Python sum() is a built-in function that calculates the sum of all numeric elements in an iterable, optionally starting from a specified initial value. The return value’s type depends on the input types.
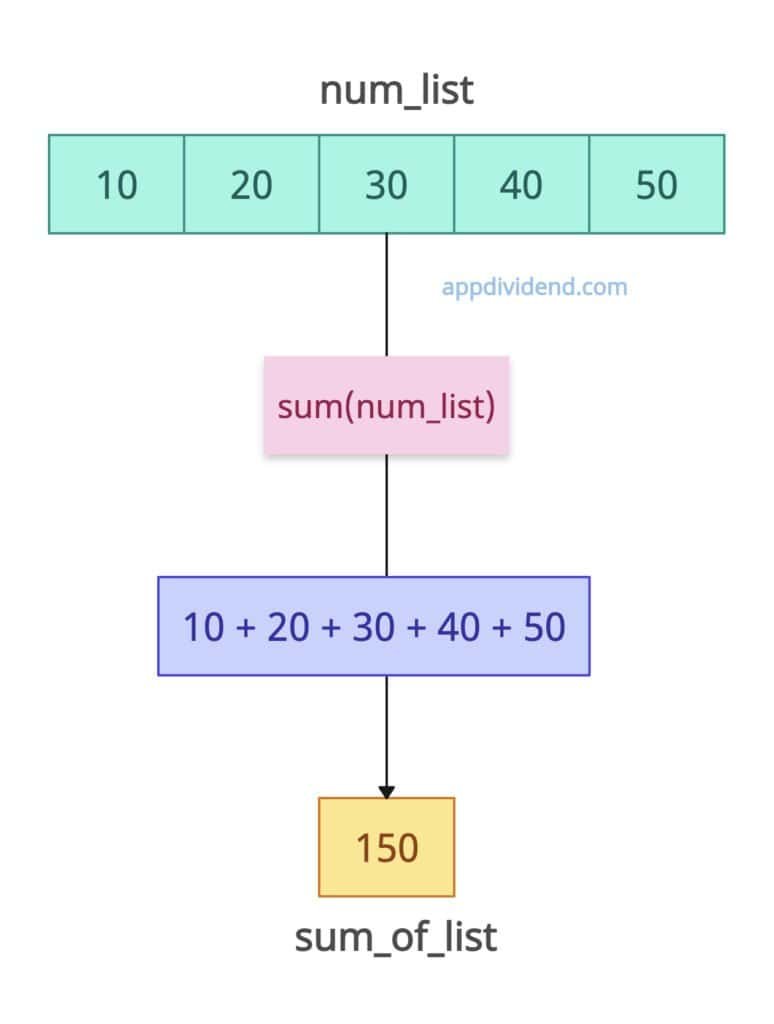
num_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] sum_of_list = sum(num_list) print(sum_of_list) # Output: 150
In this code, we defined a list with five elements. The output value is the sum of all the input elements, and its type is integer because the list contains elements of type integer.
Syntax
sum(iterable, start=0)
Parameters
| Arguments | Description |
| iterable | It represents an iterable, such as a list, tuple, set, dictionary, or generator, containing numeric elements (integers, floats, or complex numbers). |
| start (optional) |
It is a numeric value that adds to the sum of the iterable. Defaults to 0. |
Summation with a custom Start value
Let’s add an initial value to the sum of a list.
num_list = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50] list_sum_initial = sum(num_list, start=60) print(list_sum_initial) # Output: 210
Since the initial value is 60, the final sum will be 150 + 60 = 210.
Floating-point
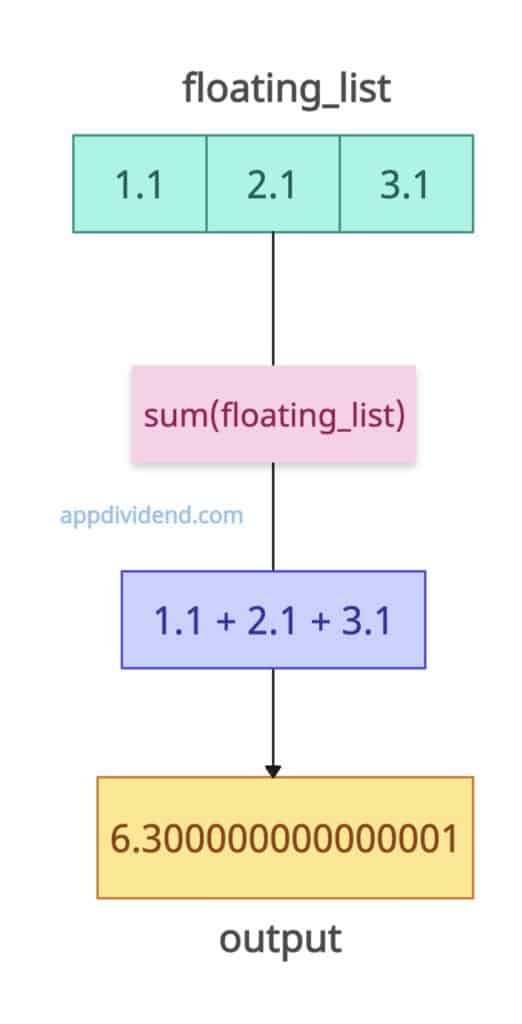
If you are working with a floating-point list, it may introduce minor precision issues.
