There’s no null in Python; instead, there’s None. The Null is called None, a special object representing the absence of a value. None is a unique value demonstrating that a variable doesn’t point to anything.
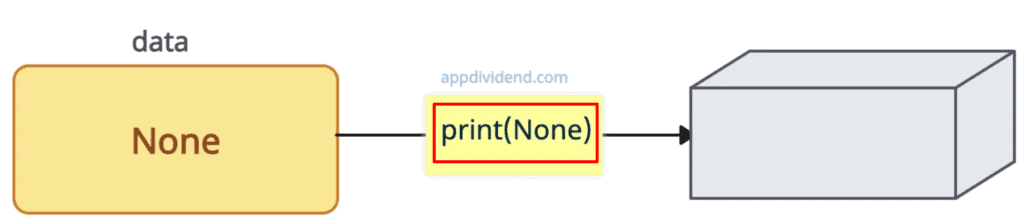
data = None print(None) # Output: None
We can assign a None object to any variable at the time of declaration, and it becomes None.
Why does it matter?
You can use None as a placeholder for an unknown or uninitialized value.
If a function does not return any value, then it returns None. It deserves a specific purpose, and it does not mean the value 0. The None or Null is a first-class citizen.
If you define a function with a return statement or no value, it returns None.
def python_none():
pass
print(python_none())
# Output: None
When you call the python_none() function, there is no return statement. Instead, there is only a pass statement. So, it returns None.
None has no output value, but printing it to the console explicitly forces us to print the output.
Type of None
None is the singleton, and the NoneType class only gives you the same instance of None.
NoneObj = type(None) print(NoneObj) # Output: <class 'NoneType'> print(NoneObj is None) # Output: False
Interesting facts
- None is not the same as False.
- None is not an empty string.
- None is not 0.
- Comparing None to anything will always return False except None itself.
is not null
To check if a variable is null, use the “is not” operator.
The “is” and “is not” operators are comparison operators that compare the identity of two objects.
For example, “is operator” is an identity test. It checks whether the right-hand and left-hand sides are the same object.
str = "Stranger Things 4 Vecna"
if str is not None:
print('String is not null')
# Output: String is not null
is None
You can use the “is operator” to check if a variable is None.
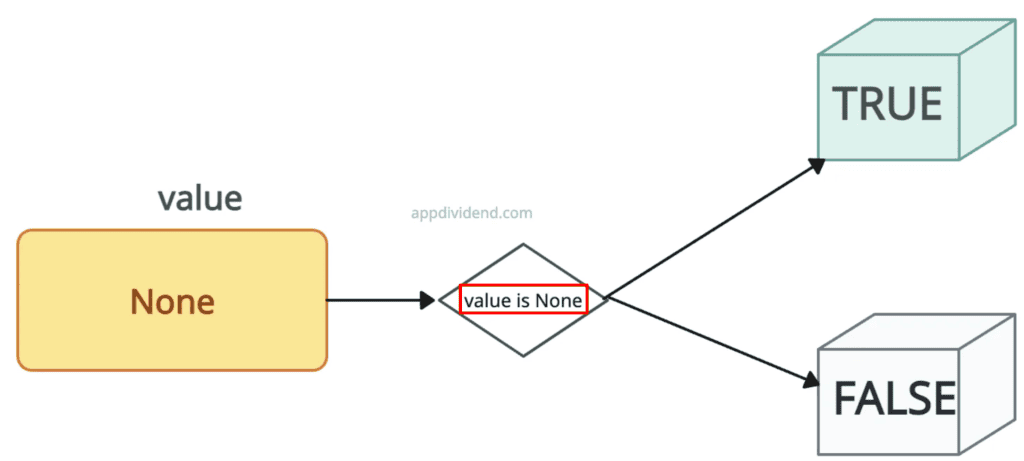
value = None
if value is None:
print('The value is null')
else:
print('The value is not null')
# Output: The value is null
In the above example, we have defined a variable called value and assigned the None value.
Then, we used the if…else condition to check for the None value, and if it is present, we return the print statement with “The value is null.”
That’s all!