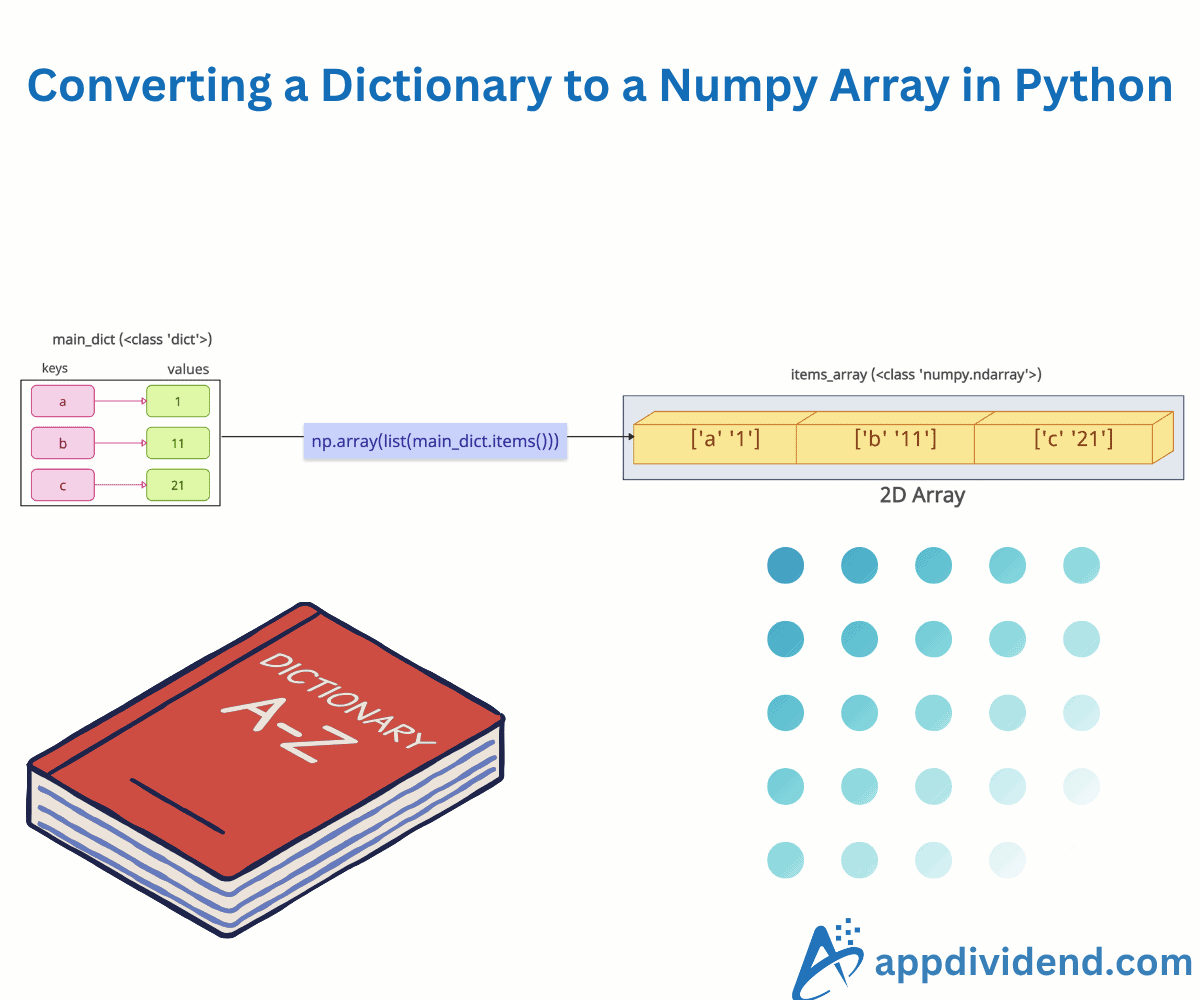
Method 3: Convert key-value pairs to a structured 2D array
To get the key-value pairs from a dictionary, use the dict.items() method and convert it to a list using list() method and pass that list to np.array() method to get the structured 2D array.
import numpy as np
mixed_dict = {'lr': 0.01, 'epochs': 100, 'mode': 'train'}
print(mixed_dict)
# Output: {'lr': 0.01, 'epochs': 100, 'mode': 'train'}
print(type(mixed_dict))
# Output: <class 'dict'>
items_list = list(mixed_dict.items())
items_array = np.array(items_list)
print(items_array)
# Output: [['lr' '0.01']
# ['epochs' '100']
# ['mode' 'train']]
print(type(items_array))
# Output: <class 'numpy.ndarray'>
print(items_array.dtype)
# Output: <U32
The output is a 2D numpy array, where each row contains key-value pairs.
The dtype of an output array is <U32 since it contains mixed values.





Hello
—————————————————————————
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
in
82 }
83 data = categories.items()
—> 84 list = list(data)
85 arr = np.array(list)
86 print(arr)
TypeError: ‘list’ object is not callable