floating_list = [1.1, 2.1, 3.1] output = sum(floating_list) print(output) # Output: 6.300000000000001
Complex numbers
If the input list has complex numbers as elements, the output will be a complex number.
complex_nums = [11+2j, 3+10j, 51+6j] complex_sum = sum(complex_nums) # (11+2j) + (3+10j) + (51+6j) = (65+18j) print(complex_sum) # Output: (65+18j)
Sum of a tuple
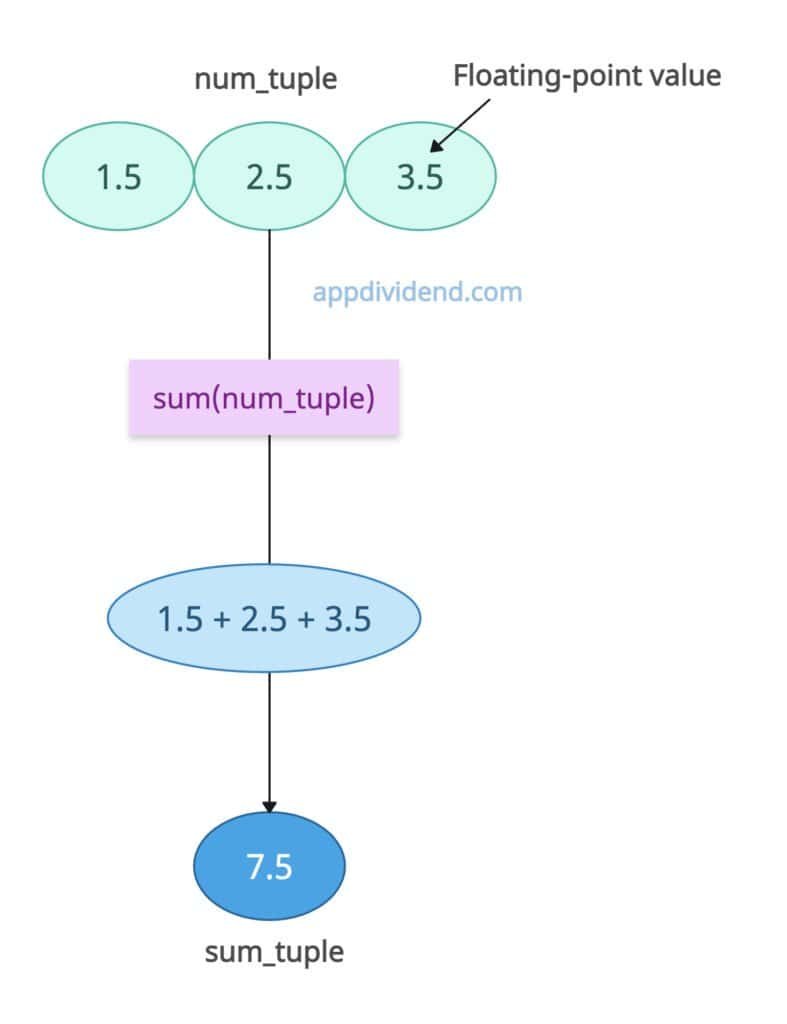
Even if the tuples are immutable, they are also compatible with sum() for numeric elements.
num_tuple = (1.5, 2.5, 3.5) sum_tuple = sum(num_tuple) print(sum_tuple) # Output: 7.5
Sum of a Set
Sum only contains unique elements, and since it is an iterable, we can add all the elements.
number_set = {2, 3, 4}
sum_of_set = sum(number_set)
print(sum_of_set)
# Output: 9
Dictionary
Dictionaries require special handling since sum() operates on iterables.
By default, iterating over a dictionary yields its keys. Since keys are often not numeric values, we can use the dict.values() method to get the values and create a sum out of them.
dict = {'a': 5, 'b': 10, 'c': 20}
sum_of_dict_values = sum(dict.values())
# Sums values: 5 + 10 + 20 = 35
print(sum_of_dict_values)
# Output: 35
That’s all!