The pi is a mathematical constant whose value is 3.14159, which is used in calculations involving circles, spheres, periodic phenomena, and converting from degrees to radians.
Here are two ways to use pi in Python:
- Using math.pi
- Using numpy.pi
import numpy as np import math print(math.pi) # Output: 3.141592653589793 print(np.pi) # Output: 3.141592653589793
Area of a Circle
The basic application of math.pi is to calculate the area of a circle.
The basic formula for calculating the circle’s area is A = π r².
import math
radius = 5
area = math.pi * radius ** 2
print("Area:", area)
# Output: Area: 78.53981633974483
Converting Degrees to Radians
You can use the pi when you want to convert degrees to radians (radians = degrees * (π/180)).
import math
def degrees_to_radians(degrees):
return degrees * (math.pi / 180)
print(degrees_to_radians(90))
# Output: 1.5707963267948966 (π/2)
print(math.sin(degrees_to_radians(90)))
# Output: 1.0
Numerical computations with NumPy
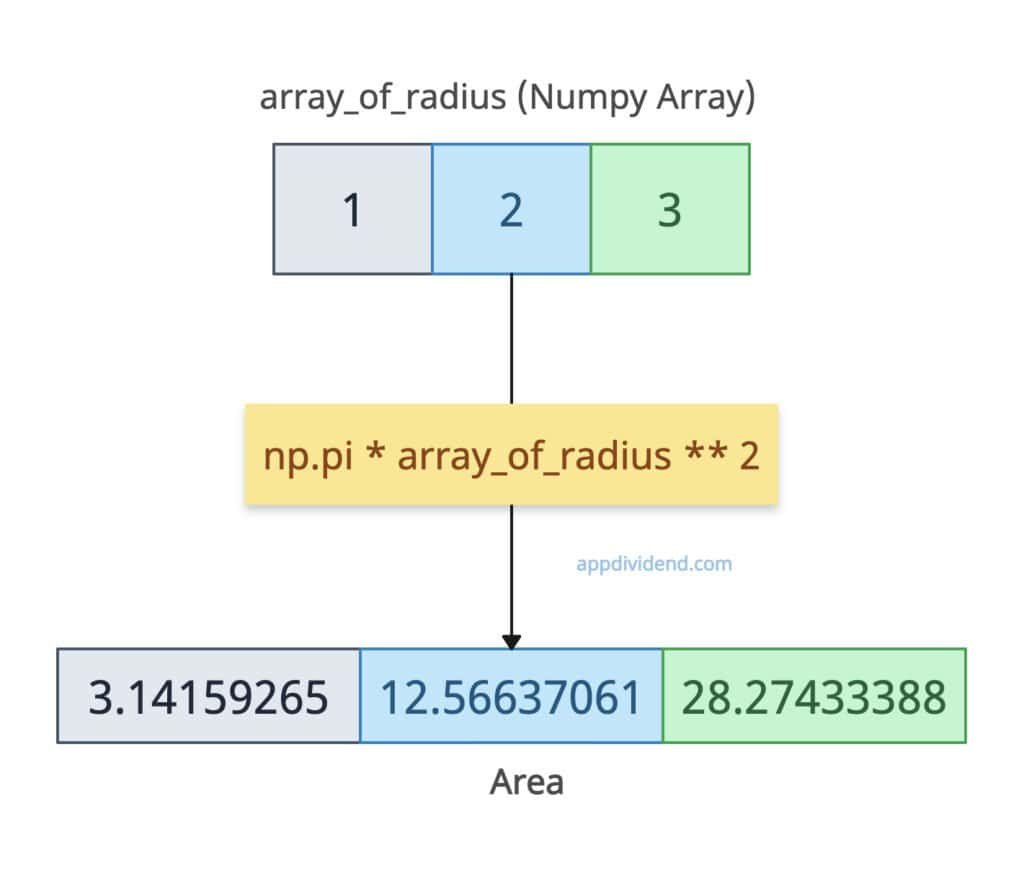
Let’s calculate the vectorized circle area calculation.
import numpy as np
array_of_radius = np.array([1, 2, 3])
area = np.pi * array_of_radius ** 2
print("Area:", area)
# Output: [ 3.14159265 12.56637061 28.27433388]
The output is also an array of area values of the respective input radius.