Python math.log2() calculates the base-2 logarithm of a given number. It is helpful in computer science and information theory, offering better performance and accuracy.
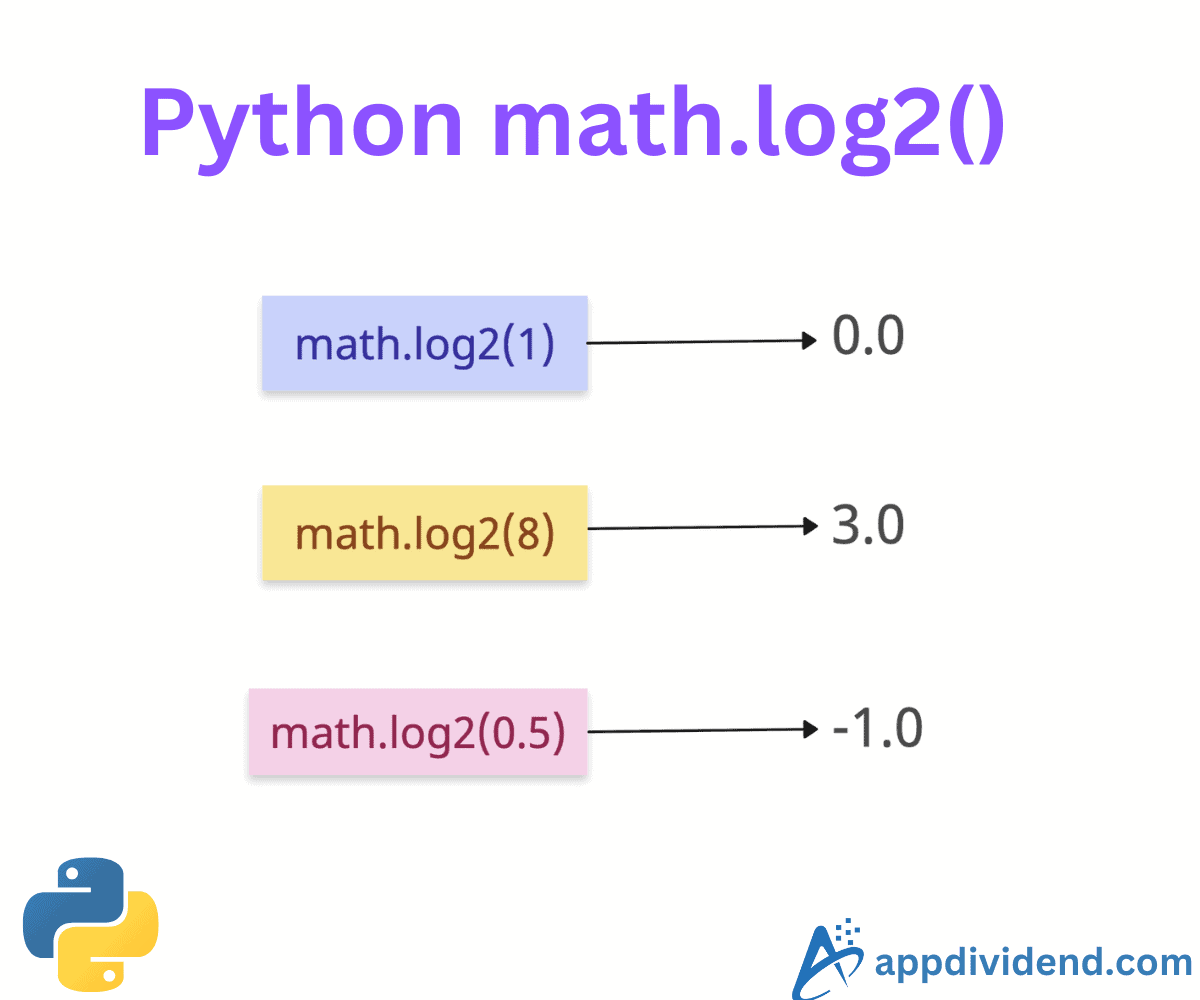
Let’s calculate the base-2 log of positive numbers.
import math print(math.log2(1)) # Log base 2 of 1 # Output: 0.0 print(math.log2(8)) # Log base 2 of 8 # Output: 3.0 print(math.log2(4.49)) # Log base 2 of 4.49 # Output: 2.1667154449664223
The above output shows that even after having an integer input, it returns a floating-point output.
Syntax
import math math.log2(num)
To use the log2() method, we need to import the built-in math module.
