The numpy.exp() method calculates the exponential of each element of an input array, returning (e^x), where (e) is the base of the natural logarithm (~2.71828) and (x) is the input value.
import numpy as np # 1D Numpy array arr = np.array([0, 1, 2]) print(np.exp(arr)) # Output: [1. 2.71828183 7.3890561 ]
The above output shows that it works element-wise, meaning if the input array contains three elements, the output array will have three elements as well, with each element being e^ corresponding to the input array’s element.
Syntax
numpy.exp(x,
out=None,
where=True,
casting='same_kind',
order='K',
dtype=None,
subok=True)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| x (array_like) | It represents either an input array or a scalar value.
The output depends on this input value. |
| out (ndarray, optional) | It is an output array to store the result.
If you define this argument, make sure that the shape of this array is the same as the input array (x). |
| where (array_like, optional) | It is a Boolean array that defines where to calculate the exponential.
By default, the whole array is True, but you can declare it as False based on your requirements. If you set it to False for that value, it won’t calculate the exponential. |
| casting ( {‘no’, ‘equiv’, ‘safe’, ‘same_kind’, ‘unsafe’}, optional) | It controls the type-casting behaviour. By default, its value is ‘same_kind’. |
| order ({‘K’, ‘A’, ‘C’, ‘F’}, optional) | It represents the desired memory layout for the output array.
By default, it is “K”, meaning it matches the input layout. |
| dtype (data-type, optional) | It defines the output value’s data type.
By default, it inferred the input’s type. |
| subok (bool, optional) |
If True, subclasses pass through; otherwise, return a base ndarray. |
Exponential of a scalar value
If the input value is not an array but a scalar, the output value shall be a scalar too!
import numpy as np # Scalar value scalar = 10 print(np.exp(scalar)) # Output: 22026.465794806718
Exponential of a 2D array
Even if the input array is a multidimensional array like 2D or 3D, it works the same and returns the output of the same shape as the input.
import numpy as np # 2D Numpy array array_2d = np.array([[0, 1], [3, 4]]) # Calculate the exponential of each element in the 2D array print(np.exp(array_2d)) # Output: # [[ 1. 2.71828183] # [20.08553692 54.59815003]]
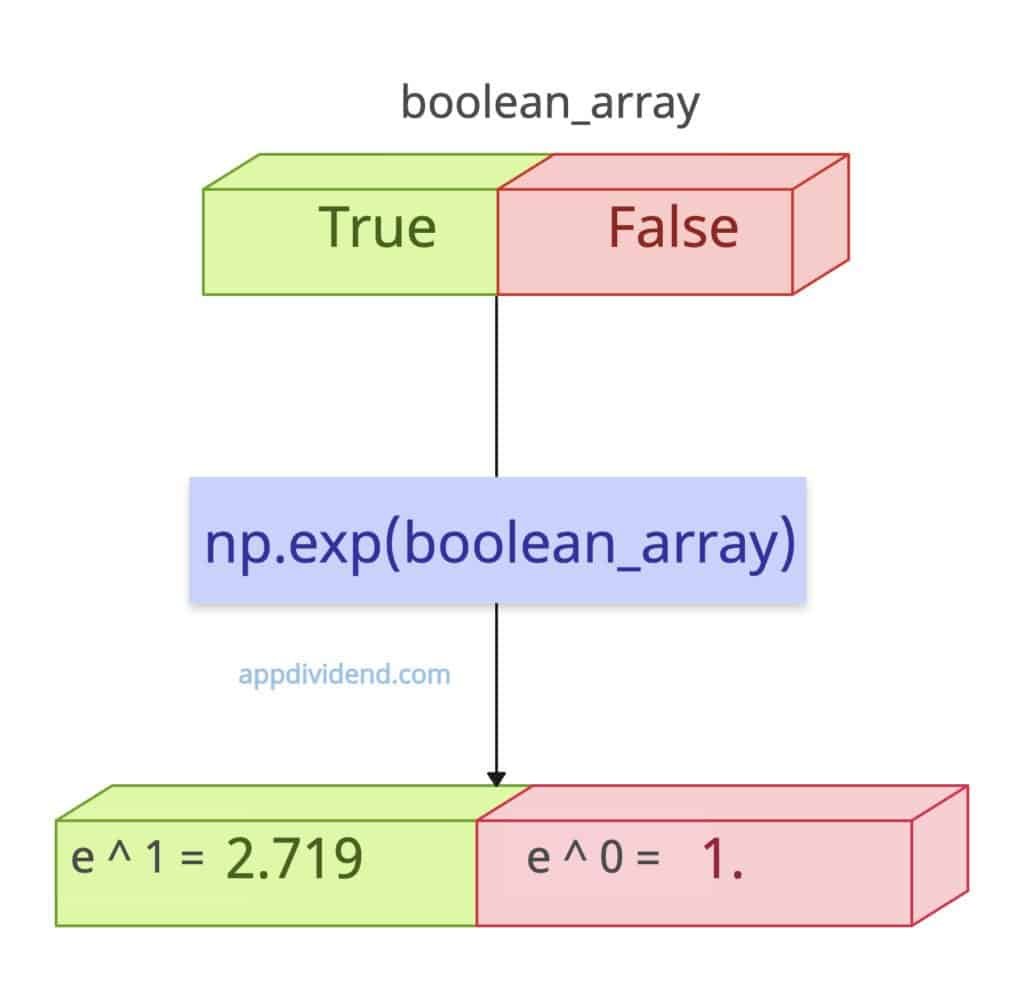
Boolean Input
The boolean values are either True or False.
If you pass True, that means 1 and e^1 = 2.719 (rounded)
