The most lightweight and efficient approach to convert JSON to CSV in Python is to load JSON using json.load() function, process it into rows, and write using csv.DictWriter.writerows() method.
Let’s say we have a JSON file called data.json that looks like this:
[
{
"name": "Marsh",
"age": 30,
"city": "New York"
},
{
"name": "Chris",
"age": 28,
"city": "San Francisco"
},
{
"name": "Mike",
"age": 26,
"city": "Los Angeles"
},
{
"name": "Robert",
"age": 23,
"city": "Orlando"
},
{
"name": "Andre",
"age": 29,
"city": "Illinois"
}
]
Let’s write a program.
import json
import csv
with open('data.json') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
header = list(data[0].keys())
with open('output.csv', 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=header)
writer.writeheader() # Write the header (column names) to the CSV
writer.writerows(data) # Write the rows of data to the CSV
print("JSON data has been converted to CSV and saved to 'output.csv'")
# Output: JSON data has been converted to CSV and saved to 'output.csv'
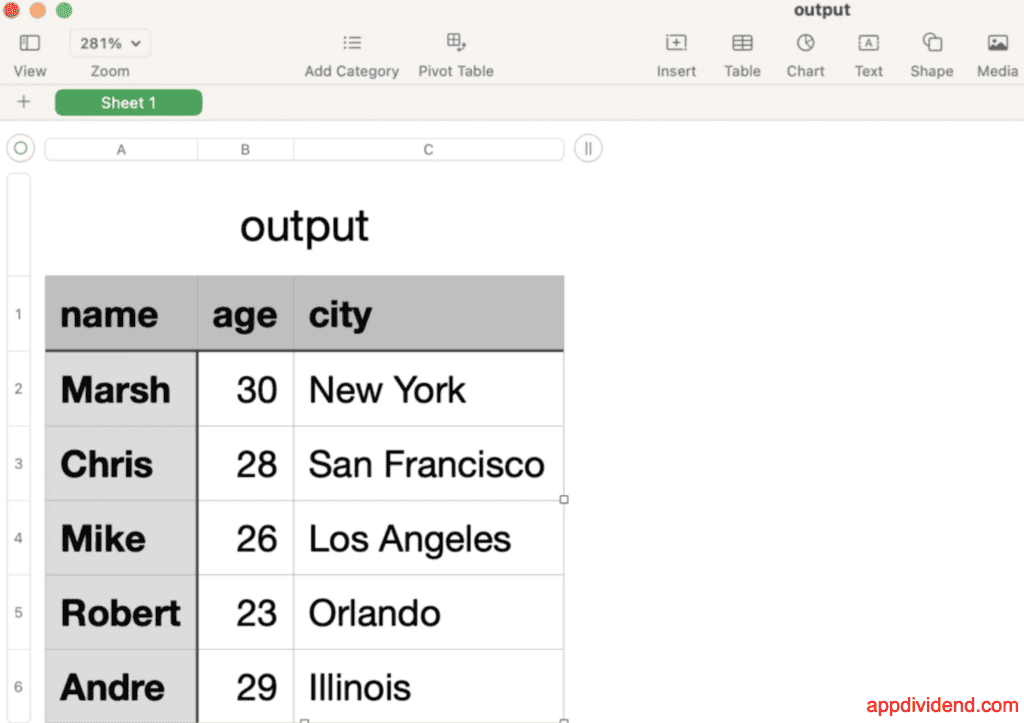
Output
In this code, we first open and read the JSON file using the json.load() method and divide the content into the header and main content.
Then, we wrote the header using csv.DictWriter().writeheader() method and content using csv.DictWriter().writerows() method.
Nested JSON (Simple Flattening)
What if your input is a complex nested json? In that case, first, we need to flatten the input and then convert it into a CSV file.