Parameter
| Argument | Description |
| num (float or int) | It represents a positive float or int value, for which the base-2 logarithm is calculated.
It should not be zero or negative. |
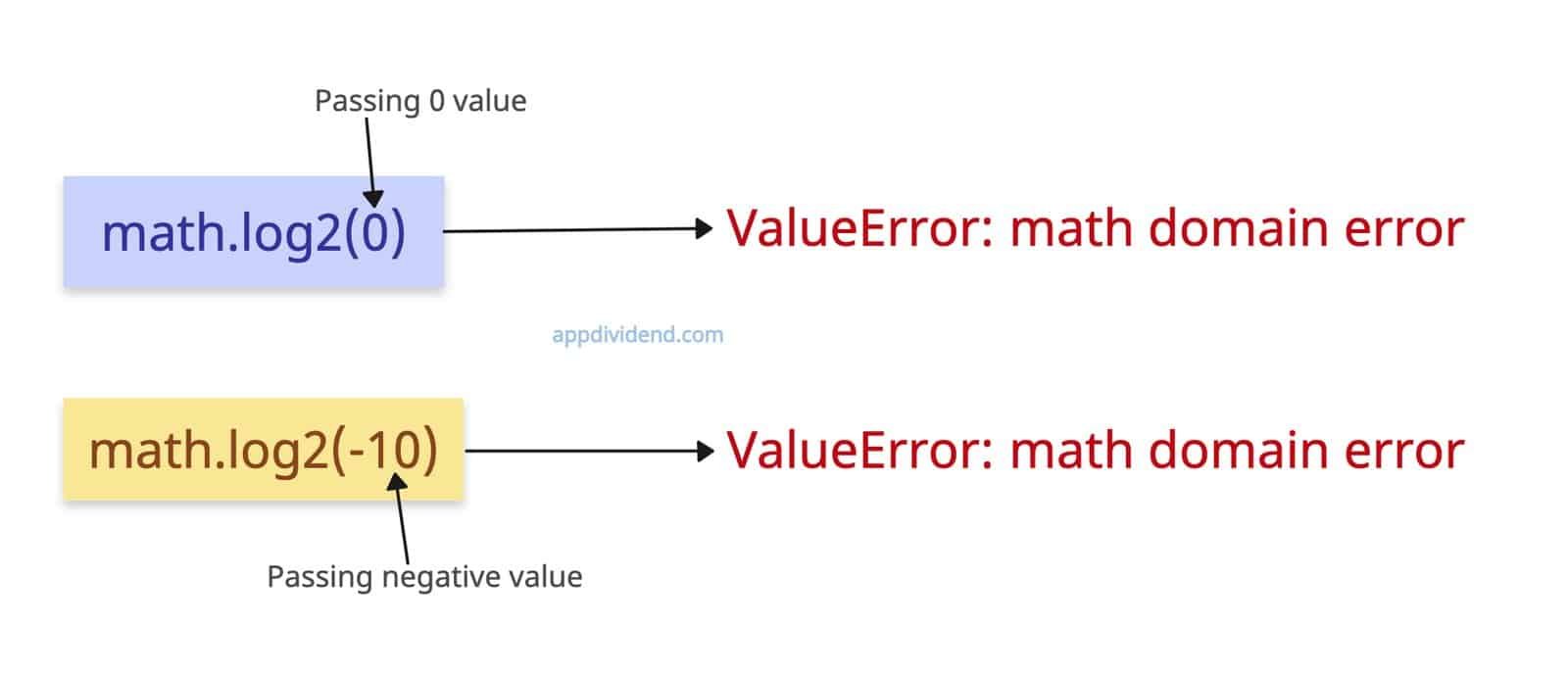
Non-positive or 0 inputs
What if you pass a negative number to the log2() method? Well, it raises the ValueError: math domain error.
If the input is 0, it still raises a ValueError because it should not be zero either.
import math
try:
x = 0
math.log2(x) # x ≤ 0
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
# Output: math domain error
try:
y = -10
math.log2(y) # Negative input
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
# Output: math domain error
Special values
The log2() of infinity is infinity, and NaN is NaN.
import math
print(math.log2(float('inf')))
# Output: inf (log₂(∞) = ∞)
print(math.log2(float('nan')))
# Output: nan (Undefined)
Non-numeric Input
If you attempt to find log2() of a string or characters, it raises ValueError: could not convert string to float: ”.
import math
print(math.log2(float('Krunal')))
# ValueError: could not convert string to float: 'Krunal'
Don’t pass variables other than float or integer.