If you pass False, that means 0, and e^0 = 1.
import numpy as np # Array with boolean values boolean_array = np.array([True, False]) print(np.exp(boolean_array)) # Output: [2.719 1.]
Using “where” Mask and “out” array
With the help of the “where” mask, we can apply a condition to select which value’s exponential we want to calculate.
Uncomputed elements are either set to zero or retain their original values, depending on implementation.
But what do I mean by implementation? Well, that’s a tricky part, and that’s where the “out” argument comes into the picture.
For uncomputed elements, the result is not always predictable. However, for predictable results in where=False positions, explicitly set an out array with 0 values.
import numpy as np arr_1d = np.array([2, 4, 6]) output_array = np.full_like(arr_1d, fill_value=0, dtype=float) condition = np.array([True, False, False]) print(np.exp(arr_1d, where=condition, out=output_array)) # Output: [7.3890561 0. 0. ]
In this code, we set a mask True, False, and False. It means we only need to calculate the exponential of the first element.
Now, we are also pre-defining an array called output_array, whose values we are explicitly setting to 0. It will have three 0s since the input array has three elements. In the future, we will store the values in it.
Based on the mask, we calculate the first element’s exponential value and store it in the output_array. The rest of the array’s values are already set to 0, resulting in the final output.
Negative elements
Even if the array contains negative values, (e^x) produces values between 0 and 1, which is helpful in decay models.
import numpy as np neg_arr = np.array([-1, -2]) print(np.exp(neg_arr)) # Output: [0.36787944 0.13533528]
Plotting
To plot a chart of exponential values, we can use the matplotlib library.
To install it if you have not, use this command: pip install matplotlib
Here, we will plot the e^x for values between -3 and 3. We will label axes and show a grid using numpy.exp() method to calculate the values.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 100) # from -3 to 3
y = np.exp(x)
# Create the plot
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
plt.plot(x, y, label=r"$e^x$", color='blue')
plt.title("NumPy exp() Function")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("exp(x)")
plt.grid(True, linestyle='--', alpha=0.6)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
The above figure shows the classic exponential curve.
That’s all!







raged
great work keep it up