Let’s say we have JSON data in the form of a string. To read it correctly, we need json.loads() function.
import json
import csv
json_data = '''
[
{"name": "Ronaldo", "age": 40, "address": {"city": "Lisbon", "zip": "1000 001"}},
{"name": "Messi", "age": 35, "address": {"city": "Rosario", "zip": "s1265"}}
]
'''
data = json.loads(json_data)
def flatten_dict(d, parent_key='', sep='.'):
items = []
for k, v in d.items():
new_key = f"{parent_key}{sep}{k}" if parent_key else k
if isinstance(v, dict):
items.extend(flatten_dict(v, new_key, sep=sep).items())
else:
items.append((new_key, v))
return dict(items)
# Flatten data
flattened_data = [flatten_dict(row) for row in data]
# Write to CSV (use union of all keys for headers)
all_keys = set().union(*(d.keys() for d in flattened_data))
with open('output_nested.csv', 'w', newline='', encoding='utf-8') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=all_keys)
writer.writeheader()
writer.writerows(flattened_data)
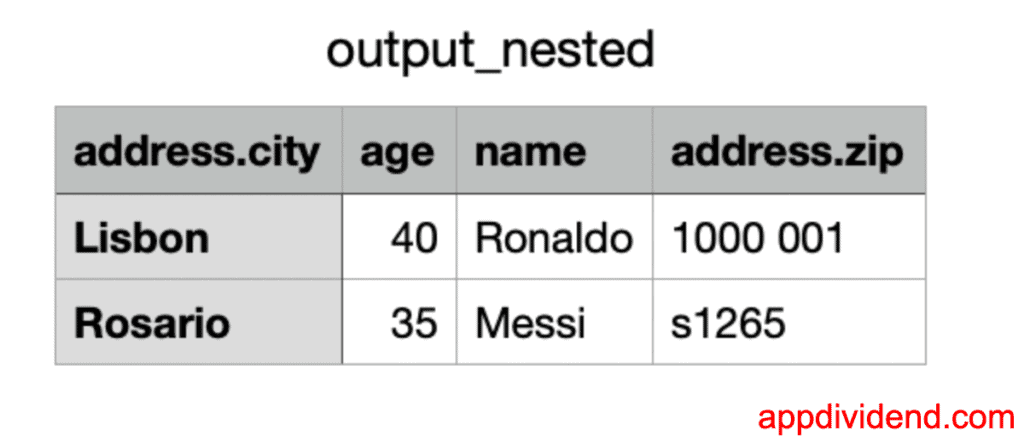
Here is the output_nexted.csv file:
Using Pandas df.to_csv()
If you are working with the Pandas library, there is a method called df.to_csv() that you can use.
First, you need to load the JSON data into a DataFrame using pd.DataFrame() method and then export that DataFrame to a CSV file using the .to_csv() method.
import pandas as pd
import json
with open('data.json') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
data_frame = pd.DataFrame(data)
data_frame.to_csv('output_2.csv', index=False)
print("JSON data has been converted to CSV and saved to 'output_2.csv'")
# Output: JSON data has been converted to CSV and saved to 'output_2.csv'
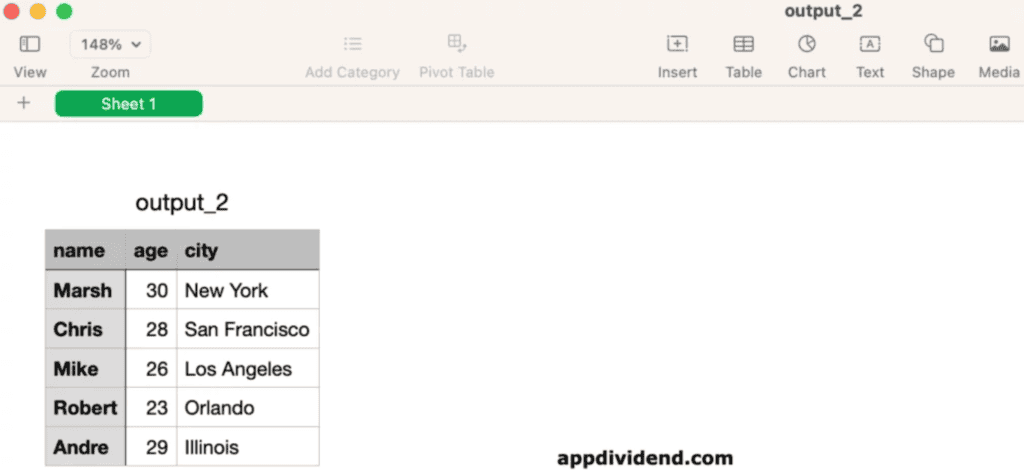
Output
That’s it.